Abstract
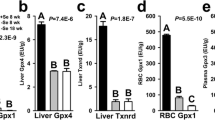
Severe selenium (Se) depletion was found in nine patients receiving long-term home parenteral nutrition because of short bowel syndrome. Plasma Se ranged from 0–0.51 (median 0.21 μmol/L) and erythrocyte Se ranged from 0.7–2.6 (median 1.8 μmol/gHgb), which was significantly lower than in the controls. Glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx) in plasma and erythrocytes was also decreased.
After bolus injections with 200 μg Se/d in the form of sodium selenite for 4 mo, followed by 100 μg/d for 8 mo, plasma Se increased to values slightly but significantly higher than in the controls. Erythrocyte Se reached normal levels in most of the patients after 4 mo substitution, but it remained lower than in the controls. Following Se supplementation, plasma and erythrocyte GSHPx did not differ between patients and controls. These data suggest that all patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition because of short bowel syndrome should receive at least 100 μg sodium selenite/d when given as bolus injections to avoid Se depletion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. E. Oldfield,J. Nutr. 117, 2002 (1987).
Keshan Disease Research Group of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Chinese Med. J. 92, 471 (1979).
C. R. Flemming, J. T. Lie, J. T. McCall, J. F. O'Brien, E. E. Baillie, and J. H. Thistle,Gastroenterology 83, 689 (1982).
W. C. Reeves, S. P. Marcuard, S. E. Willis, and A. Movahed,J.P.E.N. 13, 663 (1989).
C. L. Kien and H. E. Ganther,J. Clin. Nutr. 37, 319 (1983).
R. A. Johnson, S. S. Baker, J. T. Fallon, E. P. Maynard, J. N. Ruskin, Z. Wen, K. Ge, and H. J. Cohen,N. Engl. J. Med. 304, 1210 (1981).
J. C. Stanley, J. F. Alexander, and G. A. Nesbitt,Ulster Med. J. 51, 130 (1992).
R. A. Quercia, S. Korn, and D. O'Neill,Clin. Pharmacol. 3, 531 (1984).
K. Sriram, J. K. Peterson, J. O'Gara, and J. H. Hammond,Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 59(suppl.) 361 (1986).
P. J. Collipp and S. Y. Chen,N. Engl. J. Med. 304, 1304 (1981).
G. Lockitch, G. P. Taylor, L. T. K. Wong, A. G. E. Davidsson, P. J. Dison, and B. Massing,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 572 (1990).
A. M. Van Rij, C. D. Thomson, J. M. McKenzie, and M. F. Robinson,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32, 2076 (1979).
D. A. Kelly, A. W. Coe, A. Shenkin, B. D. Lake, and J. A. Walker-Smith,J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 7, 783 (1988).
R. D. Watson, R. A. Cannon, G. S. Kurland, K. L. Cox, and R. C. Frates,J.P.E.N. 9, 58 (1985).
M. R. Brown, H. J. Cohen, J. M. Lyons, T. W. Curtis, B. Thunberg, W. J. Cochran, and W. J. Klish,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 43, 549 (1986).
T. Rannem, K. Ladefoged, E. Hylander, J. Hegnhøj, and S. Jarnum,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 56, 933 (1992).
L. Lalonde, Y. Jean, K. D. Roberts, A. Chapdelaine, and G. Bleau,Clin. Chem. 28, 172 (1982).
D. E. Paglia and W. N. Valentine,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70, 158 (1967).
A. M. Rij, J. M. McKenzie, C. D. Thomson, and M. F. Robinson,J.P.E.N. 5, 120 (1981).
H. W. Lane, A. O. Barosso, D. A. Englert, and S. J. Dudrick,J.P.E.N. 6, 426 (1982).
S. S. Baker, R. H. Lerman, S. H. Krey, M. K. S. Croker, E. F. Hirsh, and H. Cohen,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 38, 769 (1983).
R. J. Baptista, B. R. Bistrian, G. L. Blackburn, D. G. Miller, C. D. Champagne, and L. Buchanan,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 39, 816 (1984).
H. J. Cohen, M. R. Brown, D. Hamilton, J. Lyons-Patterson, N. Avissar, and P. Liegeyne,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49, 132 (1989).
US National Research Council. Recommended Dietary allowances, National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., 9th ed. (1980).
H. E. Ganther and R. J. Kraus,J.P.E.N. 13, 185 (1989).
E. Postaire and P. Anglade,J.P.E.N. 14, 223 (1990).
G. Jang, S. Wang, R. Zhou, and S. Sun,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 37, 872 (1983).
C. D. Thomson and M. F. Robinson,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33, 303 (1980).
H. W. Lane, S. Dudrick, and D. C. Warren,Proc. Soc. Exp. Bio. Med. 167, 383 (1981).
H. M. Rea, C. D. Thomson, D. R. Campbell, and M. F. Robinsonn,Brit. J. Nutr. 42, 201 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rannem, T., Ladefoged, K., Hylander, E. et al. Selenium depletion in patients on home parenteral nutrition. Biol Trace Elem Res 39, 81–90 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783812
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783812