Abstract
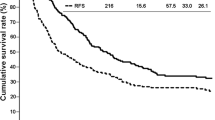
Liver resection may represent the only hope of cure for patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHC) but long-term results are still far from satisfactory and the impact of prognostic factors is still controversial. Fifty-five patients underwent hepatectomy for IHC between 1997 and 2008 in our unit. Features of the patients and the tumors, operations, postoperative and long-term results were retrospectively assessed. Twenty-one patients had HBV/HCV infection, four had congenital biliary dilatation. Thirty-two patients had increased CA 19-9; 12 had multiple (≥4) tumors. Operations included 43 major resections, with 9 resections of biliary confluence, 40 regional lymphadenectomies. Operative mortality and morbidity were 0 and 27.3%, respectively. There were 44 R0-resections (80.0%). Lymphadenectomy yielded lymph node metastases in 14 cases (14/40; 35.0%). Five-year overall and disease-free survival rates were 30.2 and 27.5%, respectively. At multivariate analysis the strongest poor prognostic factor for overall survival was tumor stage. This factor, with multiplicity of lesions (≥4) and tumor grading > 2, was significant predictor of recurrence. CA19-9 > 100 IU/mL and tumor grading > 2 were found to be significantly related with early multinodular hepatic recurrence. Patients with lymph node metastases had significantly lower overall and disease-free survival but patients who underwent lymph node dissection with negative lymph nodes at final pathology showed significantly higher 5-year disease-free survival than patients who did not underwent lymphadenectomy. In conclusion, these results support the role of hepatectomy with regional lymphadenectomy as the best available treatment for IHC. Prognosis after liver resection correlates with clinical stage and multiplicity of lesions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sano T, Shimada K, Sakamoto Y et al (2008) Prognosis of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: hilar bile duct cancer versus intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma involving the hepatic hilus. Ann Surg Oncol 15:590–599
Lesurtel M, Regimbeau JM, Farges O et al (2002) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatolithiasis: an unusual association in Western Countries. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:1025–1027
Lee CC, Wu CY, Chen GH (2002) What is the impact of coexistence of hepatolithiasis on cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:1015–1020
Jarnagin WR, Weber S, Tickoo SK et al (2002) Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma: demographic, clinical, and prognostic factors. Cancer 94:2040–2046
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC et al (2008) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg 248:84–96
Cherqui D, Tantawi B, Alon R et al (1995) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Results of aggressive surgical management. Arch Surg 130:1073–1078
Inoue K, Makuuchi M, Takayama T et al (2000) Long-term survival and prognostic factors in the surgical management of mass-forming type cholangiocarcinoma. Surgery 127:498–505
Weber SM, Jarnagin WR, Klimstra D et al (2001) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: resectability, recurrence pattern and outcomes. J Am Coll Surg 193:384–391
Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Sgourakis G et al (2009) Operations for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: single-institution experience of 158 patients. J Am Coll Surg 208:218–228
Jonas S, Thelen A, Benckert C et al (2009) Extended liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a comparison of the prognostic accuracy of the fifth and sixth editions of the TNM classification. Ann Surg 249:303–309
The Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan (1997) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. In: Classification of primary liver cancer, 1st edn. Kanehara, Tokyo, pp 6–7
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (2002) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 6th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Strasberg SM, Belghiti J, Clavien PA et al (2000) Terminology committee of the IHPBA. Terminology of liver anatomy and resections. HPB Surg 2:333–339
Nuzzo G, Giuliante F, Vellone M et al (2004) Pedicle clamping with ischemic preconditioning in liver resection. Liver Transpl 10(2 Suppl 1):S53–S57
Giuliante F, Nuzzo G, Ardito F et al (2008) Extraparenchymal control of hepatic veins during mesohepatectomy. J Am Coll Surg 206:496–502
Balzan S, Belghiti J, Farges O et al (2005) The “50–50 criteria” on postoperative day 5: an accurate predictor of liver failure and death after hepatectomy. Ann Surg 242:824–828
Maeda T, Kajiyama K, Adachi E et al (1996) The expression of cytokeratins 7, 19, and 20 in primary and metastatic carcinomas of the liver. Mod Pathol 9:901–909
Shaib YH, Davila JA, McGlynn K et al (2004) Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a true increase? J Hepatol 40:472–477
Roayaie S, Guarrera JV, Ye MQ et al (1998) Aggressive surgical treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: predictors of outcomes. J Am Coll Surg 187:365–372
