Abstract.
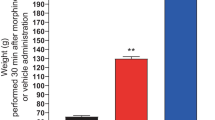
We have established that μ-opioid receptor activation causes a presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmitter release that is mediated by 12-lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid in midbrain neurons [1]. We further demonstrated that the efficacy of opioids was enhanced synergistically by treatment of brain neurons with inhibitors of the other major enzymes responsible for arachidonic acid metabolism; cyclooxygenase (COX-1) and 5-lipoxygenase. These findings explain a mechanism of analgesic action of NSAIDs in the central nervous system that is both independent of prostanoid release and inhibited by opioid antagonists, as well as the synergistic interaction of opioids with NSAIDs. These findings also suggest new avenues for development of centrally active medications involving combinations of lowered doses of opioids and specific 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 23 June 1998; returned for revision 7 July 1998; accepted by R. Day 24 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christie, M., Vaughan, C. & Ingram, S. Opioids, NSAIDs and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors act synergistically in brain via arachidonic acid metabolism. Inflamm. res. 48, 1–4 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050367