Abstract
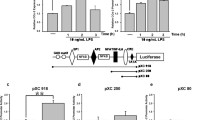
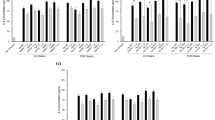
In Helicobacter pylori-associated gastricmucosal injury, interleukin (IL)-8, a potent leukocytechemoattractant, is produced by epithelial cellsinfected by H. pylori and directs neutrophils to thegastric mucosa. According to previous studies, the IL-8production requires direct contact between the bacteriaand epithelial cells. The aims of the present study wereto determine whether an H. pylori water extract (HPE) induces IL-8 production by gastricepithelial cells and to characterize IL-8-inducingsubstances in HPE. Extracts were prepared from astandard strain and from strains obtained from patientswith gastric ulcers. After addition of HPE to MKN 45cells, a gastric cancer cell line, IL-8 in supernatantsand IL-8 mRNA were measured by immunoassay and reversetranscription-polymerase chain reaction, respectively. For characterization, active fractions obtainedby gel filtration of standard-strain HPE were treated byheating or trypsinization. To study the signal pathwayleading to IL-8 production, inhibitors for protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC),or protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) were incubated withMKN45 cells before HPE stimulation. HPE from thestandard strain and one of these clinical strainsinduced IL-8 production. Lipopolysaccharide or cagA inthe strains showed no correlation with IL-8concentration. Standard-strain HPE induced IL-8 mRNAexpression in MKN 45 cells. Gel filtration localizedactivity to a low-molecular-weight fraction of about 7kDa, which was resistant to heat and trypsin digestion.PKC inhibitors significantly blocked HPE-induced IL-8production by MKN 45 cells; however, the PKA inhibitor or PTK inhibitors showed a partial inhibitoryeffect. HPE contains a nonprotein substance of lowmolecular weight that is responsible for IL-8 inductionin gastric epithelial cells. This induction is mainly dependent on the activation of PKC butpartially also dependent on PKA or PTK.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Blaser MJ: Hypotheses on the pathogene sis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced infl ammation. Gastroenterology 102:720–727, 1992
Cover TL, Blase r MJ: Helicobacter pylori and gastroduodenal disease. Annu Rev Med 43:135–145, 1992
Davie s GR, Banatvala N, Collins CE, e t al: Re lationship between infective load of Helicobacter pylori and reactive oxygen me tabolite production in antral mucosa. Scand J Gastroente rol 29:419–424, 1994
Yoshimura T, Matsushima K, Oppenheim JJ, e t al: Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocyte s: Partial characte rization and separation from interleukin-1 (IL-1). J Immunol 139:788–793, 1987
Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL: Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a nove l cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest 84:1045–1049, 1989
Oppenheim JJ, Zachariae CO, Mukaida N, et al: Prope rties of the novel proin¯ ammatory superge ne ª intercrine º cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol 9:617–648, 1991
Rieder G, Hatz RA, Moran AP, e t al: Role of adhe rence in interleukin-8 induction in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Infect Immun 65:3622–3630, 1997
Aihara M, Tsuchimoto D, Takizawa H, e t al: Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced interleukin-8 production by a gastric cance r ce ll line, MKN 45. Infect Immun 65:3218–3224, 1997
Mai UE, Perez Perez GI, Wahl LM, e t al: Soluble surface prote ins from Helico bacter pylori act iva te monoc yte s/ macrophage s by lipopolysaccharide-independent me chanism. J Clin Invest 87:894–900, 1991
Yoshida N, Granger DN, Evans DJ Jr, e t al: Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced infl ammation. Gastroente rology 105:1431–1440, 1993
Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Iinuma S, e t al: Rebamipide protects against activation of neutrophils by Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci 41:1139–1144, 1996
Hojo H: Establishment of culture cell lines of human stomachb cancer; origin and their morphological characte ristics. Niigata Med J 91:737–752, 1977
Crabtree JE, Wyatt JI, Tre jdosiewicz LK, et al: Interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori infected, normal, and neoplastic gastroduodenal mucosa. J Clin Pathol 47:61–66, 1994
Evans DJ Jr, Evans DG, Takemura T, et al: Characte rization of a Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein. Infect Immun 63:2213–2220, 1995
Mai UE, Pe re z-Perez GI, Allen JB, et al: Surface proteins from Helicobacter pylori exhibit chemotactic activity for human leukocytes and are pre sent in gastric mucosa. J Exp Med 175:517–525, 1992
Muotiala A, He lander IM, Pyhala L, et al: Low biological activity of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun 60:1714–1716, 1992
Perez-Perez GI, Shepherd VL, Morrow JD, e t al: Activation of human THP-1 cells and rat bone marrow-derived macrophage s by Helicobacter pylo ri lipopolysaccharide. Infe ct Immun 63:1183–1187, 1995
Kirkland T, Viriyakosol S, Perez-Pe re z GI, et al: Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide can activate 70Z/3 cells via CD14. Infect Immun 65:604–608, 1997
Beale s IL, Calam J: Stimulation of IL-8 production in human gastric epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori, IL-1be ta and TNFalpha requires tyrosine kinase activity, but not protein kinase C. Cytokine 9:514–200, 1997
Crabtree JE, Farmery SM, Lindley IJD, e t al: CagA/cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol 47:945–950, 1994
Crabtree JE, Covacci A, Farmery SM, et al: Helicobacter pyloriinduced interleukin-8 expression in gastric epithelial ce lls is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J Clin Pathol 48:41–45, 1995
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, et al: Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of cytokine messenge r RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroente rology 110:1744–1752, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassai, K., Yoshikawa, T., Yoshida, N. et al. Helicobacter pylori Water Extract Induces Interleukin-8 Production by Gastric Epithelial Cells. Dig Dis Sci 44, 237–242 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026629812245
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026629812245