Abstract
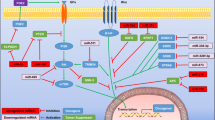
Metastasis is the most significant process affecting the clinical management of cancer patients and occurs in multiple sequential steps. However, the molecular pathways underlying each step still remain obscure. Recent research has shown that there is a microRNA (miRNA) network that functions as a regulator of tumor metastasis. In this paper, we review the role of miRNAs in tumor metastasis, including control of epithelial–mesenchymal transition, regulation of metastasis-associated genes and epigenetic alterations. More information on miRNAs will promote a better understanding of the molecular mechanism of metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acloque H, Thiery JP, Nieto MA . (2008). The physiology and pathology of the EMT. Meeting on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO Rep 9: 322–326.
Albini A, Mirisola V, Pfeffer U . (2008). Metastasis signatures: genes regulating tumor-microenvironment interactions predict metastatic behavior. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27: 75–83.
Ambros V . (2003). MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113: 673–676.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27: 2128–2136.
Bandres E, Bitarte N, Arias F, Agorreta J, Fortes P, Agirre X et al. (2009). microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2281–2290.
Bandyopadhyay S, Pai SK, Hirota S, Hosobe S, Tsukada T, Miura K et al. (2004). PTEN up-regulates the tumor metastasis suppressor gene Drg-1 in prostate and breast cancer. Cancer Res 64: 7655–7660.
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O et al. (2005). Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37: 766–770.
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, Kaczorowski AJ, Kuick R, Love RE et al. (2007). p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr Biol 17: 1298–1307.
Boyd J, Risinger JI, Wiseman RW, Merrick BA, Selkirk JK, Barrett JC . (1995). Regulation of microfilament organization and anchorage-independent growth by tropomyosin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11534–11538.
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF et al. (2008). A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68: 7846–7854.
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S et al. (2008). A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 9: 582–589.
Calin GA, Croce CM . (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 857–866.
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S et al. (2004). Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2999–3004.
Carrington JC, Ambros V . (2003). Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301: 336–338.
Carrio M, Arderiu G, Myers C, Boudreau NJ . (2005). Homeobox D10 induces phenotypic reversion of breast tumor cells in a three-dimensional culture model. Cancer Res 65: 7177–7185.
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH et al. (2007). Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell 26: 745–752.
Chang TC, Yu D, Lee YS, Wentzel EA, Arking DE, West KM et al. (2008). Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat Genet 40: 43–50.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303: 83–86.
Chen Y, Gorski DH . (2008). Regulation of angiogenesis through a microRNA (miR-130a) that down-regulates antiangiogenic homeobox genes GAX and HOXA5. Blood 111: 1217–1226.
Christoffersen NR, Silahtaroglu A, Orom UA, Kauppinen S, Lund AH . (2007). miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B. RNA 13: 1172–1178.
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G et al. (2005). Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334: 1351–1358.
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES, Hynes RO . (2000). Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 406: 532–535.
Corney DC, Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, Wang W, Nikitin AY . (2007). MicroRNA-34b and MicroRNA-34c are targets of p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res 67: 8433–8438.
Coulouarn C, Factor VM, Andersen JB, Durkin ME, Thorgeirsson SS . (2009). Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 28: 3526–3536.
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, Yu L, Hunter MG, Otterson GA et al. (2008). MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373: 607–612.
Dai R, Phillips RA, Zhang Y, Khan D, Crasta O, Ahmed SA . (2008). Suppression of LPS-induced Interferon-gamma and nitric oxide in splenic lymphocytes by select estrogen-regulated microRNAs: a novel mechanism of immune modulation. Blood 112: 4591–4597.
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, Newman M, Erkeland SJ, Hammond SM et al. (2009). Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J 28: 347–358.
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Lagna G, Hata A . (2008). SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature 454: 56–61.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E et al. (2006). Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet 38: 1060–1065.
Dong JT, Lamb PW, Rinker-Schaeffer CW, Vukanovic J, Ichikawa T, Isaacs JT et al. (1995). KAI1, a metastasis suppressor gene for prostate cancer on human chromosome 11p11.2. Science 268: 884–886.
