Abstract
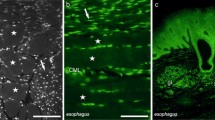
The innervation of the sphincter of Oddi (SO) has been extensively studied experimentally, but human studies have not been published, which is why this study was undertaken. Biopsies, taken by gastroscopy-biopsy forceps from duodenal epithelium of the papilla of Vater and from ampullary epithelium after sphincterotomy, did not demonstrate nerves and could not be used for studying SO innervation. Therefore SO specimens were obtained from brain-dead organ donors (N=5) and from autopsies (N=14). By staining with a myelin marker S-100, a rich network of nerves was demonstrated in SO. The occurrence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), peptide histidine-isoleucine (PHI) (or its immunologically similar human equivalent peptide histidine methioninamide, PHM), neuropeptide Y, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), galanin, substance P, enkephalin, bombesin, and somatostatin were studied by immunohistochemical technique. SO demonstrated immunoreactivity for VIP, PHI (PHM), neuropeptide Y, CGRP, galanin, somatostatin, substance P, and enkephalin, but no immunoreactivity was observed for bombesin. The SO immunoreactivity was similar in specimens from organ donors and from autopsies of victims of violence without pancreatobiliary diseases (N=3) when the specimens were taken within 48 hr of death. Autopsy specimens of SO from subjects with gallstone disease (N=5), recurrent pancreatitis (N=3) or periampullary carcinoma (N=3) also demonstrated similar immunoreactivity. We conclude that VIP-, PHI- (PHM-), neuropeptide Y-, CGRP-, galanin-, substance P-, somatostatin-, and enkephalin-like immunoreactivity occur in human SO. These neuropeptides may have role in the neural control of human SO function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parodi JE, Becker JM: Biliary motility. Gastroenterology 5:606–616, 1989
Bartlett MK: Might gallstones and recurrent pancreatitis have a common cause? Arch Surg 95:887, 1967
Toouli J, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Arndorfer RC: Sphincter of Oddi motor activity: A comparison between patients with common bile duct stones and controls. Gastroenterology 82:111–117, 1982
Toouli J, Roberts-Thomson IC, Dent J, Lee J: Sphincter of Oddi motility disorders in patients with idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis. Br J Surg 72:859–863, 1985
Todani T, Watanabe Y, Toki A, Urushihara N, Sato Y: Reoperation for congenital choledochal cyst. Ann Surg 207:142–147, 1988
Kinami Y, Ashida Y, Seto K, Takashima S, Kita I: Influence of incomplete bile duct obstruction on the occurrence of cholangiocarcinoma induced by diisopropanolnitrosamine in hamsters. Oncology 47:170–176, 1990
Grace PA, Poston GJ, Williamson RCN: Biliary motility. Gut 31:571–582, 1990
Sand J, Tainio H, Nordback I: Neuropeptides in pig sphincter of Oddi, bile duct, gallbladder, and duodenum. Dig Dis Sci 38:694–700, 1993
Coons AH: Fluorescent antibody methods.In General Cytochemical Methods. JF Danielli (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1958, pp 399–422
Vaalasti A, Tainio H, Rechardt L: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) -like immunoreactivity in the nerves of human axillary sweat glands. J Invest Dermatol 85.3:246–248, 1985
Hervonen A, Linnoila I, Tainio H, Vaalasti A, Mascorro JA: Immunohistochemical evidence for the occurrence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-containing fibres in human fetal abdominal paraganglia. J Anat 143:121–129, 1985
Vaalasti A, Tainio H, Pelto-Huikko M, Hervonen A: Light and electron microscopic demonstration of nerves containing immunoreactivity to VIP and enkephalins in human male genito-urinary tract. Anat Rec 215:21–27, 1986
Tainio H, Vaalasti A, Rechardt L: The distribution of sympathetic adrenergic tyrosine hydroxylase- and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive nerves in human axillary sweat glands. Histochemistry 85:117–120, 1986
Tainio H, Vaalasti A, Rechardt L: The distribution of substance P-, CGRP-, galanin- and ANP-like immunoreactive nerves in human sweat glands. Histochem J 19:375–380, 1987
Johansson O, Vaalasti A, Tainio H, Ljungberg A: Immunohistochemical evidence of galanin in sensory nerves of human digital skin. Acta Physiol Scand 132:261–263, 1988
Vaalasti A, Tainio H, Johansson O, Rechardt L: Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical demonstration of intraepidermal CGRP-containing nerves in human skin. Skin Pharmacol 1:225–229, 1988
