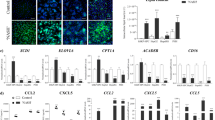
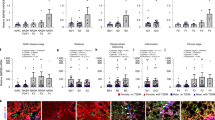
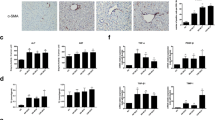
Abstract
Hepatic fibrosis is a dynamic chronic liver disease occurring as a consequence of wound-healing responses to various hepatic injuries. This disorder is one of primary predictors for liver-associated morbidity and mortality worldwide. To date, no pharmacological agent has been approved for hepatic fibrosis or could be recommended for routine use in clinical context. Cellular and molecular understanding of hepatic fibrosis has revealed that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), the functioning receptor for antidiabetic thiazolidinediones, plays a pivotal role in the pathobiology of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), whose activation is the central event in the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis. Activation of PPARγ inhibits HSC collagen production and modulates HSC adipogenic phenotype at transcriptional and epigenetic levels. These molecular insights indicate PPARγ as a promising drug target for antifibrotic chemotherapy. Intensive animal studies have demonstrated that stimulation of PPARγ regulatory system through gene therapy approaches and PPARγ ligands has therapeutic promise for hepatic fibrosis induced by a variety of etiologies. At the same time, thiazolidinedione agents have been investigated for their clinical benefits primarily in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a common metabolic liver disorder with high potential to progress to fibrosis and liver-related death. Although some studies have shown initial promise, none has established long-term efficacy in well-controlled randomized clinical trials. This comprehensive review covers the 10-year discoveries of the molecular basis for PPARγ regulation of HSC pathophysiology and then focuses on the animal investigations and clinical trials of various therapeutic modalities targeting PPARγ for hepatic fibrosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL (2011) Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 6:425–456
Thabut D, Shah V (2010) Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol 53(5):976–980
Lim YS, Kim WR (2008) The global impact of hepatic fibrosis and end-stage liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 12(4):733–746 vii
Anty R, Lemoine M (2011) Liver fibrogenesis and metabolic factors. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 35(Suppl 1):S10–S20
Romero-Gomez M, Del Mar Viloria M, Andrade RJ, Salmeron J, Diago M, Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, Corpas R, Cruz M, Grande L, Vazquez L, Munoz-De-Rueda P, Lopez-Serrano P, Gila A, Gutierrez ML, Perez C, Ruiz-Extremera A, Suarez E, Castillo J (2005) Insulin resistance impairs sustained response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Gastroenterology 128(3):636–641
Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, Bandara P, Byth K, Kench JG, McCaughan GW, George J (2003) Insulin resistance is associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and fibrosis progression. Gastroenterology 125(6):1695–1704
Bugianesi E, Marchesini G, Gentilcore E, Cua IH, Vanni E, Rizzetto M, George J (2006) Fibrosis in genotype 3 chronic hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Hepatology 44(6):1648–1655
De Minicis S, Svegliati-Baroni G (2011) Fibrogenesis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(2):179–187
Mann J, Mann DA (2009) Transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(7–8):497–512
Wagner M, Zollner G, Trauner M (2011) Nuclear receptors in liver disease. Hepatology 53(3):1023–1034
Sugii S, Evans RM (2011) Epigenetic codes of PPARgamma in metabolic disease. FEBS Lett 585(13):2121–2128
Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang YX (2004) PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med 10(4):355–361
Itoh T, Fairall L, Amin K, Inaba Y, Szanto A, Balint BL, Nagy L, Yamamoto K, Schwabe JW (2008) Structural basis for the activation of PPARgamma by oxidized fatty acids. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(9):924–931
Pascual G, Glass CK (2006) Nuclear receptors versus inflammation: mechanisms of transrepression. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17(8):321–327
Bonfield TL, Thomassen MJ, Farver CF, Abraham S, Koloze MT, Zhang X, Mosser DM, Culver DA (2008) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma regulates the expression of alveolar macrophage macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 181(1):235–242
Bassaganya-Riera J, Song R, Roberts PC, Hontecillas R (2010) PPAR-gamma activation as an anti-inflammatory therapy for respiratory virus infections. Viral Immunol 23(4):343–352
