Abstract
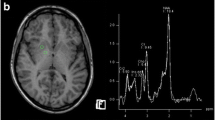
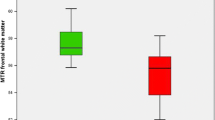
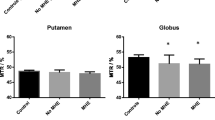
Conventional T1-weighted spin echo (T1WSE) and T1-weighted magnetization transfer (MT) images were obtained in 26 patients with biopsy-proven cirrhosis (nine Child's grade A, 10 Child's grade B and seven Child's grade C). Four subjects showed no evidence of neuropsychiatric impairment on clinical, psychometric and electrophysiological testing, seven showed evidence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy and 15 were classified as having overt hepatic encephalopathy. Signal intensities of basal ganglia nuclei (head of caudate, putamen, globus pallidus and thalamus) and adjacent brain parenchyma were measured and contrast calculated. On T1WSE imaging, contrast measurements of the globus pallidus were significantly greater in patients with neuropsychiatric dysfunction than in those who were unimpaired (p<0.05). This was not observed in the other basal ganglia nuclei. Patients with subclinical and overt hepatic encephalopathy could not be distinguished on the basis of contrast measurements of the globus pallidus or of any other nucleus. T1WSE contrast measurements of the globus pallidus were increased with elevations in blood ammonia levels (p<0.05) and with the severity of liver dysfunction, when graded according to the Pugh's score (p<0.05). Those patients with the worst liver injury (Child's grade C) had significantly greater T1WSE pallidal contrast measurements (p<0.05) than those patients with minimal liver injury (Child's grade A). The patients with intermediate liver damage (Child's grade B) could not be distinguished from the other two groups. While MT imaging highlighted the basal ganglia and showed a correlation between globus pallidus contrast and blood ammonia levels (p<0.05), no other relationship between MT contrast measurements and either the degree of hepatic encephalopathy or the severity of liver dysfunction was found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunberg, J. A., Kanal, E., Hirsch, W., and Van Thiel, D. H. (1991). Chronic acquired hepatic failure: MR imaging of the brain at 1.5 T.Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 12:909–914
Butterworth, R. F., Giguere, J. F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J., and Pomier-Layrargues, G. (1987). Ammonia: key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy.Neurochem. Pathol. 6:1–12.
Chen, S., Mahadevan, V., and Zieve, L. (1970) Volatile fatty acids in the breath of patients with cirrhosis of the liver.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 75:622–627.
Conn, H. O., Leevy, C. M., Vlahcevic, Z. R., Rodgers, J. B., Madrey, W. C., Seeff, L., and Leevy, L. L. (1977). Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a double blind trial.Gastroenterology 72:573–583.
Conn, H. O. (1977). Trail making and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy.Am. J. Dig. Dis. 22:541–550.
Cooper, A. J. L., and Plum, F. (1987). Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia.Physiol. Rev. 67:440–519.
Ferenci, P. (1991). Hepatic Encephalopathy. In McIntyre, N., Benhamou, J.-P., Bircher, J., Rizzetto, M., and Rodes, J. (eds.).Oxford Textbook of Clinical Hepatology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 473–483.
Gupta, R. K., Saraswat, V. A., Poptani, H., Dhiman, R. K., Kohli, A., Gujral, R. B., and Naik, S. R. (1993). Magnetic resonance imaging and localisedin vivo proton spectroscopy in patients with fulminant hepatic failure.Am. J. Gastroenterol. 88:670–674.
Hajnal, J. V., Baudouin, C. J., Oatridge, A., Young, I. R., and Bydder, G. M. (1992). Design and implementation of magnetization transfer pulse sequences for clinical use.J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 16:7–18.
Inoue, E., Hori, S., Narumi, Y., Fujita, M., Kuriyama, K., Kadota, T., and Kuroda, C. (1991). Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MR images.Radiology 179:551–555.
Jenner, P. (1994). Oxidative damage in neurodegeneration disease.Lancet. 344:796–798.
Kendrick, D. C., Gibson, A. J., and Moyes, I. G. A. (1979). The revised Kendrick battery: clinical studies.Br. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 18:329–339.
Kulisevsky, J., Pujol, J., Balanzo, J., Junqué, C., Deus, J., Capdevilla, A., and Villanueva, C. (1992). Pallidal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging in cirrhotic patients: clinical correlations.Hepatology 16:1382–1388.