Kawarada Y, Yamagiwa K, Das BC (2002) Analysis of the relationships between clinicopathological factors and survival time in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Surg 183:679–685
Ohtsuka M, Ito H, Kimura F et al (2002) Results of surgical treatment for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and clinicopathological factors influencing survival. Br J Surg 89:1525–1531
Morimoto Y, Tanaka Y, Ito T et al (2003) Long-term survival and prognostic factors in the surgical treatment for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 10:432–440
Terashi T, Aishima S, Taguchi K et al (2004) Decreased expression of osteopontin is related to tumor aggressiveness and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int 24:38–45
Nakagawa T, Kamiyama T, Kurauchi N et al (2005) Number of lymph node metastases is a significant prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 29:728–733
Miwa S, Miyagawa S, Kobayashi A et al (2006) Predictive factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma recurrence in the liver following surgery. J Gastroenterol 41:893–900
Shimada K, Sano T, Sakamoto Y et al (2007) Surgical outcomes of the mass-forming plus periductal infiltrating types of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a comparative study with the typical mass-forming type of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 31:2016–2022
Paik KY, Jung JC, Heo JS et al (2008) What prognostic factors are important for resected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:766–770
Uenishi T, Kubo S, Yamazaki O et al (2008) Indications for surgical treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with lymph node metastases. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 15:417–422
Yamashita Y, Taketomi A, Morita K et al (2008) The impact of surgical treatment and poor prognostic factors for patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: retrospective analysis of 60 patients. Anticancer Res 28:2353–2359
Nakagohri T, Kinoshita T, Konishi M et al (2008) Surgical outcome and prognostic factors in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 32:2675–2680
Weimann A, Varnholt H, Schlitt HJ et al (2000) Retrospective analysis of prognostic factors after liver resection and transplantation for cholangiocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg 87:1182–1187
DeOliveira ML, Cunningham SC, Cameron JL et al (2007) Cholangiocarcinoma: thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann Surg 245:755–762
Konstadoulakis MM, Roayaie S, Gomatos IP et al (2008) Fifteen-year, single-center experience with the surgical management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: operative results and long-term outcome. Surgery 143:366–374
Tamandl D, Herberger B, Gruenberger B et al (2008) Influence of hepatic resection margin on recurrence and survival in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 15:2787–2794
Portolani N, Baiocchi GL, Coniglio A et al (2008) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: a Western experience. Ann Surg Oncol 15:1880–1890
Yedibela S, Demir R, Zhang W et al (2009) Surgical treatment of mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an 11-year Western single-center experience in 107 patients. Ann Surg Oncol 16:404–412
Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Campagnaro T et al (2009) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic factors after surgical resection. World J Surg 33:1247–1254
Lee CH, Chang CJ, Lin YJ et al (2009) Viral hepatitis-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma shares common disease processes with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 100:1765–1770
Kokudo N, Makuuchi M (2002) Extent of resection and outcome after curative resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 11:969–983
Shirai K, Ebata T, Oda K et al (2008) Perineural invasion is a prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 32:2395–2402
Nathan H, Aloia TA, Vauthey JN et al (2009) A Proposed staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 16:14–22
Tamandl D, Kaczirek K, Gruenberger B et al (2009) Lymph node ratio after curative surgery for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg 96:919–925
Choi SB, Kim KS, Choi JY et al (2009) The prognosis and survival outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma following surgical resections: association of lymph node metastasis and lymph node dissection with survival. Ann Surg Oncol 16:3048–3056
Acknowledgments
We are sincerely grateful to Professor Masatoshi Makuuchi for his very helpful and constructive advice in the preparation of this manuscript. This study was supported by a contribution from the Catholic University and the Italian Ministry for University and Scientific Research (D.1 Funds).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nuzzo, G., Giuliante, F., Ardito, F. et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic factors after liver resection. Updates Surg 62, 11–19 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-010-0007-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-010-0007-x