Abstract
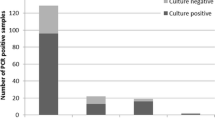
The aim of this study was to determine whether difficult-to-grow mycobacteria are present in human intestines. Intestinal tissue samples were subjected to both mycobacterial culture and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. After detection by PCR, species identity was determined by hybridizing the amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments with species-specific oligonucleotides. Intestinal biopsies from 63 patients with noninflammatory bowel diseases (n=22), Crohn's disease (n=31), or ulcerative colitis (n=10) were analyzed. Culture and PCR revealed mycobacteria in four (6%) and 25 (40%) samples, respectively. Samples positive by PCR were negative with all probes specific to nine common cultivable species but were positive with theMycobacterium genavense-specific probe in 68% of cases. Mycobacterial isolates were identified asMycobacterium gordonae andMycobacterium chelonae. Findings were similar in Crohn's disease samples compared to non-Crohn's disease samples. This study shows that difficult-to-grow mycobacteria can be detected by PCR in large and similar proportions of inflamed intestinal tissue from patients with inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal tissue that appears normal from patients with noninflammatory bowel disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Springer B, Stockman L, Teschner K, Roberts GD, Böttger EC: Two-laboratory collaborative study on identification of mycobacteria: molecular versus phenotypic methods. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1996, 34: 296–303.
Hirschel B, Chang HR, Mach N, Piguet PF, Cox J, Piguet JD, Silva MT, Larsson L, Klatser PK, Thole JER, Rigouts L, Portaels F: Fatal infection with a novel, unidentifiedMycobacterium in a man with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1990, 323: 109–113.
Bosquée L, Böttger EC, De Beenhouwer H, Fonteyne PA, Hirschel B, Larsson L, Meyers WM, Palomino JC, Realini L, Rigouts L, Silva MT, Teske A, Van Der Auwera P, Portaels F: Cervical lymphadenitis caused by fastidiousMycobacterium closely related toMycobacterium genavense in an apparently immunocompetent woman: diagnosis by culture-free microbiological methods. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1995, 33: 2670–2674.
Chiodini RJ: Crohn's disease and the mycobacterioses: a review and comparison of two disease entities. Clinical Microbiological Reviews 1989, 2: 90–117.
Fidler HM, Thurrel W, Johnson N, Rook GWA, McFadden JJ: Specific detection ofMycobacterium paratuberculosis DMA associated with granulomatous tissue in Crohn's disease. Gut 1994, 35: 506–510.
Suenaga K, Yokoyama Y, Okazaki K, Yamamoto Y: Mycobacteria in the intestine of Japanese patients with inflammatory bowel disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1995, 90: 76–80.
Portaels F: Epidemiology of mycobacterial diseases. Clinics in Dermatology 1995, 13: 207–222.
Schuppler N, Mertens F, Schon G, Gobel UB: Molecular characterization of nocardioform actinomycetes in activated sludge by 16S rRNA analysis. Microbiology 1995, 141: 513–521.
Anand BS, Schneider FE, El Zaatari GAK, Shawar M, Clarridge JE, Graham DY: Diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction on endoscopic biopsy specimens. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1994, 89: 2248–2249.
De Beenhouwer H, Liang Z, de Rijk P, van Ekeren C, Portaels F: Detection and identification of mycobacteria by DNA amplification and oligonucleotide-specific capture plate hybridization. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1995, 33: 2994–2998.
Dumonceau JM, Van Gossum A, Adler M, Fonteyne PA, Van Vooren JP, Devière J, Portaels F: NoMycobacterium paratuberculosis found in Crohn's disease using the polymerase chain reaction. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1996, 41: 421–426.
Whipple DL, Callihan DR, Jarnagin JL: Cultivation ofMycobacterium paratuberculosis from bovine fecal specimens and a suggested standardized procedure. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 1991, 3: 368–373.
Portaels F, Réalini L, Bauwens B, Hirschel WM, Meyers W, De Meurichy W: Mycobacteriosis caused byMycobacterium genavense in birds kept in a zoo: 11 -year survey. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1996, 34: 319–323.
Vincent Lévy-Frébault V, Portaels F: Proposed minimal standards for the genusMycobacterium and for description of new slowly growingMycobacterium species. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 1992, 42: 315–323.
