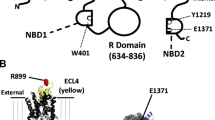
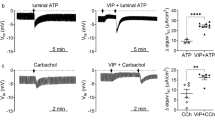
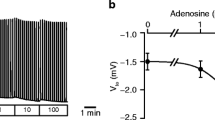
Abstract
The human colonic carcinoma cell line HT29cl.19A responds to the protein kinase C activator PDB (4-β-phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate), as it does to forskolin (an activator of adenylyl cyclase), with a secretory response when the cells are grown on filters and studied at 36 °C. Previously, we showed that when cells were grown on Petri dishes and studied at about 25 °C with the cell-attached patch-clamp technique, forskolin, but not PDB, could activate 8-pS chloride channels (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, CFTR, channels). The present work was carried out to study this discrepancy. Experiments in Ussing chambers, at different temperatures, showed that the responses to PDB and forskolin differ in their temperature sensitivity. This was also found following conventional microelectrode and Ussing chamber studies with nystatin-permeabilized epithelial layers carried out at 25 °C and at 36 °C. Pre-incubation with the microtubular disruptive agents nocodazole or colcemid did not affect the response to PDB or forskolin, suggesting that chloride secretion induced by these agonists in these cells is independent of the microtubular structure. Pre-incubation with brefeldin A strongly inhibited the response to PDB, but the response to forskolin was hardly affected. The differing effect of temperature and brefeldin A on the responses to forskolin and PDB may be due to the activation of two distinct mechanisms by protein kinases A and C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MP, Welsh MJ (1991) Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6003–6007
Bajnath RB, Augeron C, Laboisse CL, Bijman J, De Jonge HR, Groot JA (1991) Electrophysiological studies of forskolin-induced changes in ion transport in the human colon carcinoma cell line HT-29cl.19A: lack of evidence for a cAMP-activated basolateral K+-conductance. J Membr Biol 122:239–250
Bajnath RB, van Hoeve MH, De Jonge HR, Groot JA (1992) Regulation of apical Cl− conductance and basolateral K+ conductance by phorbol esters in HT-29cl.19A cells. Am J Physiol 263:C759-C766
Bajnath RB, van den Berghe N, De Jonge HR, Groot JA (1993) Activation of ion transport by combined effects of ionomycin, forskolin and phorbol ester on cultured HT-29cl.19A human colonocytes. Pflügers Arch 425:90–99
Bajnath RB, Groot JA, De Jonge HR, Kansen M, Bijman J (1993) Synergistic activation of non-rectifying small conductance chloride channels by forskolin and phorbol esters in cell-attached patches of the human colon carcinoma cell line HT-29cl.19A. Pflügers Arch 425:100–108
Bradbury NA, Bridges RJ (1992) Endocytosis is regulated by protein kinase A, but not protein kinase C in a secretory epithelial cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 184:1173–1180
Bradbury NA, Jilling J, Berta G, Sorscher EJ, Bridges RJ, Kirk KL (1992) Regulation of plasma membrane recycling by CFTR. Science 256:530–531
Capparelli AW, Heng MCY, Li L, Jo OD, Yanagawa N (1993) Brefeldin A inhibits phosphate transport in opposum kidney cells. Am J Physiol 264:C40-C47
Denning GM, Ostedgaard LS, Cheng SH, Smith AE, Welsh MJ (1992) Localization of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in chloride secretory epithelia. J Clin Invest 89:339–349
Farack UM, Gerzer R, Keravis TM, Loeschke K (1988) Discrepancy between effects of cholera toxin on net fluid movement and cAMP levels in rat jejunum, ileum, and colon. Dig. Dis Sci 33:1153–1158
Fuller CM, Bridges RJ, Benos DJ (1994) Forskolin-but not ionomycin-evoked Cl−secretion in colonic epithelia depends on intact microtubules. Am J Physiol 266:C661-C668
Gilbert T, LeBivic A, Quaroni A, Rodriquez-Boulan E (1991) Microtubular organization and its involvement in the biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 113:275–288
Huflejt ME, Blum RA, Miller SG, Hsiao-Ping, Moore H, Machen TE (1994) Regulated Cl transport, and Cl permeability, and exocytosis in T-84 cells. J Clin Invest 93:1900–1910
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yuan LC, Bonifacino JS, Klausner RD (1989) Rapid distribution of Golgi-proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane recycling from the Golgi to ER. Cell 56:801–813
Misumi Y, Miki K, Takatsuki K, Tamura G, Ikehara Y (1986) Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 261: 11398–11403
Morris AP, Cunningham SA, Tousson A, Benos DJ, Frizzell RA (1994) Polarization-dependent apical membrane CFTR targeting underlies cAMP-stimulated Cl− secretion in epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 266:C254-C268
Philips ME, Taylor A (1989) Effect of nocodazole on the water permeability response to vasopressin in rabbit collecting tubules perfused in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 411:529–544
Philips ME, Taylor A (1992) Effect of colcemid on the water permeability response to vasopressin in isolated perfused rabbit collecting tubules. J Physiol (Lond) 456:591–608
Prince LS, Tousson A, Marchase RB (1993) Cell surface labeling of CFTR in T-84 cells. Am J Physiol 26:C491-C498
Schwiebert EM, Gesek F, Ercolani L, Wjasow C, Gruenert DC, Karlson K, Stanton BA (1994) Heterotrimeric G proteins, vesicle trafficking, and CFTR Cl− channels. Am J Physiol 267:C272-C281
Sorscher EJ, Fuller CM, Bridges RJ, Tousson A, Marchase RB, Brinkley BR, Frizzell RA, Benos DJ (1992) Identification of a membrane protein from T-84 cells using antibodies made against a DIDS-binding peptide. Am J Physiol 262:C136-C147
Van den Moortele S, Picart R, Tixier-Vidal A, Tougard C (1992) Nocodazole and taxol affect subcellular compartments but not secretory activity of GH3B6 prolactin cells. Eur J Cell Biol 60:217–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajnath, R.B., Dekker, K., De Jonge, H.R. et al. Chloride secretion induced by phorbol dibutyrate and forskolin in the human colonic carcinoma cell line HT-29Cl.19A is regulated by different mechanisms. Pflugers Arch. 430, 705–712 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386165
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386165