Summary
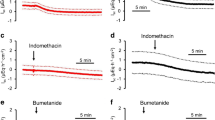
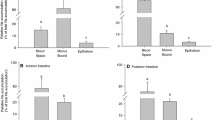
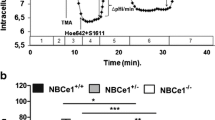
Isolated segments of hamster small intestine were perfused with oxygenated salt-fluorocarbon emulsions with or without 10–25mm glucose, alanine or leucine. Resistances of inter-cellular occluding junctions and of lateral spaces and the distributed capacitance of epithelial plasma membranes were estimated from steady-state transepithelial impedances at frequencies from 0.01–10 kHz. The segments were then fixedin situ with isorheic 2.5% glutaraldehyde while continuing to measure impedance. This method of fixation increased the resistance of lateral spaces but had little effect on the resistance of occluding junctions or on membrane capacitance. The large decreases of impedance induced by glucose or amino acids were preserved in fixed tissue and could therefore be correlated with changes in structure. The observed changes of impedance were interpreted as decreased resistance of occluding junctions and lateral spaces together with increased exposed surface of lateral membranes (capacitance). Glucose, alanine or leucine induced expansion of lateral intercellular spaces as seen by light and electron microscopy. Large dilatations within absorptive cell occluding junctions were revealed by electron microscopy. Freeze-fracture analysis revealed that these dilatations consisted of expansions of compartments bounded by strands/grooves. These solute-induced structural alterations were also associated with condensation of microfilaments in the zone of the perijunctional actomyosin ring, typical of enhanced ring tension. Similar anatomical changes were found in epithelia fixedin situ at 38°C during luminal perfusion with glucose in blood-circulated intestinal segments of anesthetized animals. These structural changes support the hypothesis that Na-coupled solute transport triggers contraction of perijunctional actomyosin, thereby increasing junctional permeability and enhancing absorption of nutrients by solvent drag as described in the two accompanying papers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulpaep, E.L. 1972. Permeability changes of proximal tubule ofNecturus during saline loading.Am. J. Physiol. 222:517–531
Bradley, S.E., Purcell, E.F. 1982. The Paracellular Pathway. pp. 203–204. Josiah Macy Jr. Foundation, New York
Burgess, D.R. 1982. Reactivation of intestinal epithelial brush border motility: ATP-dependent contraction via a terminal web contractile ring.J. Cell Biol. 95:853–863
Claude, P., Goodenough, D.A. 1973. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from tight and leaky epithelia.J. Cell Biol. 58:390–400
Fisher, R.B., Parsons, D.S. 1949. Glucose absorption from surviving rat small intestine.J. Physiol. (London) 110:281–293
Hirokawa, N., Keller, T.C.S., Chason, R., Mooseker, M.S. 1983. Mechanism of brush border contractility studied by the quick-freeze deep-etch method.J. Cell Biol. 96:1325–1336
Madara, J.L. 1983. Increases in guinea pig small intestinal transepithelial resistance induced by osmotic loads are accompanied by rapid alterations in absorptive-cell tight junction structure.J. Cell Biol. 97:125–136
Madara, J.L., Barenberg, D., Carlson, S. 1986. Effects of Cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: Further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity.J. Cell Biol. 102:2125–2136
Madara, J.L., Dharmsathaphorn, K. 1985. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer.J. Cell Biol. 101:2124–2133
Madara, J.L., Trier, J.S. 1986. Functional morphology of the mucosa of the small intestine.In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. (2nd ed.) L.R. Johnson, editor. Raven, New York
Marcial, M.A., Carlson, S.L., Madara, J.L. 1984. Partitioning of paracellular conductance along the ileal crypt-villus axis: A hypothesis based on structural analysis with detailed consideration of tight junction structure-function relationships.J. Membrane Biol. 80:59–70
Naftalin, R.J., Tripathi, S. 1986. The roles of paracellular and transcellular pathways and submucosal space in isotonic water absorption by the rabbit ileum.J. Physiol. (London) 370:409–432
Pappenheimer, J.R. 1987. Physiological regulation of transepithelial impedance in the intestinal mucosa of rat and hamsters.J. Membrane Biol. 100:137–148
Pappenheimer, J.R., Reiss, K.Z. 1987. Contribution of solvent drag through intercellular junctions to absorption of nutrients by the small intestine of the rat.J. Membrane Biol. 100:123–136
Rodewald, R.S., Newman, S.B., Karnovsky, M.S. 1976. Contraction of isolated brush borders from the intestinal epithelium.J. Cell Biol. 70:541–554
Schmidt-Nielsen, B. 1968. Fluid transport and intercellular spaces in reptilian kidneys.Science 159:1105–1108
Smulders, A.P., Tormey, J.McD., Wright, E.M. 1972. The effect of osmotically induced water flows on the permeability and ultrastructure of the rabbit gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 7:164–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madara, J.L., Pappenheimer, J.R. Structural basis for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. J. Membrain Biol. 100, 149–164 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02209147
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02209147