Abstract
Background
The best measure of the technical success of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is local recurrence (LR). The aim of this prospective study is to identify factors that predict LR.
Methods
Three hundred thirty-five patients with 1032 unresectable liver tumors underwent laparoscopic RFA between November 1999 and August 2005. All lesions were assessed prospectively regarding tumor type, size, liver segment, blood vessel proximity, and central or peripheral location in the operating room and size of ablation zone at 1-week computed tomographic (CT) scans. Lesions that recurred in follow-up CT scans were identified prospectively. LR was categorized as contiguous or adjacent. Univariate Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazard models were used for statistical analysis.
Results
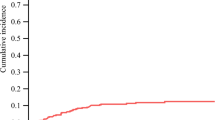
LR was identified 21.7% of tumors on CT scans with a mean follow-up of 17 months (median, 12 months; range, 3–68 months). This was contiguous in 70% and adjacent in 30%. LR rate per tumor was highest for colorectal metastasis (34%), followed by noncolorectal, nonneuroendocrine metastasis (22%), hepatocellular carcinoma (18%), and neuroendocrine metastasis (6%). By univariate analysis, tumor type and size, ablation margin, liver segmental location, blood vessel proximity, and type of ablation (first time vs. repeat) were found to affect LR. The Cox proportional hazard model identified tumor type, tumor size, ablation margin, and blood vessel proximity to be independent predictors of LR.
Conclusion
LR after RFA is predicted by certain tumor characteristics and technical factors. This information can be used intraoperatively to identify those tumors at a higher risk for failure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berber E, Pelley R, Siperstein AE. Predictors of survival after radiofrequency thermal ablation of colorectal cancer metastases to the liver: a prospective study. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23:1358–64
Machi J, Oishi AJ, Sumida K, et al. Long-term outcome of radiofrequency ablation for unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer: evaluation of prognostic factors and effectiveness in first- and second-line management. Cancer J 2006; 12:318–26
Chow DH, Sinn LH, Ng KK, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic liver tumors: a comparative study. J Surg Oncol 2006; 94:565–71
Amersi FF, McElrath-Garza A, Ahmad A, et al. Long-term survival after radiofrequency ablation of complex unresectable liver tumors. Arch Surg 2006; 141:581–7
Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 2000; 232:381–91
Adam R, Hagopian EJ, Linhares M, et al. A comparison of percutaneous cryosurgery and percutaneous radiofrequency for unresectable hepatic malignancies. Arch Surg 2002; 137:1332–9
Wood TF, Rose DM, Chung M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of 231 unresectable hepatic tumors: indications, limitations, and complications. Ann Surg Oncol 2000; 7:593–600
Siperstein A, Garland A, Engle K, et al. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of primary and metastatic liver tumors. Technical considerations. Surg Endosc 2000; 14:400–5
Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg 1999; 230:1–8
Siperstein A, Garland A, Engle K, et al. Local recurrence after laparoscopic radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 2000; 7:106–13
Ahmad A, Chen SL, Kavanagh MA, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: are newer generation probes better? Am Surg 2006; 72:875–9
Aloia TA, Vauthey JN, Loyer EM, et al. Solitary colorectal liver metastasis: resection determines outcome. Arch Surg 2006; 141:460–6
Berber E, Ari E, Herceg N, et al. Laparoscopic radiofrequency thermal ablation for unusual hepatic tumors: operative indications and outcomes. Surg Endosc 2005; 19:1613–7
Berber E, Flesher N, Siperstein AE. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of neuroendocrine liver metastases. World J Surg 2002; 26:985–90
Berber E, Rogers S, Siperstein A. Predictors of survival after laparoscopic radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular cancer: a prospective study. Surg Endosc 2005; 19:710–4
Berber E, Flesher NL, Siperstein AE. Initial clinical evaluation of the RITA 5-centimeter radiofrequency thermal ablation catheter in the treatment of liver tumors. Cancer J Sci Am 2000; 6(Suppl 4):S319–29
Bowles BJ, Machi J, Limm WM, et al. Safety and efficacy of radiofrequency thermal ablation in advanced liver tumors. Arch Surg 2001; 136:864–9
Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 2003; 228:235–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berber, E., Siperstein, A. Local Recurrence After Laparoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumors: An Analysis of 1032 Tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 2757–2764 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0043-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0043-7