Summary
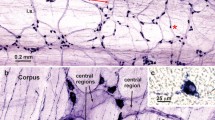
A quantitative light microscopic study has been carried out on the myenteric and submucosal ganglia of the guinea-pig ileum, after inducing hypertrophy of the wall with an experimental stenosis. The area of the profiles of nerve cells, of nerve cell nuclei and of glial nuclei, and the percentage area of the neuropil were measured, and the relative numbers of neurons and glial cells were estimated. The average size of neurons in both plexuses was greatly increased over the control values. Nearly half of the neuronal profiles measured over 500 μm2 in sectional area (less than 3% in the controls), and less than 1% measured less than 150 μm2 (21% in controls). The average size of glial nuclei (and presumably that of the glial cells too) was increased in the hypertrophic ganglia. The number of glial cells (relative to the number of neurons) was unchanged or slightly decreased in the hypertrophic myenteric ganglia; in contrast, it was markedly increased in the submucosal ganglia. In both ganglia the hypertrophy was accompanied by a decrease in the percentage volume of neuropil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benninghoff, A. (1951) Vermehrung und Vergrosserung von Nervezellen bei Hypertrophie des Innervationsgebietes.Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 6b, 38–41.
Dupont, J. -R., Jervis, H. R. &Sprinz, H. (1965) Auerbach's plexus of the rat cecum in relation to the germfree state.Journal of Comparative Neurology 125, 11–18.
Earlam, R. J. (1971) Ganglion cell changes in experimental stenosis of the gut.Gut 12, 393–8.
Filogamo, G. (1955) Iperplasia ed ipertrofia delle cellule gangliari del plesso sottomucoso (di Meissner) nel cane, in condizioni sperimentali.Rivista di Biologia 47, 331–42.
Filogamo, G. &Marchisio, P. C. (1970) Choline acetyltransferase activity in rabbit ileum wall. The effect of extrinsic and intrinsic denervation and of combined experimental hypertrophy.Archives Internationales de Physiologie et de Biochemie 78, 141–52.
Filogamo, G. &Vigliani, F. (1954) Ricerche sperimentali sulla correlazione tra estensione del territorio di innervazione e grandezza e numero delle cellule gangliari del plesso mienterico (di Auerbach), nel cane.Rivista di Patologia Nervosa e Mentale 75, 441–62.
Gabella, G. (1979) Hypertrophic smooth muscle. I. Size and shape of cells, occurrence of mitoses.Cell and Tissue Research 201, 63–78.
Gabella, G. &Trigg, P. (1984) Size of neurons and glial cells in the enteric ganglia of mice, guinea-pigs, rabbits and sheep.Journal of Neurocytology 13, 49–71.
Herczel, E. (1886) Experimentelle und histologische Untersuchungen über compensatorische Muskelhypertrophie bei Darmstenosen.Zeitschrift für klinisches Medicin 11, 321–41.
Okada, A. &Okamoto, E. (1971) Myenteric plexus in hypertrophied intestine.Journal of Neuro-Visceral Relations 32, 75–89.
Wostmann, B. &Bruckner-Kardoss, E. (1959) Development of cecal distension in germ-free baby rats.American Journal of Physiology 197, 1345–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabella, G. Size of neurons and glial cells in the intramural ganglia of the hypertrophic intestine of the guinea-pig. J Neurocytol 13, 73–84 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148319
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148319