Abstract
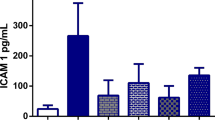
This study was aimed at an assessment of the role of oxygen-derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of L-arginine (Arg)-induced acute pancreatitis in rat, by measuring the levels of malonyl dialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase, and superoxide dismutase (Mn- and Cu,Zn-SOD) in the pancreatic tissue, and evaluating the protective effect of the xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol. Acute pancreatitis was induced in male Wistar rats by injecting 2 × 250 mg/100 g body weight of Arg intraperitoneally in a 1-hr interval, as a 20% solution in 0.15 M NaCl. Control rats received the same quantity of glycine. Allopurinol, 100 or 200 mg/kg, was administered subcutaneously 30 min before the first Arg injection. Rats were killed at 6, 12, 24, and 48 hr following Arg administration, and acute pancreatitis was confirmed by a serum amylase level elevation and typical inflammatory features observed microscopically. The serum level of amylase reached the peak level at 24 hr after the Arg injection (30,800 ± 3813 vs 6382 ± 184 units/liter in the control) and normalized at 48 hr. The tissue concentration of MDA was significantly elevated at 24 hr and reached the peak value at 48 hr (5.00 ± 1.75 vs 0.28 ± 0.05 nM/mg protein in the control). The catalase and Mn-SOD activities were significantly decreased throughout the study, while the GPx activity was significantly reduced at 6 and 12 hr, and the Cu,Zn-SOD activity was significantly lower at 12 hr after the Arg injection as compared with the controls. Allopurinol treatment markedly reduced the serum amylase elevation (12.631 ± 2.257 units/liter at 24 hr) and prevented the increase in tissue MDA concentration (0.55 ± 0.09 nM/mg protein at 48 hr). Both doses of allopurinol significantly ameliorated the pancreatic edema, necrosis, and inflammation at 48 hr after Arg administration. Oxygen-derived free radicals are generated at an early stage of Arg-induced acute pancreatitis. Prophylactic allopurinol treatment prevents the generation of reactive oxygen metabolites, reduces the serum amylase concentration, and exerts a beneficial effect on the development of histopathological changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Goldberg RC, Chaikoff IL: Selective pancre atic acinar destruction by d-ethionine. Arch Pathol 52:230 - 238, 1951
Kaufman N, Klavins JV, Kinney TD: Pancre atic damage induced by exce ss methionine. Arch Pathol 70:331- 337, 1960
Nakano S, Watanabe N, Kihara Y, Ogami Y, Otsuki M: New model of acute pancre atitis induced by exce ssive doses of lysine in rats. Int J Pancre tol 12:83, 1992
Mizunuma T, Kawamura S, Kishino Y: Effects of injecting excess arginine on rat pancre as. J Nutr 114:467- 471, 1984
Tani S, Itoh H, Koide M, Okabayashi Y, Nakamura T, Fujii M, Fujisawa T, Koide M, Otsuki M: New mode l of acute necrotizing pancre atitis induced by exce ssive does of arginine in rats. Dig Dis Sci 35:367- 374, 1990
Delaney CP, McGee ney KF, Dervan P, Fitzpatrick JM: Pancre atic atrophy: A new model using serial intra-peritoneal injections of L-arginine. Scand J Gastroenterol 28:1086 - 1090, 1993
Sanfey H, Bulkley GB, Came ron JL: The pathogenesis of acute pancre atitis: The source and role of oxyge n-derived free radicals in three different expe rimental models. Ann Surg 201:633- 639, 1985
Schoenberg MH, Büchler M, Be ge r HG: Oxygen radicals in e xpe rime ntal acute panc re ati tis. He pato-Gastroe nte rol 41:313- 319, 1994
Wisner JR, Renner IG: Allopurinol attenuates cae rulein induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Gut 29:926 - 929, 1988
Sweiry JH, Mann GE: Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of acute pancre atitis. Scand J Gastroente rol 31( suppl 219): 10 - 15, 1996
Fridovich I: The biology of oxygen radicals. Science 201:875- 880, 1978
Sies H: Oxidative stress: From basic research to clinical application. Am J Med 91(suppl 3C): 31- 38, 1991
Parks DA, Granger DN: Xanthine oxidase: Biochemistry, distribution and physiology. Acta Physiol Scand 126( suppl 548): 87- 99, 1986
Takács T, Czakó L, Jármay K, Farkas G Jr, Mándi Y, Lonovics J: Cytokine level changes in L-arginine-induced acute pancre atitis in rat. Acta Physiol Hung 84:147- 156, 1996
Ceska M, Birath K, Brown B: A new and rapid me thod for the clinical determination of amylase activities in human serum and urine. Clin Chem Acta 26:437- 444, 1969
Placer ZA, Cushman L, Johnson BC: Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehydes) in biochemical systems. Anal Biochem 16:359 - 364, 1966
Misra HP, Fridovich I: The role of superoxide anion in autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170 - 3175, 1972
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I: Superoxide dismutase: Improved assay and an assay applicable to acrylamide ge ls. Anal Biochem 44:276 - 287, 1971
Beers RF Jr, Sizer IW: Spectrophotometric me thod for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133- 140, 1951
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH: Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryls groups in tissue with Ellman's reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192- 205, 1968
Chiu DT, Stults FH, Tappe l AL: Purification and properties of rat lung soluble glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 445:558 - 566, 1976
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein me asurements with the Folin phenol reage nt. J Biol Chem 193:265- 275, 1951
Takeda Y, Tominaga T, Tei N, Kitamura M, Taga T, Murase J, Taguchi T, Miwatani T: Inhibitory effect of L-arginine on growth of rat mammary tumors induced by 7,12-dime thylbenz(α)anthrace ne. Cancer Res 35:2390 - 2393, 1975
Nakaki T, Hishikiwa K, Suzuki H, Saruta T, Kato R: L-Arginine-induced hypotension. Lancet 336:1016, 1992
Sakuma I, Sruehr D, Gross SS, Nathan C, Levi R: Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived re laxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8664 - 8667, 1988
Varga IS, Matkovics B, Czakó L, Hai DQ, Kotormán M, Takács T, Sasvári M: Oxidative stress changes in L-arginineinduced pancre atitis in rats. Pancre as 14:355- 359, 1997
Kle in AS, Joh JW, Rangan U, Wang D, Bulkley GB: Allopurinol: Discrimination of antioxidant from enzyme inhibitory activities. Fre e Radic Biol Med 21:713- 717, 1996
Lankisch PG, Pohl U, Otto J, Wereszczyns ka-Siemiatkowska U, Gröne HJ: Xanthine oxidase inhibitor in acute experimental pancre atitis in rats and mice. Pancreas 4:436 - 440, 1989
Niede rau C, Niederau M, Borchard F, Ude K, Luthen R, Strohmeyer G, Ferrell LD, Grendell JH: Effects of antioxidants and free radical scave nge rs in three different models of acute pancre atitis. Pancre as 7:486 - 496, 1992
Braganza JM: Experimental acute pancre atitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 6:763- 768, 1990
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czako, L., Takacs, T., Varga, I.S. et al. Involvement of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals in L-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 43, 1770–1777 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018839821176
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018839821176