Summary
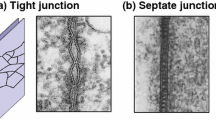
Epithelial cells are joined at their apical surfaces byzonulae occludentes. Claude and Goodenough (1973) demonstrated a correlation between the structure of thezonula occludens as seen in freeze-fracture preparations and the passive electrical permeability of several simple epithelia. In epithelia with high transepithelial resistance, thezonula occludens consisted of many strands. In epithelia with low transepithelial resistance thezonula occludens was much reduced, sometimes consisting of only one strand.
Evidence is reviewed here that indicates that in a number of simple epithelia the structure of thezonula occludens is largely responsible for the magnitude of transepithelial conductance. An equation is derived relating transepithelial junctional resistance to the number of junctional strands:R=R min p −n whereR is the transepithelial resistance of thezonula occludens,R min is the minimum resistance of the junction (as when there areno strands in the zonula occludens),p is the probability a given strand is “open” andn is the number of strands in the junction. Using published experimental values ofR andn for different epithelia, the calculated value ofp was found to be as high as 0.4, which suggests that the strands in thezonula occludens are remarkably labile.
Other morphological parameters relevant to transepithelial permeability are also considered, such as the width and depth of the intercellular spaces, and the size of the epithelial cells themselves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, R.J.C., Smyth, D.H., Wright, E.M.. 1965. Short circuit current and solute transfer by rat jejunum.J. Physiol. (London) 181:410
Berridge, M.J., Oschman, J.L. 1972.Transporting Epithelia. Academic Press, New York
Bindslev, N., Tormey, J. McD., Wright, E.M. 1974. The effects of electrical and osmotic gradients on lateral intercellular spaces and membrane conductance in a low resistance epithelium.J. Membrane Biol. 19:357
Boulpaep, E.L. 1971. Electrophysiological properties of the proximal tubule: Importance of cellular and intercellular transport pathways. In: Electrophysiology of Epithelial Cells. Symposia Medica Hoechst, 1970. G. Giebisch, editor. Schattauer Verlag, Stuttgart
Boulpaep, E.L., Seely, J.F. 1971. Electrophysiology of proximal and distal tubules in the autoperfused dog kidney.Am. J. Physiol. 221:1084
Civan, M.M., Frazier, H.S. 1968. The site of the stimulatory action of vasopressin on sodium transport in toad bladder.J. Gen. Physiol. 51:589
Claude, P. 1968. An electron microscopic study of the urinary tubules ofNecturus maculosus. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pennsylvania. University Microfilms, (No. 69–15,044) Ann Arbor
Claude, P., Goodenough, D.A. 1973. Fracture faces ofzonulae occludentes from “tight” and “leaky” epithelia.J. Cell Biol. 58:390
Dalton, A.J., Haguenau, F. 1967. Ultrastructure of the Kidney. Academic Press, New York and London
DiBona, D.R., Civan, M.M. 1973. Pathways for movement of ions and water across toad urinary bladder. I. Anatomic site of transepithelial shunt pathways.J. Membrane Biol. 12: 101
Erlij, D., Martínez-Palomo, A. 1972. Opening of tight junctions in frog skin by hypertonic urea solutions.J. Membrane Biol. 9:229
Friend, D.S., Gilula, N.B. 1972. Variations in tight and gap junctions in mammalian tissues.J. Cell Biol. 53:758
Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1972. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences.J. Gen. Physiol. 59:318
Frömter, E. 1972. The route of passive ion movement through the epithelium ofNecturus gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 8:259
Frömter, E., Diamond, J. 1972. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia.Nature, New Biol. 235:9
Graham, R.C., Karnovsky, M.J. 1966. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: Ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14:291
Higgins J.T., Jr., Cesaro, L., Gebler, B., Frömter, E. 1975. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia.Pfluegers Arch. 358:41
Humbert, F., Grandchamp, A., Pricam, C., Perrelet, A., Orci, L. 1976. Morphological changes in tight junctions ofNecturus maculosus proximal tubules undergoing saline diuresis.J. Cell Biol. 69:90
Katz, B., Miledi, R. 1972. The statistical nature of the acetylcholine potential and its molecular components.J. Physiol. (London) 224:665
Kaye, G.I., Wheeler, H.O., Whitlock, R.T., Lane, N. 1966. Fluid transport in the rabbit gallbladder. A combined physiological and electron microscope study.J. Cell Biol. 30: 237
Lewis, S.A., Eaton, D.C., Diamond, J.M. 1976. The mechanism of Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 28:41
Machen, T.E., Erlij, D., Wooding, F.B.P. 1972. Permeable junctional complexes. The movement of lanthanum across rabbit gallbladder and intestine.J. Cell Biol. 54:302
Magleby, K.L., Stevens, C.F. 1972. A quantitative description of end-plate currents.J. Physiol. (London) 223:173
Martínez-Palomo, A., Erlij, D. 1975. Structure of tight junctions in epithelia with different permeability.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 72:4487
Miller, F. 1960. Hemoglobin absorption by the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule in mouse kidney.J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 8:689
Moreno, J.H., Diamond, J. M. 1974. Discrimination of monovalent inorganic cations by “tight” junctions of gallbladder epithelium.J. Membrane Biol. 15:277
Pricam, C., Humbert, F., Perrelet, A., Orci, L. 1974. A freeze-etch study of the tight junctions of the rat kidney tubules.Lab. Invest. 30:286
Rawlins, F.A., González, E., Pérez-González, M., Whittembury, G. 1975. Effect of transtubular osmotic gradients on the paracellular pathway in toad kidney proximal tubule.Pfluegers Arch. 353:287
Reuss, L., Finn, A.L. 1974. Passive electrical properties of toad urinary bladder epithelium: Intercellular coupling and transepithelial cellular and shunt conductance.J. Gen. Physiol. 64:1
Rodewald, R. 1973. Intestinal transport of antibodies in the newborn rat.J. Cell Biol. 58:189
Smulders, A.P., Tormey, J. McD., Wright, E.M. 1972. The effect of osmotically induced water flows on the permeability and ultrastructure of the rabbit gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 7:164
Staehelin, L.A. 1974. Structure and function of intercellular junctions.Int. Rev. Cytol. 39:191
Wade, J.B., Karnovsky, M.J. 1974. Fracture faces of osmotically disruptedzonulae occludentes.J. Cell Biol. 62:344
Walser, M. 1970. Role of edge damage in sodium permeability of toad bladder and a means of avoiding it.Am. J. Physiol. 219:252
Wilson, T.H. 1962. Intestinal Absorption. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claude, P. Morphological factors influencing transepithelial permeability: A model for the resistance of theZonula Occludens . J. Membrain Biol. 39, 219–232 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870332
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870332