Abstract
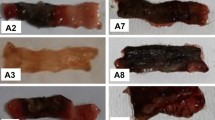
The efficacy of zileuton, a new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, was investigated in comparison with sulphasalazine in an experimental model of rat colitis. Under light anaesthesia with ether, male rats were subjected to intracolonic administration of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNB) in 50% ethanol and were then sacrificed 2, 4 and 7 days after colitis induction. Untreated rats exhibited elevated colonic levels of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and 6-keto-PGF1α, and an increase in colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity (investigated as an index of leukocyte adhesion and accumulation). Moreover ulceration and inflammation of the distal colon with formation of granuloma and pathologic connections were observed. Treated rats received zileuton or sulphasalazine (50 mg/kg per os twice a day) 24 h before the induction of colitis until they were sacrificed. Treatment with the specific 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, zileuton, resulted in significant reductions of colonic leukotriene B4 and 6-keto-PGF1α synthesis, macroscopic and histological colonic damage and colonic inflammation as assessed by the measurement of MPO activity. In contrast, sulphasalazine had a lower effect than zileuton on LTB4 and MPO levels (p<0.05), while it was able to reduce colonic damage and 6-keto-PGF1α levels as well as zileuton.
This study shows, therefore, that zileuton is effective in attenuating the lesions in an experimental model of colitis. Furthermore, the results are consistent with the hypothesis that leukotrienes play an important role in the pathogenesis of intestinal bowel diseases (IBD).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. P. Morris, P. L. Beck, M. S. Herridge, W. T. Drew, M. R. Szewczuk and J. L. Wallace,Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology96, 795–803 (1989).
M. Baggiolini,The enzymes of the granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and their function. Enzyme13, 131–160 (1972).
J. L. Wallace, C. M. Keenan and D. N. Granger,Gastric ulceration induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is a neutrophil-dependent process. Am. J. Physiol259, G462-G467 (1990).
R. A. Lewis and K. F. Austen,The biologically active leukotrienes. Biosynthesis, functions, and pharmacology, J. Clin. Invest.73, 889–897 (1984).
A. W. Ford-Hutchinson, M. A. Bray, M. V. Doig, M. E. Shipley and J. H. Smith,Leukotriene B 4,a potent chemotactic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature266, 264–265 (1980).
P. Borgeat and B. Samuelsson,Transformation of arachidonic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem.254, 2643–2646 (1979).
K. Lauritsen, L. S. Laursen, K. Burhave and J. Rask-Masden,Effects of topical 5-aminosalicylic acid and prednisolone on prostaglandin E 2 and leukotriene B 4 levels determined by equilibrium in vivo dialysis of rectum in relapsing ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology91, 837–844 (1986).
T. Nishida, H. Miwa, A. Shigematsu, M. Yamamoto, M. Iida and M. Fujishima,Increased arachidonic acid composition of phospholipids in colonic mucosa from patients with active ulcerative colitis. Gut28, 1002–1007 (1987).
P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Metabolism of arachidonic acid in acetic acid colitis in rats: Similarity to human inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology88, 55–63 (1985).
R. D. Zipser, C. C. Nast, M. Lee, H. W. Kao and R. Duke,In vivo production of leukotriene B 4 and leukotriene C 4 in rabbit colitis. Relationship to inflammation. Gastroenterology92, 33–39 (1987).
P. R. Young, R. L. Bell, C. Lanni, J. B. Summer, W. Brooks and G. W. Carter,Inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis in the rat peritoneal cavity. Eur. J. Pharmacol.205, 259–266 (1991).
J. L. Wallace, W. K. Mac Naughton, G. P. Morris and P. L. Beck,Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis markedly accelerates healing in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology96, 29–36 (1989).
L. R. Fitzpatrick, J. S. Bostwick, M. Renzetti, R. G. Pendleton and D. L. Decktor,Antiinflammatory effects of various drugs on acetic acid induced colitis in the rat. Agents and Actions30, 393–401 (1991).
C. N. Hsiao and T. Kolasa,Synthesis of chiral zileuton, a potent and selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Tetrahedron Lett.33, 2629–2632 (1992).
J. E. Krawisz, P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Quantitative assay for acute intestinal inflammation based on myeloper-oxydase activity. Assessment of inflammation in rat and hamster models. Gastroenterology87, 1344–50 (1984).
P. P. Bradley, D. A. Priebat, R. D. Christensen and G. Rothstein,Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J. Invest. Dermatol.78, 206–209 (1982).
B. J. R. Whittle,Temporal relationship between cyclo-oxygenase inhibition measured as prostacyclin biosynthesis and gastrointestinal damage induced by indomethacin in the rat. Gastroenterology80, 94–98 (1981).
J. A. Salmon,A radioimmunoassay for 6-keto-prostaglandin F 2α. Prostaglandins15, 383–397 (1978).
J. A. Salmon, P. M. Simmons and R. M. J. Palmer,A radioimmunoassay for leukotriene B 4. Prostaglandins24, 225–235 (1982).
P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B 4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology86, 453–460 (1984).
N. K. Boughton-Smith, J. L. Wallace, G. P. Morris and B. J. R. Whittle,The effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on eicosanoid formation in a chronic model of inflammatory bowel disease in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol.94, 65–72 (1988).
A. Zifroni, A. J. Treves, D. B. Sachar and D. Rachmilewitz,Prostanoid synthesis by cultured intestinal epithelial and mononuclear cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut24, 659–664 (1983).
D. K. Podolsky,Inflammatory bowel disease. New Engl. J. Med.325, 928–937 (1991).
P. Canale, F. Squadrito, B. Zingarelli, D. Altavilla, M. Ioculano, G. M. Campo and A. P. Caputi,Splanchnic artery occlusion shock: Vinblastine-induced leukopenia reduces tumour necrosis factor and thromboxane A 2 formation, and increases survival rate. Pharmacol. Res.27, 61–71 (1993).
N. R. Matheson, P. S. Wong and J. Travis,Isolation and properties of human neutrophil myeloperoxidase. Biochemistry,20, 325–330 (1981).
A. Bos, R. Wever and D. Roos,Characterization and quantification of the peroxidase in human monocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Acta525, 37–44 (1978).
E. A. Lobos, P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Chemotactic activity in inflammatory bowel disease: role of leukotriene B 4. Dig. Dis. Sci.32, 1380–1388 (1987).
S. B. Hanauer and J. B. Kirsner,Medical therapy of ulcerative colitis. InInflammation bowel disease. (Eds. J. B. Kirsner and R. G. Shorter) pp. 431–475, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia 1988.
K. Lauritsen, J. Hansen, P. Bytzer, K. Bukhave and J. Rask-Madsen.Effects of sulphasalazine and disodium azodisalicylate on colonic PGE 2 concentrations determined by equilibrium in vivo dialysis of faeces in patients with ulcerative colitis and healthy controls. Gut25, 1271–1278 (1984).
Y. Myachi, A. Yoshioka, S. Imamura and Y. Niwa,Effect of sulphasalazine and its metabolites on the generation of reactive oxygen species. Gut28, 190–195 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zingarelli, B., Squadrito, F., Graziani, P. et al. Effects of zileuton, a new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, in experimentally induced colitis in rats. Agents and Actions 39, 150–156 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01998968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01998968