Abstract
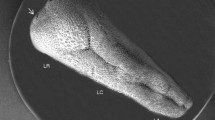
The three-dimensional configurations of the proprial papillae in the human esophagus were observed by light microscopy, routine transmission electron microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy combined with NaOH maceration. Numerous finger-like or filiform papillae with a height of about 100μm and a width at the base of approximately 30μm were clearly distributed in the uppermost proprial layer at approximately equal intervals. The adepithelial surface of the proprial papillae was bordered by a reticular fiber sheet that was stained a deep black color by silver staining. The papillae possessed blood capillaries with fenestration, nerve fibers, and free cells such as lymphocytes, eosinophils, mast cells, and Langerhans-like cells. These findings clearly demonstrate characteristic three-dimensional features of proprial papillae, and their constituent cellular and structural elements in human esophagus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawabe TT, Maccallum DK, Lillie JH (1985) Variation in basement membrane topography in human thick skin. Anat Rec 211:142–148
Misumi Y, Akiyoshi T (1984) Scanning electron microscopic structure of the finger print as related to the dermal surface. Anat Rec 208:49–55
Klein-Szanto AJP, Schroeder HE (1977) Architecture and density of the connective tissue papillae of the human oral mucosa. J Anat 123:93–109
Warfel KA, Hull MT (1984) Scanning electron microscopic study of the epithelial-mesenchymal junction of the esophagus. Scanning Electron Microsc 2:697–701
Hull MT, Warfel KA (1986) Basal lamina at the epithelialconnective tissue junction in the rat forestomach, esophagus, tongue and palate: Scanning electron microscopic study. Scanning Electron Microsc 4:1395–1401
Kobayashi S, Toh H, Tomo S, Ideguchi T, Nagamoto S, Kikuchi N, Itoh R (1992) Scanning electron microscopic study on the lingual papillae in the Manchurian chipmunk, Tamias sibiricus asiaticus. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 69:139–144
Kobayashi K, Kumakura M, Shinkai H, Ishii K (1994) Three-dimensional fine structure of the lingual papillae and their connective tissue cores in the human tongue. Acta Anat Nippon 69:624–635
Braverman IM, Yen A (1977) Ultrastructure of the human dermal microcirculation. II. The capillary loops of the dermal papillae. J Invest Dermatol 68:44–52
Umeda N, Ikeda A (1988) Scanning electron microscopic study of the capillary loops in the dermal papillae. Acta Anat 132:270–275
Imayama S (1981) Scanning and transmission electron microscope study on the terminal blood vessels of the rat skin. J Invest Dermatol 76:151–157
Suzuki H, Kurosumi K (1972) Fine structure of the cutaneous nerve endings in the mole snout. Arch Histol Jpn 34:35–50
Geboes K, De Wolf-Peeters C, Rutgeerts P, Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Desmet V (1983) Lymphocytes and Langerhans cells in human oesophageal epithelium. Virchows Arch (Pathol Anat) 401:45–55
Al Yassin TM Toner PG (1976) Langerhans cells in the human oesophagus. J Anat 122:435–445
Birbeck MS, Breathnach AS, Everall JD (1961) An electron microscopic study of basal melanocytes and high level clear cells (Langerhans cells) in vitilligo. J Invest Dermatol 37:51–64
Zelickson AS (1965) The Langerhans cell. J Invest Dematol 44:201–212
Waterhouse JP, Squire CA (1967) The Langerhans cell in human gingival epithelium. Arch Oral Biol 12:341–348
Fokkens WJ, Vroom TM, Rijntjes E, Mulder PG (1989) CD-1 (T6), HLA-DR-expressing cells, presumably Langerhans cells, in nasal mucosa. Allergy 44:167–172
Younes MS, Robertson EM, Bencosme SA (1968) Electron microscopic observation of Langerhans cells in the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 102:397–403
Carr MM, McVittie E, Guy K, Gawkrodger DJ, Hunter JAA (1986) MHC class II antigen expression in normal human epidermis. Immunology 59:223–227
Behar J, Sheahan DC (1975) Histologic abnormalities in reflux esophagitis. Arch Pathol 99:387–391
Frithiof L (1969) Ultrastructure of the basement membrane in normal and hyperplastic human oral epithelium compared with that in preinvasive and invasive carcinoma. Acta Path Microbiol Scand [Suppl cc] 3–63
Slavkin HC, Bringas P, Levene S, Stahl S, Bavetta LA (1971) Dermal-epidermal interactions in human gingival crevicular epidermis. Int Assn Dent Res Abstracts: 136
Ohtani O (1987) Three-dimensional organization of the connective tissue fibers of the human pancreas. A scanning electron microscopic study of NaOH treated tissues. Arch Histol Jpn. 50:557–566
Shimada T, Sato F, Zhang L, Ina K, Kitamura H (1993) Three-dimensional visualization of the aorta and elastic cartilage after removal of extracellular ground substance with a modified NaOH maceration method. J Electron Microsc 42:323–333
Gömöri G (1934) Der mikrotechnische Nachweis unlöslicher Kalksalze in den Geweben. Virchows Arch 286:682–689
Takita K, Shimada T, Kitamura H, Fujii S, Nakamura M (1990) Studies on the physical developer for use in immunohistochemistry. Acta Histochem Cytochem 23:647–662
Tokunaga J, Edanaga M, Fujita T, Adachi K (1974) Freeze cracking of scanniing electron microscope specimens. A study of the kidney and spleen. Arch Histol Jpn 37:165–182
Inoue T, Osatake H (1988) A new drying method of biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy: the t-buthyl alcohol freeze-drying method. Arch Histol Cytol 51:53–59
Cwikiel M, Yang MQ, Albertsson M, Hakansson CH, Palmegren M (1993) Scanning electron microscopy of human esophageal mucosa in patients with carcinoma of the esophagus. Scanning Microsc 7:933–942
Low FN, McClugage SG (1984) Microdissection by ultrasonication: scanning electron microscopy of the epithelial basal lamina of the alimentary canal in the rat. Am J Anat 169:137–147
Horstmann E (1952) Über den Papillarkörper der menschlichen Haut und seine regionalen Unterschiede. Acta Anat 14:23–42
Horstmann E (1954) Morphologie und Morphogenese des Papillarkörpers der Schleimhäute in der Mundhöhle des Menschen. Z Zellforsch 39:479–514
Selby WS, Janossy G, Jewell DP (1981) Immunohistological characterisation of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut 22:169–176
Befus AD, Johnston N, Leslie GA, Bienenstock J (1980) Gut-associated lymphoid tissue in the chicken. I. Morphology, ontogeny and some functional characteristics of Peyer's patches. J Immunol 125:2626–2632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, K., Shimada, T. & Uchida, Y. Morphology of the lamina propria in the human esophagus with special reference to the proprial papillae. Med Electron Microsc 30, 15–24 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458347
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458347