Abstract
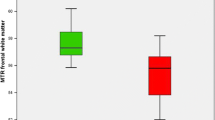
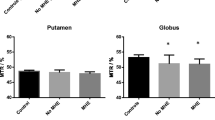
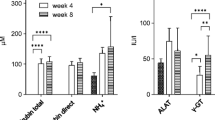
Regional variations in proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) were assessed in 26 patients and 14 healthy volunteers using a two dimensional chemical shift imaging technique. Patients were classified as being neuropsychiatrically unimpaired, or as having subclinical or overt chronic hepatic encephalopathy (CHE). Peak area ratios of choline (Cho), glutamine and glutamate (Glx) and N-acetylaspartate (NAA) relative to creatine (Cr) were measured. Significant reductions in mean Cho/Cr and elevations in mean Glx/Cr were observed in the patient population, which correlated with the severity of CHE. There were significant regional variations in these metabolite ratios with the mean Cho/Cr lowest in the occipital cortex and the mean Glx/Cr highest in the basal ganglia. NAA/Cr remained relatively constant in all areas of the brain analysed. The regional variation in the metabolite ratios suggests that spectral information from more than one voxel may be useful in the assessment of patients with CHE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruhn, H., Merboldt, K.D., Michaelis, T., Gyngell, M.L., Hänicke, W., Frahm, J., Schauder, P., Brunner, G., Held, K., Fröhlich, J., Häussinger, D., and Ross, B.D. (1991) Proton MRS of metabolic disturbances in the brain of patients with liver cirrhosis and subclinical hepatic encephalopathy.Proc 10th Ann Mtg Soc Magn Reson Med. 1: 400.
Brunberg, J.A., Kanal, E., Hirsch, W., and Van Thiel, D.H. (1991) Chronic acquired hepatic failure: MR imaging of the brain at 1.5 T.Am J Neuro Radiol. 12: 909–914
Bryant, D.J., Weeks, R.A., Marcus, C.D., Sargentoni, J., Taylor-Robinson, S., and Brooks, D.J. (1994) Glutamate in Huntington's disease.Lancet. 344: 189–190.
Butterworth, R.F., Giguere, J.F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J., and Layrargues, G.P. (1987) Ammonia: key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy.Neurochem Pathol. 6: 1–12.
Chamuleau, R.A., Bosman, D.K., Bovée, W.M.M.J., Luyten, P.R., and den Hollander, J.A. (1991) What the clinician can learn from MR glutamine/glutamate assays.NMR Biomed. 4: 103–108.
Conn, H.O. (1977a) Trail making and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy.Am J Dig Dis. 22: 541–550.
Conn, H.O., Leevy, C.M., Vlahcevic, Z.R., Rodgers, J.B., Madrey, W.C., Seeff, L., and Leevy, L.L. (1977b) Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a double blind trial.Gastroenterology. 72: 573–583.
Coutts, G.A., Cox, I.J., Gadian, D.G., Sargentoni, J., Bryant, D.J., and Collins, A.G. (1989) Phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the normal human brain. Approaches using four-dimensional chemical shift imaging and phase mapping techniques.NMR Biomed. 1: 190–197.
Ferenci, P., (1991) Hepatic Encephalopathy. In McIntyre, N., Benhamou, J-P., Bircher, J., Rizzetto, M., and Rodes, J. (eds.).Oxford Textbook of Clinical Hepatology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 473–483.
Fischer, J.E., (1992) Portal-systemic encephalopathy. In Millward-Sadler, G.H., Wright, R., Arthur, M.J.P. (eds.).Wright's Liver and Biliary Disease. W.B. Saunders Company Ltd., London, pp 1262–1295.
Frahm, J., Bruhn, H., Gyngell, M.L., Merboldt, K.D., Hänicke, W., and Sauter, R. (1989) Localised proton NMR spectroscopy in different regions of the human brainin vivo. Relaxation times and concentrations of cerebral metabolites.Magn Reson Med. 11: 47–63.
Hawkins, R.A., Mans, A.M., and Biebuyk, J.F. (1987) Changes in brain metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy.J Neurochem Pathol. 6: 35–66.
Hawkins, R.A., Jessy, J., Mans, A.M., and De Joseph, M.R. (1993) Effect of reducing brain glutamine synthesis on metabolic symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy.J Neurochem. 60: 1000–1006.
Hore, P.J., (1983) Solvent suppression in Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance.J Magn Reson. 54: 539–542.