Sisto T, Tainio H, Vaalasti A: Neuropeptides in the human internal mammary artery. Acta Physiol Scand 136:615–616, 1989
Tainio H, Kylmälä T, Heikkinen A: Peptidergic innervation of normal and obstructed human pyeloureteral junction. Urol Inter 48:31–34, 1992
Kyösola K, Rechardt L: Adrenergic innervation of the choledochoduodenal junction of the cat and dog. Histochemie 34:325–332, 1973
Kyösola K: Cholinesterase histochemistry of the innervation of the smooth muscle sphincters around the terminal intramural part of the ductus choledochus in the cat and dog. Acta Physiol Scand 90:278–280, 1974
Cai W, Gu J, Huang W, McGregor GP, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR: Peptide immunoreactive nerves and cells of the guinea pig gall bladder and biliary pathways. Gut 24:1186–1193, 1983
Dahlstrand C, Dahlström A, Theodorsson E, Rehfeld J, Ahlman H: Is the CCK-8 induced relaxation of the feline sphincter of Oddi mediated by VIP neurons? J Auton Nerv Syst 31:75–84, 1990
Dahlstrand C, Theodorsson E, Dahlström A, Ahlman H: VIP antisera inhibit the relaxatory motor responses of the feline sphincter of Oddi and gallbladder induced by VIP or vagal nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 137:375–378, 1989
Dahlstrand C, Dahlström A, Ahlman H: Adrenergic and VIP-ergic relaxatory mechanisms of the feline extrahepatic biliary tree. J Auton Nerv Syst 26:97–106, 1989
Wiley JW, O'Dorisio TM, Owyang C: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediates cholecystokinin-induced relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. J Clin Invest 81:1920–1924, 1988
Allen M, Gu J, Adrian TE, Polak JM, Bloom SR: Neuropeptide Y in the guinea pig biliary tract. Experientia 40:765–767, 1984
Lillemoe KD, Webb TH, Pitt HA: Neuropeptide Y: A candidate neurotransmitter for biliary motility. J Surg Res 45:254–260, 1988
Goehler LE, Sternini C, Brecha NC: Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the biliary pathway and liver of the guinea pig: Distribution and colocalization with substance P. Cell Tissue Res 253:145–150, 1988
Parodi JE, Zenilman ME, Becker JM: Characterization of substance P effect on sphincter of Oddi myoelectric activity. J Surg Res 46:405–412, 1989
Parodi JE, Cho N, Zenilman ME, Barteau JA, Soper NJ, Becker JM: Substance P stimulates the opossum sphincter of Oddi in vitro. J Surg Res 49:197–204, 1990
Guo YS, Singh P, Gomez G, Rajaraman S, Thompson JC: Contractile response of canine gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi to substance P and related peptides in vitro. Dig Dis Sci 34:812–817, 1989
Harling H, Messell T, Jensen ST, Poulsen SS: Distribution and effect of galanin on gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi motility in the pig. HPB Surg 3:279–289, 1991
Ahrendt SA, McGuire GE, Lillemoe KD, Trias M, Kaloo A, Pitt HA: Somatostatin inhibits sphincter of Oddi motility. Gastroenterology 98:A242, 1990
Adami GF, Leandri R, Sarles JC: Effect of somatostatin on the rabbit Oddi's sphincterin vivo. Interrelation of somatostatin and cholecystokinin. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 10:108–111, 1986
Itoh N, Obata K, Yanaihara N, Okamoto H: Human preprovasoactive intestinal peptide contains a novel PHI-27 like peptide, PHM-27. Nature 304:547–549, 1983
Bloom SR, Christofides ND, Delamarter J, Buell G, Kawashima E, Polak JM: Diarrhoea in VIPoma patients associated with cosecretion of a second active peptide, PHI, explained by a single coding gene. Lancet 2:1163–1165, 1983
Grider JR, Makhlouf GM: Prejuntional inhibition of vasoactive intestinal peptide release. Am J Physiol 253:G7-G12, 1987
Bounjoua Y, Vandermeers A, Robberecht P, Vandermeers-Piret M-C, Christophe J: Purification and amino acid sequence of vasoactive intestinal peptide, peptide histidine isoleucinamide and secretin from the ovine small intestine. Regul Pept 32:169–179, 1991
Guelrud M, Rossiter A, Souney PF, Mendoza S, Mujica V: The effect of transcutaneous nerve stimulation on sphincter of Oddi pressure in patients with biliary dyskinesia. Am J Gastroenterol 86:581–585, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sand, J., Tainio, H. & Nordback, I. Peptidergic innervation of human sphincter of Oddi. Digest Dis Sci 39, 293–300 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090200
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02090200