Levy, L. M., Yang, A., Hennigar, R., Rothstein, J., and Bryan, R. N. (1989). The brain and hepatic encephalopathy MR abnormalities [Abstract].Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 10:904.
McConnell, J., and Castaldo, P. (1990). Striatal hyperemia, transient liver failure and chorea after liver transplantation [Abstract].J. Hepatol. 10 (Suppl. 1):S16
Mirowitz, S. A., Westrich, T. J., and Hirsch, J. D. (1991). Hyperintense basal ganglia on T1-weighted MR images in patients receiving parenteral nutrition.Radiology 181:117–120
Mirowitz, S. A., Sartor, K., and Gado, M. (1989). High-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted MR images in neurofibromatosis.Am. J. Neuro. Radiol. 10:1159–1163.
Morgan, M. Y., Alonso, M., and Stanger, L. C. (1989). Lactitol and lactulose for the treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients.J Hepatol. 8:208–217.
Norenberg, M. D. (1981) The astrocyte in liver disease.Adv. Cell Neurobiol. 2:303–352.
Norenberg, M. D. (1987). The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy.J. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:13–29.
Norton, N. S., McConnell, J. R., Zetterman, R. K., and Rodriguez-Sierra, J. F. (1994). A quantitative evaluation of magnetic resonance image signal changes of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy.J. Hepatol. 21:764–770.
Pomier-Layrargues, G., Spahr, L., and Butterworth, R. F. (1995). Increased manganese concentrations in pallidum of cirrhotic patients.Lancet. 345:735
Pugh, R. N. H., Murray-Lyon, I. M., Dawson, J. L., Pietroni, M. C., and Williams, R. (1972). Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices.Br. J. Surg. 60:646–649.
Pujol, A., Graus, F., Peri, J., Mercader, J. M., Rimola, A. (1991). Hyperintensity in the globus pallidus on T1-weighted and inversion-recovery MRI: a possible marker of advanced liver disease.Neurology 41:1526–1527.
Pujol, A., Pujol, J., Graus, F., Rimola, A., Peri, J., Mercader, J. M.,et al. (1993). Hyperintense globus pallidus on T1-weighted MRI in cirrhotic patients is associated with severity of liver failure.Neurology.43:65–69.
Quero, J. C., Huizenga, J. R., Chamuleau, R. A. F. M., Blijenberg, B. G., Gips, C. H., and Schalm, S. W. (1993). Determination of ammonia in capillary and arterial blood simultaneously using the BAC II [Abstract].Hepato-Gastroenterol. 40:81.
Schenker, S., and Brady, C. E., III (1994). Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. In Conn, H. O., and Bircher, J. (eds.)Hepatic Encephalopathy: Syndromes and Therapies. Medi-Ed Press, Bloomington pp 43–61.
Syh, H. W., Chu, W. K., Mar, N., and McConnell, J. R. (1991). An image analysis on MR imaging of the brain for hepatic encephalopathy.Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 27:29–33.
Taylor-Robinson, S. D., Sargentoni, J., Marcus, C. D., Morgan, M. Y., and Bryant, D. J. (1994). Regional variations in cerebral proton spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy.Metab Brain Dis. 9:347–359.
Victor, M., Adams, R. D., and Cole, M. (1965). The acquired (non-Wilsonian) type of chronic hepatocerebral degeneration.Medicine 44:345–396.
Voorhies, T. M., Ehrlich, M. E., Duffy, T. E., Petito, C. K., and Plum, F. (1983). Acute hyperammonaemia in the young primate: physiologic and neuropathologic correlates.Pediatr. Res. 17:970–975.
Wechsler, D. (1955).Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Manual. Psychological Corporation, New York.
Zeneroli, M. L., Cioni, G., Crisi, G., Vezzelli, C., and Ventura, E. (1991). Globus pallidus alterations and brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with encephalopathy: an MR imaging study.Magn. Reson. Imaging.9:295–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor-Robinson, S.D., Oatridge, A., Hajnal, J.V. et al. MR imaging of the basal ganglia in chronic liver disease: correlation of T1-weighted and magnetisation transfer contrast measurements with liver dysfunction and neuropsychiatric status. Metab Brain Dis 10, 175–188 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991864
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991864