Abstract
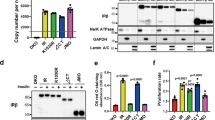
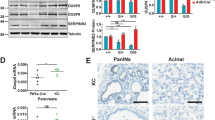
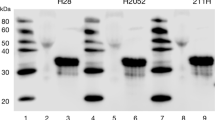
There have been few studies on the specific signaling pathways involved in the transformation of epithelial cells by oncogenic protein tyrosine kinases. Here we investigate the requirement of MAP (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol 3- (PI3K) kinases in the transformation of rat intestinal epithelial (RIE) cells by oncogenic forms of insulin receptor (gag-IR), insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (gag-IGFR), and v-Src. MAPK is not significantly activated in cells transformed by gag-IR and gag-IGFR but is activated in v-Src transformed cells. Treatment with PD98059, a MEK inhibitor, at concentrations where MAPK activity was reduced below the basal level showed that MAPK is partially required for the monolayer growth of parental and transformed RIE cells. However, MAPK is not essential for the focus forming ability of the three oncogene-transformed cells. It is also not necessary for the colony forming ability of gag-IR- and gag-IGFR-, but is partially required for v-Src-transformed cells. PI3K is significantly activated in all three oncogene transformed RIE cells. LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, potently inhibited monolayer growth of all three oncogene-transformed cells. However, at concentrations of LY294002 where activated forms of Akt, a downstream component of the PI3K pathway, were undetectable, colony and focus forming abilities of the v-Src-RIE cells were only slightly affected whereas those of gag-IR/IGFR-RIE cells were greatly inhibited. These results were confirmed using a different pharmacological inhibitor, wortmannin, and a dominant negative form of PI3K, Δp85. Similarly, rapamycin, known to inhibit p70S6 kinase, a downstream component of the PI3K-Akt pathway, also inhibited gag-IR/IGFR-induced, but not v-Src-induced, focus and colony formation. We conclude that the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways are differentially required for transformation of RIE cells by oncogenic IR and IGFR versus Src and the pattern of requirements is different from that of fibroblast transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aftab DT, Kwan J and Martin GS. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94: 3028–3033.
Amfo K, Neyns B, Teugels E, Lissens W, Bourgain C, De Sutter P, Vandamme B, Vamos E and De Greve J. . 1995 Oncogene 11: 351–358.
Baserga R. . 1995 Cancer Res. 55: 249–252.
Beck EP, Russo P, Liozzo B, Jaeger W, Papa V, Wildt L, Pezzino V and Lang N. . 1994 Gynecol. Oncol. 53: 196–201.
Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, McCormick F, Feng J and Tsichlis P. . 1998 Oncogene 17: 323–325.
Biscardi JS, Tice DA and Parsons SJ. . 1999 Adv. Cancer. Res. 76: 61–119.
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem WW and Darnell Jr JE. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 2553–2558.
Brown MT and Cooper JA. . 1996 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1287: 121–149.
Chan JL-K, Lai M and Wang L-H. . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 146–153.
Chen J, Sadowski HB, Kohanski RA and Wang L-H. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94: 2295–2300.
Chung J, Kuo CJ, Crabtree GR and Blenis J. . 1992 Cell. 69: 1227–1236.
Conway AM, Rakhit S, Pyne S and Pyne NJ. . 1999 Biochem J. 337: 171–177.
Dennis PB, Fumagalli S and Thomas G. . 1999 Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 9: 49–54.
Downward J. . 1998 Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 10: 262–267.
Frittitta L, Sciacca L, Catalfamo R, Ippolito R, Gangemi P, Pezzino V, Filetti S and Vigneri R. . 1999 Cancer 85: 492–498.
Fukui Y, Kornbluth S, Jong S, Wang L-H and Hanafusa H. . 1989 Oncogene Res. 4: 283–292.
Garcia R, Parikh NU, Saya H and Gallick GE. . 1991 Oncogene. 6: 1983–1989.
Giorgetti S, Ballotti R, Kowalski-Chauvel A, Tartare S and Van Obberghen E. . 1993 J. Biol. Chem. 268: 7358–7364.
Greulich H, Reichman C and Hanafusa H. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 1689–1695.
Guo YS, Narayan S, Yallampalli C and Singh P. . 1992 Gastroenterology 102: 1101–1108.
Jiang Y, Chan JL-K, Zong CS and Wang L-H. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 160–167.
Kaleko M, Rutter WJ and Miller AD. . 1990 Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 464–473.
Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM and Schlessinger J. . 1996 Cell. 85: 621–624.
Ligon AH, Pershouse MA, Jasser S, Hong YK, Yung WK and Steck PA. . 1998 J. Neurovirol. 4: 217–226.
Lin X and Gelman IH. . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 2402–2412.
Liu D, Rutter WJ and Wang L-H. . 1992 J. Virol. 66: 374–385.
