Summary
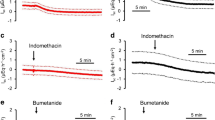
Intestinal net fluid transport was measured in vivo continuously with a gravimetric method. Chemical stimulation of the jejunal serosa with hydrochloric acid (0.1 M), ethanol (20%), cat bile or 7-deoxycholic acid (10 mM) evoked an intestinal fluid secretion. Hexamethonium (10 mg/kg b. wt. i. v.) or serosal application of lidocaine (1% solution) partially blocked this secretory response. Bradykinin and prostaglandin E1, two important inflammatory mediators, elicited fluid secretion when applied to the serosal surface at a concentration of 10−4M. This secretion was also partly inhibited by hexamethonium. Furthermore indomethacin (10 mg/kg b. wt. i. v.) or pyrilamine (10 mg/kg b. wt. i. v.), a H1-receptor blocker, partly inhibited the secretory response caused by chemical stimulation of the serosa while cimetidine (1 mg/kg b. wt. i. v.), a H2-receptor blocker, had no effect. Freeze sectioned samples from chemically stimulated intestines were examined by fluorescence microscopy. A leakage of i. v. administrated Evans blue labelled albumin into the interstitial space of the serosa and the outer layer of the muscularis was found.
It is concluded: (1) The intestinal fluid secretion studied is mainly elicited by nociceptive stimulation of nerves in the serosa or the outer muscularis. (2) The reflex may be activated by the local release of histamine, kinins and prostaglandins. (3) The reflex studied is part of an inflammatory response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Awqati Q, Cameron JL, Field M, Greenough III WB (1970) Effect of prostaglandin E1 on electrolyte transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest 49:2a
Beubler E, Juan H (1978) PGE-release, blood flow and transmucosal water movement after mechanical stimulation of the rat jejunal mucosa. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 305:91–95
beubler E, Lembeck F, Schweditsch M (1978) Effects of PGE2 and cholchicine on the intestinal fluid volume. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 301:195–199
Cassuto J, Jodal M, Tuttle R, Lundgren O (1981) On the role of intramural nerves in the pathogenesis of cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion. Scand J Gastroent 16:377–384
Cassuto J, Jodal M, Tuttle R, Lundgren O (1982a) 5-Hydroxytryptamine and cholera secretion: physiological and pharmacological studies in cats and rats. Scand J Gastroent 16:377–384
Cassuto J, Jodal M, Lundgren O (1982b) The effect of nicotinic and muscarinic receptor blockade on cholera toxin induced intestinal secretion in rats and cats. Acta Physiol Scand 114:573–577
Cassuto J, Siewert A, Jodal M, Lundgren O (1983) The involvement of intramural nerves in cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion. Acta Physiol Scand 117:195–202
Chahl LA (1979) Pain induced by inflammatory mediators. In: Beers Jr RF, Bassett EG (eds) Mechanisms of pain and analgesic compounds. Raven Press, New York, pp 273–284
Cooke HJ, Nemeth P, Wood JD (1983) Nerve mediated histamine action on guinea pig ileal mucosa. In: Proceedings of the International Union of Physiological Sciences, vol XV, XXIth Congress. Sidney, Australia, p 452
Crocker AD, Willavoys SP (1975) Effect of bradykinin on transepithelial transfer of sodium and water in vitro. J Physiol 253:401–410
Cuthbert AW, Margolius HS (1982) Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the cat colon. Br J Pharmacol 75:587–598
Di Rosa M, Giroud JP, Willoughby DA (1971) Studies of the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J Phathology 104:15–29
Fischer J, Kolis M, Fromm D, Shang A (1981) Effects of histamine receptor antagonists on alkali secretion by ileum. J Surg Res 30:1–5
Juan H (1979) The pain enhancing effect of PGI2. Agents and Action 6:204–212
Juan H, Seewann S (1980) Selective reduction by some vasodilators and the prostaglandin antagonist SC-19220 of a response to the algesic effect of bradykinin. Eur J Pharmacol 65:267–278
Karlström L, Cassuto J, Jodal M, Lundgren O (1981) The effect of hexamethonium on the secretion induced by sodium deoxycholate in the rat jejunum. Experientia 37:991–992
Lee JS, Silverberg JW (1976) Effect of histamine on intestinal fluid secretion in the dog. Amer J Physiol 231:793–798
Matuchansky C, Bernier J-J (1973) Effect of prostaglandin E1 on glucose, water, and electrolyte absorption in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology 64:1111–1118
Mense S (1981) Sensitization of group IV muscle receptors to bradykinin by 5-hydroxytryptamine and prostaglandin E1. Brain Res 225:95–105
Milton-Thompson GJ, Cummings JH, Newman A, Billings JA, Misiewicz JJ (1975) Colonic and small intestinal response to intravenous prostaglandin F1 and E1 in man. Gut 16:42–46
Moncada S, Ferreira SH, Vane JR (1975) Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis as the mechanism of analgesia of aspirinlike drugs in the dog knee joint. Eur J Pharmacol 31:250–260
Musch MW, Kachur JF, Miller R, Field M (1983) Bradykininstimulated electrolyte secretion in rabbit and guinea pig intestine. J Clin Invest 71:1073–1083
Newson B, Dahlström A, Enerbäck L, Ahlman H (1983) Suggestive evidence for a direct innervation of mucosal mast cells. Neuroscience 10:565–570
Pierce NF, Carpenter CCJ, Elliott HL, Greenough III WB (1971) Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology 60:22–32
Samuelsson B, Granström E, Green K, Hamberg M, Hammarström (1975) Prostaglandins. Ann Rev Biochem 44:669–695
Sjöqvist A, Cassuto J, Jodal M, Brunsson I, Lundgren O (1982) The effect on intestinal fluid transport of exposing the serosa to hydrochloric acid. A study of mechanisms. Acta Physiol Scand 116:447–454
Staszewska-Barczak J, Ferreira SH, Vane JR (1976) An exitatory nociceptive cardiac reflex elecited by bradykinin and potentiated by prostaglandins and myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res 10:314–327
Tyers MB, Haywood H (1979) Effects of prostaglandins on peripheral nociceptors in acute inflammation. Agents and Actions 6:65–78
Westwick J (1979) Prostaglandins as mediators of inflammation —vascular aspects. Agents and Action 6:59–63
Yaksh TL, Hammond DL (1982) Peripheral and central substrates involved in the rostral transmission of nociceptive information. Pain 13:1–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunsson, I., Sjöqvist, A., Jodal, M. et al. Mechanisms underlying the intestinal fluid secretion evoked by nociceptive serosal stimulation of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 328, 439–445 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692913
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692913