Suzuki S, Sasaki S, Morita H, Oki Y, Turiya D, Ito T, Misawa H, Ishizuka K, Nakamura H (2010) The role of the amino-terminal domain in the interaction of unliganded peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-2 with nuclear receptor co-repressor. J Mol Endocrinol 45(3):133–145
Floyd ZE, Stephens JM (2002) Interferon-gamma-mediated activation and ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation of PPARgamma in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 277(6):4062–4068
Hosooka T, Noguchi T, Kotani K, Nakamura T, Sakaue H, Inoue H, Ogawa W, Tobimatsu K, Takazawa K, Sakai M, Matsuki Y, Hiramatsu R, Yasuda T, Lazar MA, Yamanashi Y, Kasuga M (2008) Dok1 mediates high-fat diet-induced adipocyte hypertrophy and obesity through modulation of PPAR-gamma phosphorylation. Nat Med 14(2):188–193
Doshi LS, Brahma MK, Bahirat UA, Dixit AV, Nemmani KV (2010) Discovery and development of selective PPAR gamma modulators as safe and effective antidiabetic agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19(4):489–512
Abbott BD (2009) Review of the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha (PPAR alpha), beta (PPAR beta), and gamma (PPAR gamma) in rodent and human development. Reprod Toxicol 27(3–4):246–257
Semple RK, Chatterjee VK, O’Rahilly S (2006) PPAR gamma and human metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 116(3):581–589
Hao GH, Niu XL, Gao DF, Wei J, Wang NP (2008) Agonists at PPAR-gamma suppress angiotensin II-induced production of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and extracellular matrix in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Br J Pharmacol 153(7):1409–1419
Ren Y, Sun C, Sun Y, Tan H, Wu Y, Cui B, Wu Z (2009) PPAR gamma protects cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress and apoptosis via Bcl-2 upregulation. Vascul Pharmacol 51(2–3):169–174
Alleva DG, Johnson EB, Lio FM, Boehme SA, Conlon PJ, Crowe PD (2002) Regulation of murine macrophage proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines by ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: counter-regulatory activity by IFN-gamma. J Leukoc Biol 71(4):677–685
Bouhlel MA, Derudas B, Rigamonti E, Dievart R, Brozek J, Haulon S, Zawadzki C, Jude B, Torpier G, Marx N, Staels B, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G (2007) PPARgamma activation primes human monocytes into alternative M2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties. Cell Metab 6(2):137–143
Bouhlel MA, Staels B, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G (2008) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors—from active regulators of macrophage biology to pharmacological targets in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med 263(1):28–42
Milam JE, Keshamouni VG, Phan SH, Hu B, Gangireddy SR, Hogaboam CM, Standiford TJ, Thannickal VJ, Reddy RC (2008) PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit profibrotic phenotypes in human lung fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294(5):L891–L901
Dionne S, Levy E, Levesque D, Seidman EG (2010) PPARgamma ligand 15-deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 sensitizes human colon carcinoma cells to TWEAK-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Res 30(1):157–166
Yang X, Downes M, Yu RT, Bookout AL, He W, Straume M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (2006) Nuclear receptor expression links the circadian clock to metabolism. Cell 126(4):801–810
Botolin S, McCabe LR (2006) Inhibition of PPARgamma prevents type I diabetic bone marrow adiposity but not bone loss. J Cell Physiol 209(3):967–976
Wasmuth HE, Tacke F, Trautwein C (2010) Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis 30(3):215–225
Higashi N, Sato M, Kojima N, Irie T, Kawamura K, Mabuchi A, Senoo H (2005) Vitamin A storage in hepatic stellate cells in the regenerating rat liver: with special reference to zonal heterogeneity. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 286(2):899–907
Friedman SL (2008) Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 88(1):125–172
Miyahara T, Schrum L, Rippe R, Xiong S, Yee HF Jr, Motomura K, Anania FA, Willson TM, Tsukamoto H (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and hepatic stellate cell activation. J Biol Chem 275(46):35715–35722
Sun K, Wang Q, Huang XH (2006) PPAR gamma inhibits growth of rat hepatic stellate cells and TGF beta-induced connective tissue growth factor expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27(6):715–723
Higashi Y, Holder K, Delafontaine P (2010) Thiazolidinediones up-regulate insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor via a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-independent pathway. J Biol Chem 285(47):36361–36368
