Abstract
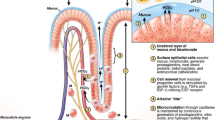
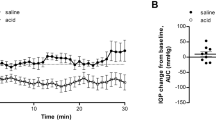
The exact mechanisms by which Helicobacter pylori infection results in gastric mucosal injury are unclear. However, it has been demonstrated that surface protein extracts of the bacterium can induce a number of disturbances within the rat gastric mucosal microcirculation, including platelet aggregation and macromolecular leakage (MML) of labeled albumin. This study aimed to determine the mechanisms involved in inducing these events using the technique of fluorescent in vivo microscopy. Male Wistar rats were pretreated with either ketotifen, a mast cell stabilizer (1 mg/kg), pyrilamine, an H1-receptor antagonist (30 mg/kg), hexanolamine-PAF, a PAF-receptor antagonist (10 μg/kg), l-arginine, the nitric oxide precursor (300 mg/kg) or vehicle, saline. Then 0.5 ml of H. pylori extract was administered to the exteriorized gastric mucosa of the anesthetized rat. Alterations in fluorescein-labeled albumin leak, vessel diameters, and acridine red-labeled leukocyte and platelet activity were determined over a 2-hr period. Saline pretreated animals demonstrated significant MML with a peak at 5 min (11%, P < 0.02). This was prevented with ketotifen and pyrilamine, but not with hexanolamine-PAF (17.5%, P < 0.05) and l-arginine (13%, P < 0.05). Significant numbers of platelet emboli and thrombi were observed within mucosal capillaries and postcapillary venules with vehicle pretreatment; this was prevented with hexanolamine-PAF and l-arginine, but not with ketotifen and pyrilamine. In conclusion, these studies demonstrate that more than one mediator is involved in inducing the rat gastric mucosal microcirculatory disturbances associated with H. pylori administration. Mast cells and histamine are linked to MML, with PAF, probably not derived from mast cells, involved in platelet activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Neilson H, Anderson LP: Chemotactic activity of Helicobacter pylori sonicate for human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. Gut 33:738–742, 1992
Craig PM, Territo MC, Karnes WE, Walsh JH: Helicobacter pylori secretes a chemotactic factor for monocytes and neutrophils. Gut 33:1020–1023, 1992
Mai UE, Perez-Perez GI, Wahl LM, Wahl SM, Blaser MJ, Smith PD: Soluble surface proteins from Helicobacter pylori activate monocytes/macrophages by lipopolysaccharideindependent mechanism. J Clin Invest 87:894–900, 1991
Reymunde A, Deren J, Nachamkin I, Oppenheim D, Weinbaum G: Production of chemoattractant by Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci 38:1697–1701, 1993
Yoshida N, Granger DN, Evans DJ, Evans DG, Graham DY, Anderson DC, Wolf RE, Kvietys PR: Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology 105:1431–1440, 1993
Kurose I, Granger DN, Evans DJ, Evans DG, Graham DY, Miyasuki M, Anderson DC, Wolf RE, Cepinskas G, Kvietys PR: Helicobacter pylori-induced microvascular protein leakage in rats: Role of neutrophils, mast cells and platelets. Gastroenterology 107:70–79, 1994
Mai UE, Perez-Perez GI, Allen JB, Wahl SM, Blaser MJ, Smith PD: Surface proteins from Helicobacter pylori exhibit chemotactic activity for human leukocytes and are present within the gastric mucosa. J Exp Med 175:517–525, 1992
Kalia N, Jacob S, Brown NJ, Reed MWR, Morton D, Bardhan KD: Studies on the gastric mucosal microcirculation 2. Helicobacter pylori water extracts induce platelet aggregation in the gastric mucosal microcirculation in vivo. Gut 41:748–752, 1997
Elizalde JI, Gomez J, Lozano M, Casadevall M, Ramirez J, Pizcueta P, Marco F, Diaz de Rojas F, Granger DN, Pique JM: J Clin Invest 100:996–1005, 1997
Kvietys PR, Granger DN: The vascular endothelium in gastrointestinal inflammation. In Immunopharmacology of the GI Tract, Vol 5. J Wallace (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1993, pp 69–93
Kvietys PR, Twohig B, Danzell J, Specian RD: Ethanolinduced injury to the rat gastric mucosa-role of neutrophils and xanthine oxidase-derived free radicals. Gastroenterology 98:909–920, 1990
Wallace JL, Keenan CM, Granger DN: Gastric ulceration induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is a neutrophil dependent process. Am J Physiol 259:G462–G467, 1990
Wyatt JI: Histopathology of gastroduodenal inflammation: The impact of Helicobacter pylori. Histopathology 26:1–15, 1995
Lagunoff D, Martin TW: Agents that release histamine from mast cells. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 23:331–351, 1983