Dong JT, Suzuki H, Pin SS, Bova GS, Schalken JA, Isaacs WB et al. (1996). Down-regulation of the KAI1 metastasis suppressor gene during the progression of human prostatic cancer infrequently involves gene mutation or allelic loss. Cancer Res 56: 4387–4390.
Du J, Yang S, An D, Hu F, Yuan W, Zhai C et al. (2009). BMP-6 inhibits microRNA-21 expression in breast cancer through repressing deltaEF1 and AP-1. Cell Res 19: 487–496.
Duursma AM, Kedde M, Schrier M, le Sage C, Agami R . (2008). miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region. RNA 14: 872–877.
Edmonds MD, Hurst DR, Vaidya KS, Stafford LJ, Chen D, Welch DR . (2009). Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 coordinately regulates metastasis-associated microRNA expression. Int J Cancer 125: 1778–1785.
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z, Zanesi N, Callegari E et al. (2007). MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 15805–15810.
Fidler IJ . (2003). The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 453–458.
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP, de Weerd V, Boersma AW et al. (2008). Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 13021–13026.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH . (2008). Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283: 1026–1033.
Friedman JM, Liang G, Liu CC, Wolff EM, Tsai YC, Ye W et al. (2009). The putative tumor suppressor microRNA-101 modulates the cancer epigenome by repressing the polycomb group protein EZH2. Cancer Res 69: 2623–2629.
Fujita S, Ito T, Mizutani T, Minoguchi S, Yamamichi N, Sakurai K et al. (2008). miR-21 gene expression triggered by AP-1 is sustained through a double-negative feedback mechanism. J Mol Biol 378: 492–504.
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S, Esau CC, Burchard J, Linsley PS et al. (2008). MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol Cell Biol 28: 5369–5380.
Gebeshuber CA, Zatloukal K, Martinez J . (2009). miR-29a suppresses tristetraprolin, which is a regulator of epithelial polarity and metastasis. EMBO Rep 10: 400–405.
Gee HE, Camps C, Buffa FM, Colella S, Sheldon H, Gleadle JM et al. (2008). MicroRNA-10b and breast cancer metastasis. Nature 455: E8–E9; author reply E9.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G et al. (2008). The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10: 593–601.
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y et al. (2007). A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 447: 1130–1134.
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage C, Nagel R, Nair S et al. (2008). The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10: 202–210.
Hunter KW, Crawford NP, Alsarraj J . (2008). Mechanisms of metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 10 (Suppl 1): S2.
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Scott GK, Benz CC, Vaidya KS, Welch DR . (2009). Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 up-regulates miR-146, which suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 69: 1279–1283.
Hurteau GJ, Carlson JA, Spivack SD, Brock GJ . (2007). Overexpression of the microRNA hsa-miR-200c leads to reduced expression of transcription factor 8 and increased expression of E-cadherin. Cancer Res 67: 7972–7976.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S et al. (2005). MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65: 7065–7070.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A et al. (2005). RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120: 635–647.
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y, Abounader R, Hawkinson M et al. (2008). microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 68: 3566–3572.
Kim YI, Shin MK, Lee JW, Chung JH, Lee MH . (2009). Decreased expression of KAI1/CD82 metastasis suppressor gene is associated with loss of heterozygosity in melanoma cell lines. Oncol Rep 21: 159–164.
Kondo N, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Fujii Y, Yamashita H . (2008). miR-206 expression is down-regulated in estrogen receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer. Cancer Res 68: 5004–5008.
Kong W, Yang H, He L, Zhao JJ, Coppola D, Dalton WS et al. (2008). MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA. Mol Cell Biol 28: 6773–6784.
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y . (2008). The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283: 14910–14914.
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G . (2009). miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med 13: 39–53.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . (2002). Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 12: 735–739.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A et al. (2007). A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 129: 1401–1414.
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH, Yang BB . (2007). MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 20350–20355.