Hazra S, Xiong S, Wang J, Rippe RA, Krishna V, Chatterjee K, Tsukamoto H (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma induces a phenotypic switch from activated to quiescent hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 279(12):11392–11401
Galli A, Crabb DW, Ceni E, Salzano R, Mello T, Svegliati-Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Trozzi L, Surrenti C, Casini A (2002) Antidiabetic thiazolidinediones inhibit collagen synthesis and hepatic stellate cell activation in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology 122(7):1924–1940
Yavrom S, Chen L, Xiong S, Wang J, Rippe RA, Tsukamoto H (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma suppresses proximal alpha1(I) collagen promoter via inhibition of p300-facilitated NF-I binding to DNA in hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 280(49):40650–40659
Fiorucci S, Rizzo G, Antonelli E, Renga B, Mencarelli A, Riccardi L, Morelli A, Pruzanski M, Pellicciari R (2005) Cross-talk between farnesoid-X-receptor (FXR) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma contributes to the antifibrotic activity of FXR ligands in rodent models of liver cirrhosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315(1):58–68
Renga B, Mencarelli A, Migliorati M, Cipriani S, D’Amore C, Distrutti E, Fiorucci S (2011) SHP-dependent and -independent induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by the bile acid sensor farnesoid X receptor counter-regulates the pro-inflammatory phenotype of liver myofibroblasts. Inflamm Res 60(6):577–587
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Rizzo G, Renga B, Mencarelli A, Riccardi L, Orlandi S, Pellicciari R, Morelli A (2004) The nuclear receptor SHP mediates inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by FXR and protects against liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 127(5):1497–1512
Fiorucci S, Rizzo G, Antonelli E, Renga B, Mencarelli A, Riccardi L, Orlandi S, Pruzanski M, Morelli A, Pellicciari R (2005) A farnesoid x receptor-small heterodimer partner regulatory cascade modulates tissue metalloproteinase inhibitor-1 and matrix metalloprotease expression in hepatic stellate cells and promotes resolution of liver fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314(2):584–595
Fickert P, Fuchsbichler A, Moustafa T, Wagner M, Zollner G, Halilbasic E, Stoger U, Arrese M, Pizarro M, Solis N, Carrasco G, Caligiuri A, Sombetzki M, Reisinger E, Tsybrovskyy O, Zatloukal K, Denk H, Jaeschke H, Pinzani M, Trauner M (2009) Farnesoid X receptor critically determines the fibrotic response in mice but is expressed to a low extent in human hepatic stellate cells and periductal myofibroblasts. Am J Pathol 175(6):2392–2405
Sauvant P, Cansell M, Atgie C (2011) Vitamin A and lipid metabolism: relationship between hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and adipocytes. J Physiol Biochem 67(3):487–496
Tsukamoto H, She H, Hazra S, Cheng J, Miyahara T (2006) Anti-adipogenic regulation underlies hepatic stellate cell transdifferentiation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21(Suppl 3):S102–S105
De Minicis S, Seki E, Uchinami H, Kluwe J, Zhang Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF (2007) Gene expression profiles during hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Gastroenterology 132(5):1937–1946
She H, Xiong S, Hazra S, Tsukamoto H (2005) Adipogenic transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 280(6):4959–4967
Guimaraes EL, Franceschi MF, Andrade CM, Guaragna RM, Borojevic R, Margis R, Bernard EA, Guma FC (2007) Hepatic stellate cell line modulates lipogenic transcription factors. Liver Int 27(9):1255–1264
Kim N, Choi S, Lim C, Lee H, Oh J (2010) Albumin mediates PPAR-gamma or C/EBP-alpha-induced phenotypic changes in pancreatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):640–644
Bedoucha M, Atzpodien E, Boelsterli UA (2001) Diabetic KKAy mice exhibit increased hepatic PPARgamma1 gene expression and develop hepatic steatosis upon chronic treatment with antidiabetic thiazolidinediones. J Hepatol 35(1):17–23
Yu S, Matsusue K, Kashireddy P, Cao WQ, Yeldandi V, Yeldandi AV, Rao MS, Gonzalez FJ, Reddy JK (2003) Adipocyte-specific gene expression and adipogenic steatosis in the mouse liver due to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 (PPARgamma1) overexpression. J Biol Chem 278(1):498–505
Tsukamoto H (2005) Fat paradox in liver disease. Keio J Med 54(4):190–192
Kluwe J, Wongsiriroj N, Troeger JS, Gwak GY, Dapito DH, Pradere JP, Jiang H, Siddiqi M, Piantedosi R, O’Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Schwabe RF (2011) Absence of hepatic stellate cell retinoid lipid droplets does not enhance hepatic fibrosis but decreases hepatic carcinogenesis. Gut 60(9):1260–1268