Inoue, E., Hori, S., Narumi, Y., Fujita, M., Kuriyama, K., Kadota, T., and Kuroda, C. (1991). Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MR images.Radiology.179: 551–555
James, J.H., Escourrou, J., and Fischer, J.E. (1978) Blood-brain neutral amino acid transport activity is increased after portacaval anastomosis.Science.200: 1395–1397.
Kendrick, D.C., Gibson, A.J., and Moyes, I.G.A. (1979) The revised Kendrick battery: clinical studies.Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 18: 329–339.
Kreis, R., Ernst, T., and Ross, B.D. (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the brain. II Metabolite concentrations.J Magn Reson. 102: 9–19.
Kreis, R., Farrow, N., and Ross, B.D. (1991) Localised1H NMR spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Analysis of changes in cerebral glutamine, choline and inositols.NMR Biomed. 4: 109–116.
Kreis, R., Ross, B.D., Farrow, N.A., and Ackerman, Z. (1990) Diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Lancet. 336: 635–636
Kreis, R., Ross, B.D., Farrow, N.A., and Ackerman, Z. (1992) Metabolic disorders of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy detected with H-1 MR spectroscopy.Radiology.182: 19–27.
Kulisevsky, J., Pujol, J., Balanzo, J., Junqué, C., Deus, J., Capdevilla, A., and Villanueva, C. (1992) Pallidal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging in cirrhotic patients: clinical correlations.Hepatology. 16: 1382–1388.
Miller, L. (1991) A review of chemical issues in1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl aspartate, creatine and choline.NMR in Biomed. 4: 47–52.
Morgan, M.Y., Jakobovitz, A.W., James, I.M., and Sherlock, S. (1980) Successful use of bromocriptine in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy.Gastroenterology.78: 663–670.
Morgan, M.Y., Alonso, M., and Stanger, L.C. (1989) Lactitol and lactulose for the treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients.J Hepatol. 8: 208–217.
Norenberg, M.D. (1987) The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy.Neurochem Pathol. 6: 13–33.
Pugh, R.N.H., Murray-Lyon, I.M., Dawson, J.L., Pietroni, M.C., and Williams, R. (1972) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices.Br J Surg. 60: 646–649.
Pujol, A., Graus, F., Peri, J., Mercader, J.M., and Rimola, A. (1991) Hyperintensity in the globus pallidus on T1-weighted and inversion-recovery MRI: a possible marker of advanced liver disease.Neurology 41: 1526–1527
Pujol, A., Pujol, J., Graus, F., Rimola, A., Peri, J., Mercader, J.M., García-Pagan, J.C. Bosch, J., Rodes, J., and Tolosa, E. (1993) Hyperintense globus pallidus on T1-weighted MRI in cirrhotic patients is associated with severity of liver failure.Neurology 43: 65–69
Quero, J.C., Huizenga, J.R., Chamuleau, R.A.F.M., Blijenberg, B.G., Gips, C.H., and Schalm, S.W. (1993) Determination of ammonia in capillary and arterial blood simultaneously using the BAC II.Hepato-Gastroenterol. 40: 81.
Ross, B.D., Kreis, R., and Ernst, T. (1992) Clinical tools for the 90s: magnetic resonance spectroscopy and metabolite imaging.Eur J Rad. 14: 128–140.
Saeed, N. (1993) A knowledge based approach to suppress water component inin vivo proton spectroscopy.Proc 12th Soc Magn Reson Med. 1: 403.
Stahl, J. (1963) Studies of the blood ammonia in liver disease. Its diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic significance.Ann Int Med. 58: 1–24.
Syh, H.W., Chu, W.K., Mar N., and McConnell, J.R. (1991) An image analysis on MR imaging of the brain for hepatic encephalopathy.Biomed Sci Instrum. 27: 29–33
Taylor-Robinson, S.D., Weeks, R.A., Sargentoni, J., Marcus C.D., Bryant, D.J., Harding, A.C., and Brooks, D.J. (1994) Evidence for glutamate excitotoxicity in Huntington's disease with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Lancet. 343: 1170
Wechsler, D. (1955)Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Manual. New York: Psychological Corporation.
Zeneroli, M.L., Cioni, G., Crisi, G., Vezzelli, C., and Ventura, E. (1991) Globus pallidus alterations and brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with encephalopathy: an MR imaging study.Magn Reson Imaging. 9: 295–302
Zieve, L., Doizaki, W.M., and Zieve, F.J. (1974) Synergysm between mercaptans and ammonia or fatty acids in the production of coma: a possible role for mercaptans in the pathogenesis of hepatic coma.J Lab Clin Med. 83: 16–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor-Robinson, S.D., Sargentoni, J., Marcus, C.D. et al. Regional variations in cerebral proton spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 9, 347–359 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098881
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098881