Lehmann U, Hasemeier B, Christgen M, Muller M, Romermann D, Langer F et al. (2008). Epigenetic inactivation of microRNA gene hsa-mir-9-1 in human breast cancer. J Pathol 214: 17–24.
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y . (2009a). MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383: 280–285.
Li XF, Yan PJ, Shao ZM . (2009b). Downregulation of miR-193b contributes to enhance urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) expression and tumor progression and invasion in human breast cancer. Oncogene 28: 3937–3948.
Liu X, Nelson A, Wang X, Kanaji N, Kim M, Sato T et al. (2009a). MicroRNA-146a modulates human bronchial epithelial cell survival in response to the cytokine-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380: 177–182.
Liu X, Yu J, Jiang L, Wang A, Shi F, Ye H et al. (2009b). MicroRNA-222 regulates cell invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 6: 131–139.
Liu Y, El-Naggar S, Darling DS, Higashi Y, Dean DC . (2008). Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence. Development 135: 579–588.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435: 834–838.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D et al. (2008). A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 13556–13561.
Lukes L, Crawford NP, Walker R, Hunter KW . (2009). The origins of breast cancer prognostic gene expression profiles. Cancer Res 69: 310–318.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA . (2007). Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449: 682–688.
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP . (2007). Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 315: 1576–1579.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T . (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133: 647–658.
Merkerova M, Belickova M, Bruchova H . (2008). Differential expression of microRNAs in hematopoietic cell lineages. Eur J Haematol 81: 304–310.
Miska EA . (2005). How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15: 563–568.
Myers C, Charboneau A, Cheung I, Hanks D, Boudreau N . (2002). Sustained expression of homeobox D10 inhibits angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 161: 2099–2109.
Neilson JR, Zheng GX, Burge CB, Sharp PA . (2007). Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development. Genes Dev 21: 578–589.
Nuyten DS, van de Vijver MJ . (2006). Gene expression signatures to predict the development of metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Dis 26: 149–156.
Papagiannakopoulos T, Shapiro A, Kosik KS . (2008). MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 68: 8164–8172.
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, Peter ME . (2008). The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22: 894–907.
Park SY, Lee JH, Ha M, Nam JW, Kim VN . (2009). miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85 alpha and CDC42. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16: 23–29.
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK, Kumar R . (2008). MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res 68: 8195–8200.
Rinker-Schaeffer CW, O’Keefe JP, Welch DR, Theodorescu D . (2006). Metastasis suppressor proteins: discovery, molecular mechanisms, and clinical application. Clin Cancer Res 12: 3882–3889.
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, Falconi M, Capelli P, Bersani S et al. (2006). MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol 24: 4677–4684.
Rybak A, Fuchs H, Smirnova L, Brandt C, Pohl EE, Nitsch R et al. (2008). A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat Cell Biol 10: 987–993.
Salvi A, Sabelli C, Moncini S, Venturin M, Arici B, Riva P et al. (2009). MicroRNA-23b mediates urokinase and c-met downmodulation and a decreased migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS J 276: 2966–2982.
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris V, Soteropoulos P et al. (2007). MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res 67: 9762–9770.
Sayed D, Rane S, Lypowy J, He M, Chen IY, Vashistha H et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol Biol Cell 19: 3272–3282.
Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, Reavie L, Zou X, Alvarez-Diaz S et al. (2009). Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 1814–1819.
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, David S, Cheng Y, Mori Y et al. (2009). MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology 49: 1595–1601.
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton MA, Stanhope SA, Cheng YJ et al. (2008). MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 5874–5878.
Song G, Zhang Y, Wang L . (2009). MICRORNA-206 targets NOTCH3, activates apoptosis, inhibits tumor cell migration and foci formation. J Biol Chem 284: 31921–31927.
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D . (2006). NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 12481–12486.
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H et al. (2004). Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64: 3753–3756.
Talmadge JE . (2007). Clonal selection of metastasis within the life history of a tumor. Cancer Res 67: 11471–11475.