Liu D, Zong CS and Wang L-H. . 1993 J. Virol. 67: 6835–6840.
Louvi A, Accili D and Efstratiadis A. . 1997 Dev. Biol. 189: 33–48.
Luttrel LM, Hawes BE, van Biesen T, Luttrell DK, Lansing TJ and Lefkowitz RJ. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 19443–19450.
Meyers MG, Sun XJ, Cheatham B, Jachna BR, Glasheen EM, Backer JM and White MF. . 1993 Endocrinology 132: 1421–1430.
Oldham SM, Cox AD, Reynolds ER, Sizemore NS, Coffey Jr RJ and Der CJ. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 2565–2573.
Ottenhoff-Kalff AE, Rijksen G, van Beurden EA, Hennipman A, Michels AA and Staal GE. . 1992 Cancer Res. 52: 4773–4778.
Papa V, Gliozzo B, Clark G, McGuire WI, Moore D, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Vigneri R, Goldfine ID and Pezzino V. . 1993 Cancer Res. 53: 3736–3740.
Penuel E and Martin GS. . 1999 Mol. Biol. Cell. 10: 1693–1703.
Peterson JE, Kulik G, Jelinek T, Reuter CW, Shannon JA and Weber MJ. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 31562–31571.
Poon B, Dixon D, Ellis L, Roth RA, Rutter WJ and Wang L-H. . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 88: 877–881.
Ralston R and Bishop JM. . 1985 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82: 7845–7849.
Rotsch M, Maasberg M, Erbil C, Jaques G, Worsch U and Havemann K. . 1992 J. Cancer Res. Oncol. 118: 502–508.
Sciacca L, Costantino A, Pandini G, Mineo R, Frasca F, Scalia P, Sbraccia P, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R and Belfiore A. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 2471–2479.
Schaeffer HJ and Webber MJ. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 2435–2444.
Schlaepfer DD, Jones KC and Hunter T. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 2571–2585.
Sell C, Dumenil L, Deveaud C, Miura M, Coppola D, DeAngelis T, Rubin R, Efstratiadis A and Baserga R. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 3604–3612.
Sell C, Rubini M, Rubin R, Liu J-P, Efstratiadis A and Baserga R. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90: 11217–11221.
Shoji S, Kurosawa T, Inoue H, Funakoshi T and Kubota U. . 1990 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 173: 894–901.
Staley CA, Parikh NJ and Gallick GE. . 1997 Cell Growth Diff. 8: 269–274.
Stofega MR, Yu C-L, Wu J and Jove R. . 1997 Cell Growth Diff. 8: 113–119.
Takeya T, Feldman RA and Hanafusa H. . 1982 J. Virology. 44: 1–11.
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven E, De Groot RP and Jove R. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 2545–2552.
Van der Greer P, Hunter T and Lindberg RA. . 1994 Annu. Rev. Cell. Biol. 10: 251–337.
Wang L-H, Lin B, Jong S-MJ, Dixon D, Ellis L, Roth RA and Rutter WJ. . 1987 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 84: 5725–5729.
Werner H and LeRoith D. . 1996 Adv. Cancer Res. 68: 183–223.
Werner H, Re GG, Drummond IA, Sukhatme VP, Rauscher FJ III, Sens DA, Garvin AJ, LeRoith D and Roberts Jr CT. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90: 5828–5832.
Yamaguchi Y, Flier JS, Yokota A, Benecke H, Backer JM and Moller DE. . 1991 Endocrinology 129: 2058–2066.
Yashiro T, Ohba Y, Murakami H, Obara O, Tsushima T, Fujimoto Y, Shirzume K and Ito K. . 1989 Acta Endocrinol. (Copenhagen). 121: 112–120.
Zong CS, Zeng L, Jiang Y, Sadowski HB and Wang L-H. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 28065–28072.
Acknowledgements
We thank CJ Der for the gift of RIE cells; I Gelman for ts-v-src plasmid; J Downward for the gift of Δp85 plasmid; M-T Le, P Sachdev and CS Zong for their assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported by NIH grant CA55054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, K., Wang, WJ., Chan, JK. et al. Differential requirements of the MAP kinase and PI3 kinase signaling pathways in Src- versus insulin and IGF-1 receptors-induced growth and transformation of rat intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 19, 5385–5397 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203911
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203911
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of human airway smooth muscle cell migration and relevance to asthma
Respiratory Research (2017)
-
Synergistic effect between EGF and TGF-β1 in inducing oncogenic properties of intestinal epithelial cells
Oncogene (2008)
-
Delineating v-Src downstream effector pathways in transformed myoblasts
Oncogene (2008)
-
Cellular retinol-binding protein-I inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling through a retinoic acid receptor-dependent mechanism that regulates p85–p110 heterodimerization
Oncogene (2005)
-
Increased Bcl-xL expression mediates v-Src-induced resistance to anoikis in intestinal epithelial cells
Oncogene (2002)