Abstract
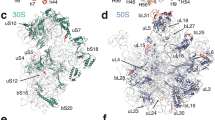
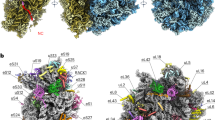
We have calculated at 5.0 Å resolution an electron-density map of the large 50S ribosomal subunit from the bacterium Haloarcula marismortui by using phases derived from four heavy-atom derivatives, intercrystal density averaging and density-modification procedures. More than 300 base pairs of A-form RNA duplex have been fitted into this map, as have regions of non-A-form duplex, single-stranded segments and tetraloops. The long rods of RNA crisscrossing the subunit arise from the stacking of short, separate double helices, not all of which are A-form, and in many places proteins crosslink two or more of these rods. The polypeptide exit channel was marked by tungsten cluster compounds bound in one heavy-atom-derivatized crystal. We have determined the structure of the translation-factor-binding centre by fitting the crystal structures of the ribosomal proteins L6, L11 and L14, the sarcin–ricin loop RNA, and the RNA sequence that binds L11 into the electron density. We can position either elongation factor G or elongation factor Tu complexed with an aminoacylated transfer RNA and GTP onto the factor-binding centre in a manner that is consistent with results from biochemical and electron microscopy studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monro, R. E. Catalysis of peptide bond formation by 50S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 26, 147–151 (1967).
Wittmann-Liebold, B., in Structure, Function, and Genetics of Ribosomes (eds Hardesty, B. & Kramer, G.) 326–361 (Springer, New York, 1986).
Frank, J. et al. Amodel for protein synthesis based on cryo-electron microscopy of the E. coli ribosome. Nature 376, 441–444 (1995).
Stark, H. et al. Arrangement of tRNAs in pre- and posttranslocational ribosomes revealed by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell 88, 19–28 (1997).
Milligan, R. A. & Unwin, P. N. T. Location of exit channel for nascent protein in 80S ribosome. Nature 319, 693–695 (1986).
Beckmann, R. et al. Alignment of conduits for the nascent polypeptide chain in the ribosome–Sec61 complex. Science 278, 2123–2128 (1997).
Liljas, A. in The Ribosome. Structure, Function & Evolution (eds Hill, W. E. et al.) 309–317 (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington DC, 1990).
Capel, M. S. et al. Acomplete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of E. coli. Science 238, 1403–1406 (1987).
May, R. P., Nowotny, V., Nowotny, P., Voss, H. & Nierhaus, K. H. Inter-protein distances within the large subunit from Escherichia coli ribosomes. EMBO J. 11, 373–378 (1992).
Oakes, M. Henderson, E., Scheinman, A., Clark, M. & Lake, J. A. in Structure, Function and Genetics of Ribosomes (eds Hardesty, B. & Kramer, G.) 47–67 (Springer, New York, 1986).
Stoeffler, G. & Stoeffler-Meilicke, M. in Structure, Function, and Genetics of Ribosomes (eds Hardesty, B. & Kramer, G.) 28–46 (Springer, New York, 1986).
Ramakrishnan, A. & White, S. W. Ribosomal protein structures: insights into the architecture, machinery and evolution of the ribosome. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 208–212 (1998).
Szewczak, A. A. & Moore, P. B. The sarcin/ricin loop, a modular RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 247, 81–98 (1995).
Correll, C. C. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosomal RNA loop essential for binding both elongation factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 13436–13441 (1998).
Correll, C. C., Freeborn, B., Moore, P. B. & Steitz, T. A. Metals, motifs and recognition in the crystal structure of a 5S rRNA domain. Cell 91, 705–712 (1997).
Dallas, A. & Moore, P. B. The solution structure of the loop E/loop D regio of E. coli 5S rRNA. Structure 5, 1639–1653 (1997).
Wimberly, B. T., Guymon, R., McCutcheon, J. P., White, S. W. & Ramakrishnan, V. R. Adetailed view of a ribosomal active site: the structure of the L11–RNA complex. Cell 97, 491–502 (1999).
Conn, G. L., Draper, D. E., Lattman, E. E. & Gittis, A. G. Crystal structure of a conserved ribosomal protein RNA complex. Science 284, 1171–1174 (1999).
Agrawal, R. K., Penczek, P., Grassucci, R. A. & Frank, J. Visualization of elongation factor G on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: the mechanism of translocation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6134–6138 (1998).
Stark, H. et al. Visualization of elongation factor Tu on the Escherichia coli ribosome. Nature 389, 403–406 (1997).
Ban, N. et al. A9 Å resolution X-ray crystallographic map of the large ribosomal subunit. Cell 93, 1105–1115 (1998).
Cowtan, K. D. An automated procedure for phase improvement by density modification. Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter on Protein Crystallography 31, 34–38 (1994).
Jones, T. A. in CCP4 Study Weekend, Molecular Replacement (eds Dodson, E. J., Glover, S. & Wolf, W.) 91–105 (SSRC, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, Cheshire, UK, 1992).
Bernabeu, C. & Lake, J. A. Nascent polypeptide chains emerge from the exit domain of the large ribosomal subunit: Immune mapping of the nascent chain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 3111–3115 (1982).