Talotta F, Cimmino A, Matarazzo MR, Casalino L, De Vita G, D’Esposito M et al. (2009). An autoregulatory loop mediated by miR-21 and PDCD4 controls the AP-1 activity in RAS transformation. Oncogene 28: 73–84.
Tam W, Ben-Yehuda D, Hayward WS . (1997). bic, A novel gene activated by proviral insertions in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas, is likely to function through its noncoding RNA. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1490–1502.
Tavazoie SF, Alarcon C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD et al. (2008). Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 451: 147–152.
Thiery JP . (2002). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 442–454.
Tomida S, Yanagisawa K, Koshikawa K, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T, Osada H et al. (2007). Identification of a metastasis signature and the DLX4 homeobox protein as a regulator of metastasis by combined transcriptome approach. Oncogene 26: 4600–4608.
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC, Chau GY, Lin CW, Chen CM et al. (2009). MicroRNA-122, a tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49: 1571–1582.
Tsuchiya S, Oku M, Imanaka Y, Kunimoto R, Okuno Y, Terasawa K et al. (2009). MicroRNA-338-3p and microRNA-451 contribute to the formation of basolateral polarity in epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 3821–3827.
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, Calogrias D, Szasz AM, Wang ZC et al. (2009). A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell 137: 1032–1046.
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S, Wang X, Ateeq B et al. (2008). Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 322: 1695–1699.
Veerla S, Lindgren D, Kvist A, Frigyesi A, Staaf J, Persson H et al. (2009). MiRNA expression in urothelial carcinomas: important roles of miR-10a, miR-222, miR-125b, miR-7 and miR-452 for tumor stage and metastasis, and frequent homozygous losses of miR-31. Int J Cancer 124: 2236–2242.
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU et al. (2007). Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 109: 4399–4405.
Vigorito E, Perks KL, Abreu-Goodger C, Bunting S, Xiang Z, Kohlhaas S et al. (2007). microRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity 27: 847–859.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2257–2261.
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R et al. (2006). A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 124: 1169–1181.
Wang G, Mao W, Zheng S . (2008). MicroRNA-183 regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett 582: 3663–3668.
Watanabe S, Ueda Y, Akaboshi S, Hino Y, Sekita Y, Nakao M . (2009). HMGA2 maintains oncogenic RAS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic cancer cells. Am J Pathol 174: 854–868.
Webster RJ, Giles KM, Price KJ, Zhang PM, Mattick JS, Leedman PJ . (2009). Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human cancer cells by microRNA-7. J Biol Chem 284: 5731–5741.
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty SM, Riggs KA, Li Y, Klinge CM . (2009). Estradiol downregulates miR-21 expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 2584–2595.
Williams AE, Moschos SA, Perry MM, Barnes PJ, Lindsay MA . (2007). Maternally imprinted microRNAs are differentially expressed during mouse and human lung development. Dev Dyn 236: 572–580.
Xia H, Qi Y, Ng SS, Chen X, Li D, Chen S et al. (2009). microRNA-146b inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMPs. Brain Res 1269: 158–165.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M et al. (2006). Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9: 189–198.
Yang K, Handorean AM, Iczkowski KA . (2009). MicroRNAs 373 and 520c are downregulated in prostate cancer, suppress CD44 translation and enhance invasion of prostate cancer cells in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2: 361–369.
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C et al. (2007). let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131: 1109–1123.
Zhang X, Liu S, Hu T, He Y, Sun S . (2009). Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology 50: 490–499.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY . (2007). MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282: 14328–14336.
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY . (2008). MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 18: 350–359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Li, Y. & Lai, M. The microRNA network and tumor metastasis. Oncogene 29, 937–948 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.406
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.406
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Network regulatory mechanism of ncRNA on the Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis
Cell Division (2023)
-
Impaired AGO2/miR-185-3p/NRP1 axis promotes colorectal cancer metastasis
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Regulation of breast cancer metastasis signaling by miRNAs
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2020)
-
Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
GATA6 suppresses migration and metastasis by regulating the miR-520b/CREB1 axis in gastric cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2019)