Abstract
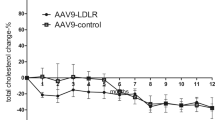
An ex vivo approach to gene therapy for familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) has been developed in which the recipient is transplanted with autologous hepatocytes that are genetically corrected with recombinant retroviruses carrying the LDL receptor. We describe the treatment of a 29 year old woman with homozygous FH by ex vivo gene therapy directed to liver. She tolerated the procedures well and in situ hybridization of liver tissue four months after therapy revealed evidence for engraftment of transgene expressing cells. The patient's LDL/HDL ratio declined from 10–13 before gene therapy to 5–8 following gene therapy, improvements which have remained stable for the duration of the treatment (18 months). This represents the first report of human gene therapy in which stable correction of a therapeutic endpoint has been achieved.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, M.S. & Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232, 34–37 (1986).
Starzl, T.E. et al. Heart-liver transplantation in a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia. Lancet 1, 1382–1383 (1984).
Bilheimer, D.W. et al. Liver transplantation to provide low density lipoprotein receptors and lower plasma cholesterol in a child with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. New Engl. J. Med. 311, 1658–1664 (1984).
Chowdhury, J.R. et al. Long term improvement of hypercholesterolemia after ex vivo gene therapy in LDLR deficient rabbits. Science 254, 1802–1805 (1991).
Grossman, M., Wilson, J.M. & Raper, S.E. A novel approach for introducing genetically modified hepatocytes into the portal circulation. J. Lab. clin. Med. 121, 472–478 (1993).
Grossman, M., Raper, S.E. & Wilson, J.M. Transplantation of genetically-modified autologous hepatocytes in non-human primates. Hum. gene Ther. 3, 501–510 (1992).
Leitersdorf, E., Tobin, E.J., Davignon, J. & Hobbs, H. Common low-density lipoprotein receptor mutations in the French Canadian population. J. clin. Invest. 85, 1014–1023 (1990).
Wilson, J.M. et al. Clinical protocol: ex vivo gene therapy of familial hypercholesterolemia. Hum. gene Ther. 3, 179–222 (1992).
Armentano, D., Thompson, A.R., Darlington, G. & Woo, S.L.C. Expression of human factor IX in rabbit hepatocytes by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer: potential for gene therapy of hemophilia B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 6141–6145 (1990).
Kay, M.A. et al. Expression of human α1-antitrypsin in dogs after autologous transplantation of retroviral transduced hepatocytes. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 89–93 (1992).
Südhof, T.C., Russell, D.W., Brown, M.S. & Goldstein, J.L. 42 bp element from LDL receptor gene confers end-product repression by sterols when inserted into viral TK promoter. Cell 48, 1061–1069 (1987).
Sharkey, M.F. et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of retroviral vector-transduced low density lipoprotein receptor activity. J. lipid Res. 31, 2167–2178 (1990).
Jaffe, H.A. et al. Adenovirus-mediated in vivo gene transfer and expression in normal rat liver. Nature Genet. 1, 372–378 (1992).
Kaneda, Y., Iwai, K. & Uchida, T. Increased expression of DNA cointroduced with nuclear protein in adult rat liver. Science 243, 375–378 (1989).
Wu, C.H., Wilson, J.M. & Wu, G.Y. Targeting gene: delivery and persistent expression of a foreign gene driven by mammalian regulatory elements in vivo. J. biol. Chem. 264, 16985–16987 (1989).
Grossman, M., Raper, S. & Wilson, J.M. Towards liver-directed gene therapy: retrovirus mediated gene transfer into human hepatocytes. Som. Cell molec. Gen. 17, 601–607 (1991).
Engelhardt, J.F. et al. Submucosal glands are the predominate site of CFTR expression in human bronchus. Nature Genet. 2, 240–248 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grossman, M., Raper, S., Kozarsky, K. et al. Successful ex vivo gene therapy directed to liver in a patient with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nat Genet 6, 335–341 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-335
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-335
This article is cited by
-
Helper-dependent adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of a secreted LDL receptor/transferrin chimeric protein reduces aortic atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice
Gene Therapy (2019)
-
Bile-duct proliferation as an unexpected side-effect after AAV2-LDLR gene transfer to rabbit liver
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Biomanufacturing for clinically advanced cell therapies
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2018)
-
Gene therapy for monogenic liver diseases: clinical successes, current challenges and future prospects
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2017)
-
Sleeping Beauty Transposon Vectors in Liver-directed Gene Delivery of LDLR and VLDLR for Gene Therapy of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Molecular Therapy (2016)