Abstract
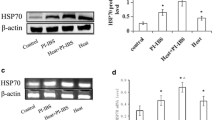
Heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 is stress-inducibleand exhibits both protective and antigenic properties.This study investigated the mucosal expression of theconstitutive (Hsp70c) and inducible form (Hsp70i) as well as antibodies against human Hsp70 ininflammatory bowel disease and controls. Biopsies wereassessed by immunoblot and immunofluorescence, resectionspecimens by immunohistochemistry, and mucosal antibody content by isoelectric focusing.Compared to controls, expression of Hsp70 was enhancedin ulcerative colitis (P < 0.05), less so in Crohn'sdisease and infectious colitis. Strong epithelial staining was found for Hsp70c and Hsp70i inboth diseases. Mucosal and submucosal mononuclear cellsshowed enhanced Hsp70c expression in Crohn's disease andto a lesser degree in ulcerative colitis. Antibodies of isotypes A or M were detected in nearly allpatients and controls. The different pattern of Hsp70expression in Crohn's disease compared to ulcerativecolitis points to a distinct protective andimmunological function, whereas a role in autoimmunity seemsunlikely.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Lindquist S, Craig EA: The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet 22:631–637, 1988
Ang D, Liberek K, Skowyra D, Zyclicz M, Georgopoulos C: Biological role and regulation of the universally conserved heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem 266:24233–24236, 1991
Kaufmann SHE: Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today 11:129–136, 1990
Welch WJ: How cells respond to stress. Sci Am 268:56–64, 1993
Musch MW, Ciancio MJ, Sarge K, Chang EB: Induction of heat shock protein 70 protects intestinal epithelial cells from oxidant and thermal injury. Am J Physiol 270:C429-C436, 1996
Blake MJ, Gershon D, Fargnoli J, Holbrook NJ: Discordant expression of heat shock protein mRNA' s in tissues of heatstressed rats. J Biol Chem 265:15275–15279, 1990
Georgopoulos C, Welch WJ: Role of major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9:601–643, 1993
Domanico SZ, DeNagel WE, Dahlseid JN, Green JM, Pierce SK: Cloning of the gene encoding peptide-binding protein 74 shows that it is a new member of the heat shock protein 70 family. Mol Cell Biol 13:3598–3610, 1993
De Graeff-Meeder ER, Voorhorst M, van Eden W, Schuurmann HJ, Huber J, Barkley D, Maini RN, Kuis W, Rijkers GT, Zegers BJM: Antibodies to the mycobacteria 65-kd heat-shock protein are reactive with synovial tissue of adjuvant arthritic rats and patient with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Am J Pathol 137:1013–1017, 1990
Minota S, Koyasu S, Yahara I, Winfield J: Autoantibodies to the heat-shock protein hsp90 in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest 81:106–109, 1988
Elsaghier A, Prantera C, Bothamley G, Wilkins E, Jindal S, Ivanyi J: Disease association of antibodies to human and mycobacterial hsp70 and hsp60 stress proteins. Clin Exp Immunol 89:305–309, 1992
Pirzer U, Schönhaar A, Fleischer B, Hermann E, Meyer zum Büschenfelde K-H: Reactivity of infiltrating T lymphocyte s with microbial antigens in Crohn's disease. Lancet 338:1238–1239, 1991
Sanderson JD, Moss MT, Tizard MLV, Hermann-Taylor J: Mycobacterium paratube rculosis DNA in Crohn's disease tissue. Gut 33:890–896, 1992
Stainsby KJ, Lowes JR, Allan RN, Ibbotson JP: Antibodies to mycobacte rium paratuberculosis and nine species of environmental mycobacte ria in Crohn' s disease and control subjects. Gut 34:371–374, 1993
Winrow VR, Mojdehi GM, Ryder SD, Rhodes JM, Blake DR, Rampton DS: Stress proteins in the colorectal mucosa: Enhanced expression in ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 38:1994–2000, 1993
Peetermans WE, D'Haens GR, Ceuppens JL, Rutgeerts P, Geboes K: Mucosal expre ssion by B7-positive ce lls of the 60-kilodalton heat-shock protein in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 108:75–82, 1995
Morson BC, Dawson IMP: Gastrointestinal pathology. Oxford, Blackwell Scientific, 1972, pp 458–475
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F: Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. Gastroenterology 70:439–444, 1976
