Abstract
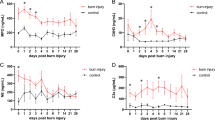
Burn death based on circulatory shock is often encountered after recovery from primary shock in patients with deep and extensive burns,i.e., late death. Several toxic substances have been proposed, however, the responsible substance remains obscure. Since we have found leukotoxin, a highly cytotoxic linoleate epoxide biosynthesized by neutrophils, in the burned skin, in the present study we determined plasma leukotoxin concentrations in various degree of 30 burn patients. C-reactive protein and circulatory white blood cells were also measured. A significantly high mortality rate of patients with extensive burns (burn surface area over 70%) was observed compared with that in patients with burn surface area under 70%, and significantly high leukotoxin concentrations were observed within a week, and 3 weeks after the thermal injury in patients with extensive burns compared with those in patients with burn surface area under 70%. There were two peaks of plasma leukotoxin concentrations,i.e., the early phase (within 1 week) and the late phase (over 1 week) in patients with extensive burns. Plasma leukotoxin concentrations significantly correlated with burn surface area in the early phase, and similar correlations were observed in the late phase. A significantly high mortality rate (61%) of patients with peak leukotoxin concentrations over 30 nmol/ml was observed compared with 8% for those below 30 nmol/ml. Plasma leukotoxin concentration correlated significantly to C-reactive protein concentration, log (leukotoxin nmol/ml)=0.042×C-reactive protein (mg/dl)+0.74, (r=0.83,P<0.01) in the late phase. From these results, it is concluded that leukotoxin is produced in patients with burns particularly in the late phase of extensive burns, and leukotoxin might play an important role in the tissue destructive procedure associated with severe burns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenthal SR, Hawley PL, Hakim AA: Purified burn toxic factor and its competition. Surgery 71: 527–536, 1971
Raffa J, Trunkey DD: Myocardial depression in acute thermal injury. J Trauma 18: 90–93, 1978
Moatii F, Sepulchre C, Miskulin M, Huisman O, Moczar E, Robert AM, Monteil R, Guilbaud J: Biochemical and pharmacological properties of a cardiotoxic factor isolated from the blood serum of burned patients. J Pathol 127: 147–156, 1979
Aoyama H, Izawa Y, Ozawa T: Toxic effects of extracts from burned skin, serum and blister fluid of burned patients on mitochondrial function. Burns 7: 33–37, 1980
Suzuki K, Aoyama H, Izawa Y, Kobayashi M, Ozawa T: Isolation of a substance toxic to mitochondrial function from the burned skin of rats. Burns 8: 110–117, 1981
Yokoo K, Hayakawa M, Sugiyama S, Ozawa T, Aoyama H, Izawa Y, Kondo T, Hayakawa Y: A novel uncoupler of mitochondrial respiration, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate, exists in human burned skin. J Clin Biochem Nutr 1: 121–127, 1986
Hayakawa M, Sugiyama S, Takamura T, Tokoo K, Iwata M, Suzuki K, Taki F, Takahashi S, Ozawa T: Neutrophils biosynthesize leukotoxin, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 137: 424–430, 1986
Hayakawa M, Kosaka K, Sugiyama S, Yokoo K, Aoyama H, Izawa Y, Ozawa T: Proposal of leukotoxin, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate, as a burn toxin. Biochem Int 21:573–579, 1990
Takahashi H, Ishizaki T, Ameshima S, Kishi Y, Sasaki F, Nakai T, Miyabo S, Ozawa T: Leukotoxin, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate causes vasodilation in isolated pulmonary artery rings preconstricted with endothelin 1. Jpn J Thorac Dis 30: 418–424, 1992
Akabane H, Nagao M, Zhang W, Yamada Y, Oono T, Takatori T: Production and characterization of antibodies reactive with leukotoxin. Jpn J Legal Med 47: 93–97, 1993
Hayakawa M, Ogawa T, Sugiyama S, Ozawa T: Hydroxyl radical and leukotoxin biosynthesis in neutrophil plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161: 1077–1085, 1989
Ozawa T, Nishikimi M, Sugiyama S, Taki F, Hayakawa M, Shionoya H: Cytotoxic activity of leukotoxin, a neutrophil-derived fatty acid epoxide, on cultured human cells. Biochem Int 16: 369–373, 1988
Ozawa T, Sugiyama S, Hayakawa M, Satake T, Taka F, Iwata M, Taki K: Existence of leukotoxin 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate in lung lavages from rats breathing pure oxygen and from patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 137: 535–540, 1988
Hanaki Y, Kamiya H, Ohno M, Hayakawa M, Sugiyama S, Ozawa T: Leukotoxin, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate: a possible responsible factor in circulatory shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Jpn J Med 30: 224–228, 1991
Fukushima A, Hayakawa M, Sugiyama S, Ajioka M, Ito T, Satake T, Ozawa T: Cardiovascular effects of leukotoxin, (9,10-epoxy-12 octadecenoate) and free fatty acids in dogs. Cardiovasc Res 22: 213–218, 1988
Sugiyama S, Hayakawa M, Hanaki Y, Hieda N, Asai J, Ozawa T: The role of leukotoxin (9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate) in the genesis of coagulation abnormalities. Life Sci 43: 221–227, 1988
Deich EA: The management of burns. N Eng J Med 323: 1249–1253, 1990
Itaya K, Ui M: Colorimetric determination of free fatty acids in biological fluids. J Lipid Res 6: 16–20, 1965
Wallenstein SL, Zucker CL, Fleiss J: Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47: 1–9, 1980
Ichihara K: Statistics for bioscience. Nankodo Publishers, Tokyo, 1990, pp 224–225
Sugiyama S, Hayakawa M, Nagai S, Ajioka M, Ozawa T: Leukotoxin, 9,10-epoxy-12-octadenenoate, causes cardiac failure in dogs. Lift Sci 8: 1373–1379, 1987
Hu J, Taki F, Sugiyama S, Asai J, Izawa Y, Satake T, Ozawa T: Neutrophil-derived epoxide, 9,10-epoxy 12-octadecenoate, induces pulmonary edema. Lung 166: 327–333, 1988
Yano K, Hattori H, Imai A, Nozawa Y: Modification of positional distribution of fatty acids in phosphatidilinositol of rabbit neurtrophils stimulated wiht formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Biochim Biophys Acta 752: 137–144, 1983
Kato T, Yamaguchi Y, Uyehara T, Yokoyama T, Namai T, Yamanaka S: Self defensive substances in rice plant against rice plast disease. Tetrahedron Lett 24: 4715–4718, 1983
Ozawa T, Sugiyama S, Hayakawa M, Taki F, Hanaki Y: Neutrophil microsomes biosynthesize lenoleate epoxide (9,10-epoxy-12-octadecenoate), a biological active substance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 152: 1310–1318, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosaka, K., Suzuki, K., Hayakawa, M. et al. Leukotoxin, a linoleate epoxide: Its implication in the late death of patients with extensive burns. Mol Cell Biochem 139, 141–148 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01081737
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01081737