Abstract
Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a hepatic manifestation of the metabolic syndrome. The aim of this study was to evaluate a 6-month home-based lifestyle modification intervention delivered in collaboration with physicians, hygienists, registered dietitians, and nurses.
Methods
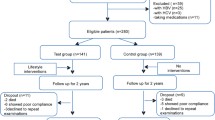
Outpatients with NAFLD diagnosed by abdominal ultrasonography were eligible for this study. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan evaluated liver fat deposition by the liver–spleen ratio (L/S ratio) and visceral fat accumulation as the visceral fat area (VFA; cm2). During the 6-month home-based lifestyle modification intervention, each patient was examined by physicians, nurses, hygienists, and registered dietitians, who provided individualized advice to the patients. Patients recorded their daily weight for self-control of weight with recommended diet and exercise regimens.
Results
Sixty-seven NAFLD patients were enrolled in this study and 22 patients (32.8%) completed the 6-month intervention. Nineteen of the 22 patients achieved significant improvements in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, VFA, L/S ratio, and systolic blood pressure, with improved laboratory data. Overall, 39 patients withdrew from the intervention. The mean age of the patients who withdrew was 50.0 ± 11.0 years, which was significantly younger than that of the patients who were followed up (60.1 ± 10.1 years; P < 0.01).
Conclusions
The reduction in body weight achieved by NAFLD patients during the 6-month intervention was associated with improved fat deposition and liver function. This intervention offers a practical approach for treating a large number of NAFLD patients with lifestyle modification therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, et al. Expanding the natural history of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:134–40.
Day CP. Natural history of NAFLD: remarkably benign in the absence of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:375–8.
Huang MA, Greenson JK, Chao C, Anderson L, Peterman D, Jacobson J, et al. One-year intense nutritional counseling results in histological improvement in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1072–81.
Suzuki A, Lindor K, St Saver J, Lymp J, Mendes F, Muto A, et al. Effects of changes on body weight and lifestyle in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2005;43:1060–6.
Riley P, Sudarshi D, Johal M, Benedict A, Panteli J, Crook M, et al. Weight loss, dietary advice and statin therapy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a retrospective study. Int J Clin Pract. 2008;62:374–81.
Tamura Y, Tanaka Y, Sato F, Choi JB, Watada H, Niwa M, et al. Effects of diet and exercise on muscle and liver intracellular lipid contents and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:3191–6.
Foster GD, Wyatt HR, Hill JO, McGuckin BG, Brill C, Mohammed BS, et al. A randomized trial of a low-carbohydrate diet for obesity. N Engl J Med. 2003;22:2082–90.
Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, Gramlich T, Ong JP, Hurley M, et al. The utility of radiological imaging in fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:745–50.
de Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, Sagrado MG, Conde R, Gonzalez JM. Effect of a hypocaloric diet on transaminases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients, relation with insulin resistance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79:74–8.
Fujimoto K, Sakata T, Etou H, Fukagawa K, Ookuma K, Terada K, et al. Charting of daily weight pattern reinforces maintenance of weight reduction in moderately obese patients. Am J Med Sci. 1992;303:145–50.
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, et al. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(Suppl):S498–516.
Nakagaichi M, Tanaka K. Development of a 12-min treadmill walk test at a self-selected pace for the evaluation of cardiorespiratory fitness in adult men. Appl Human Sci. 1998;17:281–8.
Astrand PO, Rodahl K. Applied sports physiology. In: Astrand PO, Rodahl K, Dahl HA, editors. Textbook of work physiology. Physiological bases of exercise. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1986. p. 646–82.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Exercise and physical activity reference for health promotion 2006. http://www.nih.go.jp/eiken/programs/pdf/epar2006.pdf. Jul 2006.
Haffner SM, Kennedy E, Gonzalez C, Stern MP, Miettinen H. A prospective analysis of the HOMA model. The Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:1138–41.
International Diabetes Federation. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome. http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/MetS_def_update2006.pdf. Cited 21 Jan 2009.
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J, IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome––a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–61.
Yoshizumi T, Nakamura T, Yamane M, Islam AH, Menju M, Yamasaki K, et al. Abdominal fat: standardized technique for measurement at CT. Radiology. 1999;211:283–6.
Ishibashi E, Eguchi Y, Eguchi T, Matsunobu A, Oza N, Nakashita S, et al. Waist circumference correlates with hepatic fat accumulation in male Japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, but not in females. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:908–13.
Ballentani S, Dalle Grave R, Suppini A, Marchesini G, Fatty Liver Italian Network. Behavior therapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the need for a multidisciplinary approach. Hepatology. 2008;47:746–54.
Chan HL, de Silva HJ, Leung NW, Lim SG, Farrell GC, Asia-Pacific Working Party on NAFLD. How should we manage patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in 2007? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:801–8.
de Piano A, Prado WL, Caranti DA, Siqueira KO, Stella SG, Lofrano M, et al. Metabolic and nutritional profile of obese adolescents with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007;44:446–52.
Gillies CL, Abrams KR, Lambert PC, Cooper NJ, Sutton AJ, Hsu RT, et al. Pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br Med J. 2007;334:299.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the medical staff at Eguchi Hospital; Ms. Yukie Watanabe, Chieko Ogawa, and Reiko Sonoda for their assistance, and Professor Kyuichi Tanikawa (International Institute for Liver Research) for his excellent advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oza, N., Eguchi, Y., Mizuta, T. et al. A pilot trial of body weight reduction for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with a home-based lifestyle modification intervention delivered in collaboration with interdisciplinary medical staff. J Gastroenterol 44, 1203–1208 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0115-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0115-x