Mary JY, Modigliani R: Development and validation of an endoscopic index of the severity for Crohn's disease: A prospective multicentre study [Groupedé tudes thérapeutiques des affections inflammatoires du tube digestif (GETAID) ]. Gut 30:983–989, 1989
Rachmilewitz D: Coated me salazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) versus sulphasalazine in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis: A randomized trial. BMJ 298:82–86, 1989
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC: Measurement of protein using bicinchonicic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85, 1985
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacte riophage T4. Nature 227:680–685, 1970
Wenzel BE, Franke TF, Heufelder AE, Heesemann J: Autoimmune thyroid diseases and enteropathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica. Autoimmunology 7:295–303, 1990
Merz H, Malisius R, Mannweiler S, Zhou R, Hartmann W, Orscheschek K, Moubayed P, Feller AC: ImmunoMax. A maximize d immunohistochemical method for the retrieval and enhancement of hidden antigens. Lab Invest 73:1–8, 1995
Nagamine T, Takehara K, Fukui T, Mori M: Clinical evaluation of biotin-binding immunoglobulin in patients with Grave s' s disease. Clin Chim Acta 226:47–54, 1994
Stahl M, Ludwig D, Fellermann K, Stange EF: Intestinal expression of human heat shock protein 90 in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 43:1079–1087, 1998
Deitch EA, Beck SC, Cruz NC, De Maio A: Induction of heat shock gene expression in colonic epithelial cells after incubation with Escherichia coli or endotoxin. Crit Care Med 23:1371–1376, 1995
Burress GC, Musch MW, Jurivich DA, Welk J, Chang EB: Effects of mesalamine on the hsp72 stress response in rat IEC-18 intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 113:1474–1479, 1997
Pratt WB: The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem 268:21455–21458, 1993
VanBuskirk AM, DeNagel DC, Guagliardi LE, Brodsky FM, Pierce SK: Cellular and subcellular distribution of PBP72/74, a peptide binding protein that plays a role in antigen processing. J Immunol 146:500–506, 1991
Haas IG, Meo T: cDNA cloning of the immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2250–2254, 1988
Woywodt A, Neustock P, Kruse A, Schwarting K, Ludwig D, Stange EF, Kirchner H: Cytokine expre ssion in intistinal mucosal biopsies. In situ hybridisation of the mRNA for interleukin-1b, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-a in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur Cytokine Netw 5:387–395, 1994
Ferm MT, Söderström K, Jindal S, Grönberg A, Ivanyi J, Young R, Kiessling R: Induction of human Hsp60 expression in monocytic cell lines. Int Immunol 4:305–311, 1992
Elsaghier A, Prantera C, Moreno C, Ivanyi J: Antibodies to mycobacte rium paratube rculosis-specific protein antigens in Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol 90:503–508, 1992
Jones DB, Coulson AF, Duff GW: Sequence homologies between hsp60 and autoantigens. Immunol Today 14:115–118,1993
Stevens TJR, Winrow VR, Blake DR, Rampton DS: Circulating antibodies to heat-shock protein 60 in Crohn' s disease and ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 90:271–274, 1992
Macpherson A, Khoo UY, Forgacs I, Philpott-Horward J, Bjarnason I:Mucosal antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease are directed against intestinal bacteria. Gut 38:365–375, 1996
Khoo UY, Macpherson AJS, Philpott-Howard J, Forgacs I, Bjarnason I: Alterations in the mucosal immunoglobulin response in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 34( suppl):W35, 1993
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease (First of two parts). N Engl J Med 325:928–937, 1991
Sartor RB: Pathogenesis and immune mechanisms of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Am J Gastroenterol 92:5S-11S, 1997
Jurivich DA, Sistonen L, Kroes RA, Morimoto RI: Effect of sodium salicylate on the human heat shock response. Science 255:1243–1245, 1992
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, D., Stahl, M., Ibrahim, M.E.T. et al. Enhanced Intestinal Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig Dis Sci 44, 1440–1447 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026616221950
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026616221950