Salvemini D, Masini E, Anggard E, Mannaioni PF, Vane J: Synthesis of a nitric oxide-like factor from L-arginine by rat serosal mast cells: Stimulation of guanylate cyclase and inhibition of platelet aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 169:596–601, 1990
Queiroz DMM, Mendes EN, Rocha GA, Barbosa AJA, Carvalho AST, Cunha-Melo JR: Histamine concentration of gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori positive and negative children. Gut 32:464–466, 1991
Bechi P, Dei R, Di Bello MG, Masini E: Helicobacter pylori potentiates histamine release from serosal rat mast cells in vitro. Dig Dis Sci 38:944–949, 1993
Wallace JL, Whittle BJR: Gastrointestinal damage induced by platelet-activating factor-inhibition by corticoid, dexamethasone. Dig Dis Sci 33:225–232, 1988
Denziot Y, Sobhani J-C, Lewin M, Thomas Y, Benveniste J: PAF-acether synthesis by Helicobacter pylori. Gut 31:1242–1245, 1990
Sharon P, Cohen F, Zifroni A, Karmeli F, Ligumsky M, Racmilewitz D, et al: Prostanoid synthesis by cultured gastric and duodenal mucosa. Possible role in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 18:1045–1049, 1983
Rachmilewitz DR, Ligumsky M, Fich A, et al: Role of endogenous gastric prostanoids in the pathogenesis and therapy of duodenal ulcers. Gastroenterology 90:963–969, 1986
Laine L, Cominelle F, Sloane R, Casiniraggi V, Weinstein WM: Interaction of NSAIDs and H. pylori on gastrointestinal injury and prostaglandin production-a controlled double blind trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 9:127–135, 1995
Feuerstein G, Hallenbeck JM: Prostaglindins, leukotrienes and platelet-activating factor in shock. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 27:301–313, 1987
Kubes P: Nitric oxide: A modulator of mast cells and leukocytes in the microvasculature. Gastroenterology 16(suppl 1):S158, 1996
Karmeli F, Eliakim R, Okon E, Rachmilewitz D: Gastric mucosal damage by ethanol is mediated by substance P and prevented by Ketotifen, a mast cell stabiliser. Gastroenterology 100:1206–1216, 1991
Minnicozzi M, Ramirez MM, Egan RW, Gleich GJ, Kobayashi I, Kim D, Duran WN: Polyarginine and eosinophil-derived major basic protein increase microvascular permeability independently of NO and histamine release. Microvasc Res 50:56–70, 1995
Fujji E, Irie K, Uchida Y, Ohba K, Muraki T: Role of eicosanoids but not nitric oxide in the platelet-activating factorinduced increase in vascular permeability in the mouse skin. Eur J Pharmacol 273:267–272, 1995
Miller FN, Joshua IG, Anderson GL: Quantitation of vasodilator-induced macromolecular leakage by in vivo fluorescent microscopy. Microvasc Res 24:56–67, 1982
Whittle BJR, Salmon JA: Biosynthesis of prostacyclin and PGE2 in gastrointestinal tissue. In Proceedings of the 3rd BSG-SKF International Workshop 1982. LA Turnberg (ed). Smith, Kline and French.
Kalia N, Jacob S, Brown NJ, Reed MWR, Bardhan KDB: Studies on the gastric mucosal microcirculation. 1. The nature of regional variations in response to ethanol injury. Gut 40:31–35, 1997
Nosál R, Jancinová V, Petrilova M: The H1–histamine receptor antagonist diatheden inhibits stimulated platelet aggregation, malondialdehyde formation and TxA2 production in vitro. Inflamm Res 44(suppl 1):S14–S15, 1995
Rosam AC, Wallace JL, Whittle BJR: Potent ulcerogenic actions of PAF on the stomach. Nature 319:54–56, 1986
Braquet P, Touqui L, Shen TY, Vargaftig BB: Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharm Rev 39:97–145, 1987
Wallace JL, Whittle BJR: Picomole doses of platelet-activating factor predispose the gastric mucosa to damage by topical irritants. Prostaglandins 31:989–998, 1986
Moncada S, Palmer RJ, Higgs EA: Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 3:109–142, 1991
Kubes P, Granger DN: Nitric oxide modulates microvascular permeability. Am J Physiol 262:H611–H615, 1992
Ahmed A, Holton J, Vaira D, Smith SK, Hoult JRS: Eicosanoid synthesis and Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis-increase in LTC4 generation associated with H. pylori colonisation. Prostaglandins 44:75–86, 1992
Hudson N, Balsitis M, Filipowicz F, Hawkey CJ: Effect of Helicobacter pylori colonisation on gastric mucosal eicosanoid synthesis in patients taking NSAIDs. Gut 34:748–751, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalia, N., Bardhan, K., Reed, M. et al. Mechanisms of Helicobacter pylori-Induced Rat Gastric Mucosal Microcirculatory Disturbances In Vivo. Dig Dis Sci 45, 763–772 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005456029396
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005456029396