Mann J, Oakley F, Akiboye F, Elsharkawy A, Thorne AW, Mann DA (2007) Regulation of myofibroblast transdifferentiation by DNA methylation and MeCP2: implications for wound healing and fibrogenesis. Cell Death Differ 14(2):275–285
Mann J, Chu DC, Maxwell A, Oakley F, Zhu NL, Tsukamoto H, Mann DA (2010) MeCP2 controls an epigenetic pathway that promotes myofibroblast transdifferentiation and fibrosis. Gastroenterology 138(2):705–714
Zhu NL, Wang J, Tsukamoto H (2010) The Necdin-Wnt pathway causes epigenetic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma repression in hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 285(40):30463–30471
Zhu NL, Asahina K, Wang J, Ueno A, Lazaro R, Miyaoka Y, Miyajima A, Tsukamoto H (2012) Hepatic stellate cell-derived delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) protein in liver regeneration. J Biol Chem 287(13):10355–10367
Smas CM, Kachinskas D, Liu CM, Xie X, Dircks LK, Sul HS (1998) Transcriptional control of the pref-1 gene in 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. Sequence requirement for differentiation-dependent suppression. J Biol Chem 273(48):31751–31758
Fritz D, Stefanovic B (2007) RNA-binding protein RBMS3 is expressed in activated hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis and increases expression of transcription factor Prx1. J Mol Biol 371(3):585–595
Venugopal SK, Jiang J, Kim TH, Li Y, Wang SS, Torok NJ, Wu J, Zern MA (2010) Liver fibrosis causes downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298(1):G101–G106
Lindquist JN, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B, Brenner DA (2004) Regulation of alpha1(I) collagen messenger RNA decay by interactions with alphaCP at the 3′-untranslated region. J Biol Chem 279(22):23822–23829
Yang MD, Chiang YM, Higashiyama R, Asahina K, Mann DA, Mann J, Wang CC, Tsukamoto H (2012) Rosmarinic acid and baicalin epigenetically derepress peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gamma in hepatic stellate cells for their antifibrotic effect. Hepatology 55(4):1271–1281
Yang L, Chan CC, Kwon OS, Liu S, McGhee J, Stimpson SA, Chen LZ, Harrington WW, Symonds WT, Rockey DC (2006) Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291(5):G902–G911
Wu CW, Chu ES, Lam CN, Cheng AS, Lee CW, Wong VW, Sung JJ, Yu J (2010) PPARgamma is essential for protection against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gene Ther 17(6):790–798
Yu J, Zhang S, Chu ES, Go MY, Lau RH, Zhao J, Wu CW, Tong L, Poon TC, Sung JJ (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma reverses hepatic nutritional fibrosis in mice and suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42(6):948–957
Nan YM, Han F, Kong LB, Zhao SX, Wang RQ, Wu WJ, Yu J (2011) Adenovirus-mediated peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma overexpression prevents nutritional fibrotic steatohepatitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol 46(3):358–369
Wang Z, Xu JP, Zheng YC, Chen W, Sun YW, Wu ZY, Luo M (2011) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits hepatic fibrosis in rats. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 10(1):64–71
Li F, Wang JY (2009) Targeted delivery of drugs for liver fibrosis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 6(5):531–541
Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem 270(22):12953–12956
Faich GA, Moseley RH (2001) Troglitazone (Rezulin) and hepatic injury. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 10(6):537–547
Marra F, Efsen E, Romanelli RG, Caligiuri A, Pastacaldi S, Batignani G, Bonacchi A, Caporale R, Laffi G, Pinzani M, Gentilini P (2000) Ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulate profibrogenic and proinflammatory actions in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 119(2):466–478
Marra F, DeFranco R, Robino G, Novo E, Efsen E, Pastacaldi S, Zamara E, Vercelli A, Lottini B, Spirli C, Strazzabosco M, Pinzani M, Parola M (2005) Thiazolidinedione treatment inhibits bile duct proliferation and fibrosis in a rat model of chronic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol 11(32):4931–4938
Zeisberg M, Yang C, Martino M, Duncan MB, Rieder F, Tanjore H, Kalluri R (2007) Fibroblasts derive from hepatocytes in liver fibrosis via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 282(32):23337–23347
Omenetti A, Porrello A, Jung Y, Yang L, Popov Y, Choi SS, Witek RP, Alpini G, Venter J, Vandongen HM, Syn WK, Baroni GS, Benedetti A, Schuppan D, Diehl AM (2008) Hedgehog signaling regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during biliary fibrosis in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 118(10):3331–3342
