Abstract
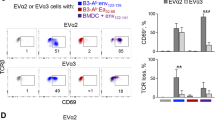
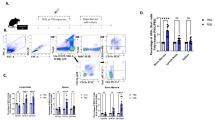
ACTIVATION of CD4+ T helper cells results from the occupancy of the T-cell receptor (TCR) by immunogenic peptide bound to a class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule1, together with a co-stimulatory signal from the antigen-presenting cell (APC)2. This activation leads to proliferation, cytokine production (Th1 or Th2 profile) and cytolysis3. Engagement of the TCR in the absence of co-stimulation causes Th1 cells to become unresponsive to subsequent antigenic stimulation4–6. We have previously demonstrated that analogues of an immunogenic peptide could stimulate Th1 and Th2 cells to carry out some effector functions without inducing proliferation7,25, a phenomenon we term partial activation. Here we study the consequences of such partial activation through the TCR of two Th1 clones using peptide analogues presented by a live APC. A peptide analogue that is unable to stimulate clonal proliferation or production of cytokine or inositol phosphate can induce the T cells to become profoundly unresponsive to subsequent stimulation with the immunogenic peptide. Thus, altering the ligand of the TCR by using a peptide analogue on a functional APC sends a signal to Th1 clones that results in anergy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babbitt, B. P., Allen, P. M., Matsueda, G., Haber, E. & Unanue, E. R. Nature 317, 359–361 (1985).
Mueller, D. L., Jenkins, M. K. & Schwartz, R. H. A. Rev. Immun. 7, 445–480 (1989).
Crabtree, G. R. Science 243, 355–361 (1989).
Jenkins, M. K. & Schwartz, R. H. J. exp. Med. 165, 302–319 (1987).
Quill, H. & Schwartz, R. H. J. Immun. 138, 3704–3712 (1987).
Jenkins, M. K., Pardoll, D. M., Mizuguchi, J., Chused, T. M. & Schwartz, R. H. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 84, 5409–5413 (1987).
Evavold, B. D. & Allen, P. M. Science 252, 1308–1310 (1991).
Evavold, B. D., Williams, S. G., Hsu, B. L., Buus, S. & Allen, P. M. J. Immun. 148, 347–353 (1992).
Ronchese, F., Schwartz, R. H. & Germain, R. N. Nature 329, 254–256 (1987).
Smith, K. A. Science 240, 1169–1176 (1988).
Kurzinger, K. et al. J. Immun. 127, 596–602 (1981).
De Silva, D. R., Urdahl, K. B. & Jenkins, M. K. J. Immun. 147, 3261–3267 (1991).
Wilde, D. B. & Fitch, F. W. J. Immun. 132, 1632–1638 (1984).
Wilde, D. B. et al. J. Immun. 133, 636–641 (1984).
Jenkins, M. K., Ashwell, J. D. & Schwartz, R. H. J. Immun. 140, 3324–3330 (1988).
Harding, F. A., McArthur, J. G., Gross, J. A., Raulet, D. H. & Allison, J. P. Nature 356, 607–609 (1992).
De Magistris, M. T. et al. Cell 68, 625–634 (1992).
Letourneur, F. & Klausner, R. D. Science 255, 79–82 (1992).
Wegener, A. -M. K. et al. Cell 68, 83–95 (1992).
Irving, B. A. & Weiss, A. Cell 64, 891–901 (1991).
Allen, P. M. & Unanue, E. R. J. Immun. 132, 1077–1079 (1984).
Lorenz, R. G. & Allen, P. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 5220–5223 (1988).
Schreiber, R. D., Hicks, L. J., Celada, A., Buchmeier, N. A. & Gray, P. W. J. Immun. 134, 1609–1618 (1985).
Mueller, D. L., Jenkins, M. K. & Schwartz, R. H. J. Immun. 142, 2617–2628 (1989).
Evavold, B. D., Sloan-Lancaster, J. & Allen, P. M. J. Immun. (in the press).
Racioppi, L., Ronchese, F., Matis, L. A. & Germain, R. N. J. exp. Med. 177, 1047–1060 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sloan-Lancaster, J., Evavold, B. & Allen, P. Induction of T-cell anergy by altered T-cell-receptor ligand on live antigen-presenting cells. Nature 363, 156–159 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363156a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/363156a0
This article is cited by
-
The Role of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Agents in Melanoma: Progress to Date
Drugs (2015)
-
Low expression of dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and a significant correlation with β2-microglobulin
Medical Oncology (2014)
-
How the TCR balances sensitivity and specificity for the recognition of self and pathogens
Nature Immunology (2012)
-
T cell recognition of weak ligands: roles of signaling, receptor number, and affinity
Immunologic Research (2011)
-
Receptor signaling in immune cell development and function
Immunologic Research (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.