Roberts GD, Koneman EW, Kim YK:Mycobacterium. In: Balows A, Hausler WJ, Herrmann KL Jr, Isenberg HD, Shadomy HJ (ed): Manual of clinical microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, 1991, p. 304–339.
Dumonceau JM, Fonteyne PA, Réalini L, Van Gossum A, Van Vooren JP, Portaels F: Species-specificMycobacterium genavense DNA in intestinal tissues of individuals not infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1995, 33: 2514–2515.
Fraser VJ, Zuckerman G, Clouse RE, O'Rourke S, Jones M, Klasner J, Murray P: A prospective randomized trial comparing manual and automated disinfection methods. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 1993,14: 383–389.
Shepard CC, McRae DH: A method for counting acidfast bacteria. International Journal of Leprosy and Other Mycobacterial Diseases 1968, 36: 78–82.
Brosius J, Palmer ML, Poindexter J, Kennedy J, Noller HF: Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene fromEscherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 1978, 75: 4801–4805.
Böttger EC, Teske A, Kirschner P, Bost S, Chang HR, Beer V, Hirschel B: Disseminated“Mycobacterium genavense” infection in patients with AIDS. Lancet 1992, 340: 76–80.
Kaul K, Luke S, McGurn C, Snowden N, Monti C, Fry WA: Amplification of residual DNA sequences in sterile bronchoscopes leading to false-positive PCR results. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1996, 34: 1949–1951.
Mortatti RC, Maia LC, Fonseca LS: Absorption ofMycobacterium bovis BCG administered by the oral route. Vaccine 1987, 5: 109–114.
Allen BW: Isolation ofMycobacterium tuberculosis from faeces. Medical Laboratory Sciences 1989, 46: 101–106.
Portaels F, Larsson L, Smeets P: Isolation of mycobacteria from healthy persons' stools. International Journal of Leprosy 1988, 56: 468–470.
Portaels F, Fissette K, De Ridder K, Macedo PM, De Muynck A, Silva MT: Effects of freezing and thawing on the viability and the ultrastructure of in vivo grown mycobacteria. International Journal of Leprosy 1988, 56: 580–587.
Mashek H, Georgii A, Schmidt RE, Kirschner P, Böttger EC:Mycobacterium genavense: autopsy findings in three patients. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1994, 101: 95–99.
Nadal D, Caduff R, Kraft R, Slazenger M, Boomer T, Kirschner P, Böttger EC, Stead UB: Invasive infection withMycobacterium genavense in three children with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1993, 12: 37–43.
Tortoli E, Simonetti MT, Dionisio D, Meli M: Cultural studies on two isolates ofMycobacterium genavense from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1994, 18: 7–12.
Péchère M, Opravil M, Wald A, Chave JP, Bessesen M, Sievers A, Hein R, von Overbeck J, Clark RA, Tortoli E, Emicr S, Kirschner P, Gabriel V, Böttger EC, Hirschel B: Clinical and epidemiologic features of infection withMycobacterium genavense. Archives of Internal Medicine 1995,155: 400–404.
Collins CH, Grange JM, Yates MD: Mycobacteria in water, a review. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 1984, 57: 193–211.
Peters M, Müller C, Rüsch-Gerdes S, Seidel C, Göbel U, Pohle HD, Ruf B: Isolation of atypical mycobacteria from tap water in hospital and homes: is this a possible source of disseminated MAC infection of AIDS patients? Journal of Infection 1995, 31: 39–44.
Sanderson JD, Moss MT, Tizard MLV, Hermon-Taylor J:Mycobacterium paratuberculosis DNA in Crohn's disease tissues. Gut 1992, 33: 890–896.
Kreuzpaintner GP, Kirschner A, Wallner R, Kölble R, Hesterberg R, Thomas L, Borchard F: Mycobacteria of Runyon groups I, II and IV do not play an aetiological role in Crohn's disease. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1995, 7: 1177–1182.
Rowbotham DS, Mapstone NP, Trejdosiewicz LK, Howdie PD, Quirke P:Mycobacterium paratuberculosis DNA not detected in Crohn's disease tissue by fluorescent polymerase chain reaction. Gut 1996, 37: 660–667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumonceau, J.M., Van Gossum, A., Adler, M. et al. Detection of fastidious mycobacteria in human intestines by the polymerase chain reaction. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 16, 358–363 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01726363
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01726363