Kleywegt, G. J. & Jones, T. A. Template convolution to enhance or detect structural features in macromolecular electron-density maps. Acta. Crystallogr. D 53, 179–185 (1997).
Cate, J. et al. Crystal structure of a group I ribozyme domain: principles of RNA packing. Science 273, 1678–1685 (1996).
Jucker, F. M., Heus, H. A., Yip, P. F., Moors, E. H. M. & Pardi, A. Anetwork of heterogeneous hydrogen bonds in GNRA tetraloops. J. Mol. Biol. 264, 968–980 (1996).
Stern, S., Powers, T., Changchien, L.-I. & Noller, H. F. RNA–proteins interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science 244, 783–790 (1989).
Golden, B. L., Ramakrishnan, V. & White, S. W. Ribosomal protein L6. Structural evidence of gene duplication from a primitive RNA binding protein. EMBO J. 12, 4901–4908 (1993).
Leffers, H., Kjems, J., Ostergaard, L., Larsen, N. & Garrett, R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria: a comparative study of 23S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile, and a thermophilic mechanogen. J. Mol. Biol. 195, 43–61 (1987).
Leffers, H., Egeberg, J., Andersen, A., Christensen, T. & Garrett, R. A. Domain VI of Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA structure, assembly and function. J. Mol. Biol. 204, 507–522 (1988).
Uchiumi, T., Sato, N., Wada, A. & Hachimori, A. Interaction of the sarcin/ricin domain of 23S ribosomal RNA with proteins L3 and L6. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 681–686 (1999).
Urlaub, H., Kruft, V., Bischof, O., Muller, E. C. & Wittmann-Liebold, B. Protein–rRNA binding features and their structural and functional implications in ribosomes as determined by crosslinking studies. EMBO J. 14, 4578–4588 (1995).
Davies, C., White, S. W. & Ramakrishnan, V. The crystal structure of ribosomal protein L14 reveals an important organizational component of the translational apparatus. Structure 4, 55–66 (1996).
Walleczek, J., Schuler, D., Stoeffler-Meilicke, M., Brimacombe, R. & Stoeffler, G. Amodel for the spatial arrangement of the proteins in the large subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. EMBO J. 7, 3571–3576 (1988).
Nakagawa, A. et al. The three-dimensional structure of the RNA-binding domain of ribosomal protein L2; a protein at the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome. EMBO J. 18, 1459–1467 (1999).
Wilson, K. S. & Noller, H. H. Mapping the position of translational elongation factor EF-G in the ribosome by directed hydroxyl radical probing. Cell 92, 131–139 (1998).
Aevarsson, A. et al. Three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal translocase: elongation factor G from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 13, 3669–3677 (1994).
Czworkowski, J., Wang, J., Steitz, T. A. & Moore, P. B. The crystal structure of elongation factor G complexed with GDP at 2.7 Å resolution. EMBO J. 13, 3661–3668 (1994).
Nissen, P. et al. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu and a GTP analog. Science 270, 1464–1472 (1995).
Moazed, D., Robertson, J. M. & Noller, H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature 334, 362–364 (1988).
Traut, R. R. et al. in Structure, Function, and Genetics of Ribosomes (eds Hardesty, B. & Kramer, G.) 286–308 (Springer, New York, 1986).
Skold, S. E. Chemical crosslinking of elongation factor G to both subunits of the 70S ribosome from E. coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 127, 225–229 (1982).
Skold, S. E. Chemical crosslinking of elongation factor G to the 23S rRNA in 70S ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 4923–4932 (1983).
Nevskaya, N. et al. Structure of archaeal ribosomal protein L1 provides new insights into the RNA binding for the L1 protein family. J. Mol. Biol.(in the press).
von Bohlen, K. et al. Characterization and preliminary attempts for derivitization of crystals of large ribosomal subunits from Haloarcula marismortui diffracting to 3 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 222, 11–15 (1991).
Otwinowski, Z. in Data Collection and Processing (eds Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, D.) 52–62 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, UK, 1993).
Brünger, A. T. et al. Crystallography and NMR system (CNS): a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Yeates, T. O. Detecting and overcoming crystal twinning. Methods Enzymol. 276, 344–358 (1997).
Abrahams, J. P. & Leslie, A. G. W. Methods used in the structural determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D 52, 30–43 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Freeborn for biochemical support; R. Sweet for helping us with data collection at the National Synchrotron Light Source; and I.Tanaka, M. Garber and S. Al-Karadaghi for providing coordinates before publication. This investigation was supported by grants from NIH to T.A.S. and P.B.M. N.B. was a Damon Runyon-Walter Winchell Postdoctoral Fellow during part of this study, and P.N. is supported by the Danish Research Council. The coordinates of all identified RNA and protein structures have been deposited in the protein data bank with accession number IC04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J. et al. Placement of protein and RNA structures into a 5 Å-resolution map of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Nature 400, 841–847 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/23641
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/23641
This article is cited by
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and cell sorting of living bacteria
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Polyoxometalates: more than a phasing tool in protein crystallography
ChemTexts (2018)
-
Crystal structure of the open conformation of the mammalian chaperonin CCT in complex with tubulin
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2011)
-
Protein folding and aggregation in bacteria
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)
-
Enabling technologies in discovery: the 2009 Nobel Prize and its implications in antibiotic design
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.