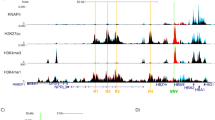
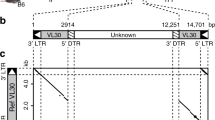
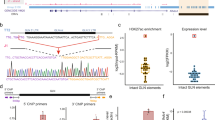
Abstract
Primate Alu and rodent Alu- like elements comprise major families of mammalian small dispersed repetitive DNAs. These elements are repeated more than 105 times per haploid genome and are found between known genes, in introns and in satellite DNA1–5. Their dispersion throughout the genome and the presence of directly repeated DNA sequences flanking the elements suggest, but do not prove, that they are capable of transposition. We describe here an allelic variation in the 5′-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene that offers the opportunity to examine the sequences of matching regions of two homologous chromosomes which differ in the presence of an Alu-like repetitive DNA element. Our findings support the hypothesis that these elements are integrated into the genome by generating short direct repeats of host DNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jelinek, W. R. & Schmid, C. W. A. Rev. Biochem. 51, 813–844 (1982).
Page, G. S., Smith, S. & Goodman, H. M. Nucleic Acids Res. 9, 2087–2104 (1981).
Barta, A., Richards, R., Baxter, J. D. & Shine, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 4867–4871 (1981).
Lemischka, I. & Sharp, P. A. Nature 300, 330–335 (1982).
Grimaldi, G. & Singer, M. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 1497–1500 (1982).
Chien, Y., Thompson, E. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 4583–4587 (1980).
Gubbins, E. J., Maurer, R. A., Legrimiui, M., Erwin, C. R. & Donelson, J. E. J. biol. Chem. 255, 8655–8662 (1980).
Cooke, N. E. & Baxter, J. D. Nature 297, 603–606 (1982).
Weber, J. L., Durrin, L. K. & Gorski, J. (in preparation).
Van Arsdell, S. W. et al. Cell 26, 11–17 (1981).
Jagadeeswaran, P., Forget, B. G. & Weissman, S. M. Cell 26, 141–142 (1981).
Sharp, P. A. Nature 301, 471–472 (1983).
Sutcliffe, J. G., Milner, R. J., Bloom, F. E. & Lerner, R. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 4942–4946 (1982).
Bertelsen, A. H., Humayun, M. Z., Karfopoulos, S. G. & Rush, M. G. Biochemistry 21, 2076–2085 (1982).
Sargent, T. D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 3256–3260 (1979).
Messing, J. & Vieira, J. Gene 19, 269–276 (1982).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Galli, G., Hofstelter, H. & Birnstiel, M. L. Nature 294, 626–631 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuler, L., Weber, J. & Gorski, J. Polymorphism near the rat prolactin gene caused by insertion of an Alu-like element. Nature 305, 159–160 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/305159a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/305159a0
This article is cited by
-
Allelic dimorphism in the human tissue-type plasminogen activator (TPA) gene as a result of an Alu insertion/deletion event
Human Genetics (1992)
-
Novel restriction fragment length polymorphism of the growth hormone gene in inbred rats
Biochemical Genetics (1989)
-
‘Brain-specific’ transcription and evolution of the identifier sequence
Nature (1986)
-
Developmental fate of a human insulin gene in a transgenic mouse
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1984)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.