Taura K, Miura K, Iwaisako K, Osterreicher CH, Kodama Y, Penz-Osterreicher M, Brenner DA (2010) Hepatocytes do not undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 51(3):1027–1036
Scholten D, Osterreicher CH, Scholten A, Iwaisako K, Gu G, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T (2010) Genetic labeling does not detect epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cholangiocytes in liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 139(3):987–998
Chu AS, Diaz R, Hui JJ, Yanger K, Zong Y, Alpini G, Stanger BZ, Wells RG (2011) Lineage tracing demonstrates no evidence of cholangiocyte epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in murine models of hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 53(5):1685–1695
Tahan V, Eren F, Avsar E, Yavuz D, Yuksel M, Emekli E, Imeryuz N, Celikel C, Uzun H, Haklar G, Tozun N (2007) Rosiglitazone attenuates liver inflammation in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 52(12):3465–3472
Chen H, He YW, Liu WQ, Zhang JH (2008) Rosiglitazone prevents murine hepatic fibrosis induced by Schistosoma japonicum. World J Gastroenterol 14(18):2905–2911
Nan YM, Fu N, Wu WJ, Liang BL, Wang RQ, Zhao SX, Zhao JM, Yu J (2009) Rosiglitazone prevents nutritional fibrosis and steatohepatitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol 44(3):358–365
Gupte AA, Liu JZ, Ren Y, Minze LJ, Wiles JR, Collins AR, Lyon CJ, Pratico D, Finegold MJ, Wong ST, Webb P, Baxter JD, Moore DD, Hsueh WA (2010) Rosiglitazone attenuates age- and diet-associated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in male low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Hepatology 52(6):2001–2011
Bruck R, Weiss S, Aeed H, Pines M, Halpern Z, Zvibel I (2009) Additive inhibitory effect of experimentally induced hepatic cirrhosis by agonists of peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma and retinoic acid receptor. Dig Dis Sci 54(2):292–299
Shen Z, Liang X, Rogers CQ, Rideout D, You M (2010) Involvement of adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK signaling in the protective action of rosiglitazone against alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298(3):G364–G374
Garcia-Ruiz I, Rodriguez-Juan C, Diaz-Sanjuan T, Martinez MA, Munoz-Yague T, Solis-Herruzo JA (2007) Effects of rosiglitazone on the liver histology and mitochondrial function in ob/ob mice. Hepatology 46(2):414–423
Kon K, Ikejima K, Hirose M, Yoshikawa M, Enomoto N, Kitamura T, Takei Y, Sato N (2002) Pioglitazone prevents early-phase hepatic fibrogenesis caused by carbon tetrachloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291(1):55–61
Yuan GJ, Zhang ML, Gong ZJ (2004) Effects of PPARg agonist pioglitazone on rat hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 10(7):1047–1051
Enomoto N, Takei Y, Hirose M, Konno A, Shibuya T, Matsuyama S, Suzuki S, Kitamura KI, Sato N (2003) Prevention of ethanol-induced liver injury in rats by an agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, pioglitazone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306(3):846–854
Enomoto N, Takei Y, Yamashima S, Ikejima K, Kitamura T, Sato N (2005) Protective effect of pioglitazone against endotoxin-induced liver injury through prevention of Kupffer cell sensitization. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(12 Suppl):216S–219S
Ohata M, Suzuki H, Sakamoto K, Hashimoto K, Nakajima H, Yamauchi M, Hokkyo K, Yamada H, Toda G (2004) Pioglitazone prevents acute liver injury induced by ethanol and lipopolysaccharide through the suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28(8 Suppl Proceedings):139S–144S
Tomita K, Azuma T, Kitamura N, Nishida J, Tamiya G, Oka A, Inokuchi S, Nishimura T, Suematsu M, Ishii H (2004) Pioglitazone prevents alcohol-induced fatty liver in rats through up-regulation of c-Met. Gastroenterology 126(3):873–885
Kawaguchi K, Sakaida I, Tsuchiya M, Omori K, Takami T, Okita K (2004) Pioglitazone prevents hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and enzyme-altered lesions in rat liver cirrhosis induced by a choline-deficient l-amino acid-defined diet. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315(1):187–195
Uto H, Nakanishi C, Ido A, Hasuike S, Kusumoto K, Abe H, Numata M, Nagata K, Hayashi K, Tsubouchi H (2005) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist, pioglitazone, inhibits fat accumulation and fibrosis in the livers of rats fed a choline-deficient, l-amino acid-defined diet. Hepatol Res 32(4):235–242
Collino M, Aragno M, Castiglia S, Miglio G, Tomasinelli C, Boccuzzi G, Thiemermann C, Fantozzi R (2010) Pioglitazone improves lipid and insulin levels in overweight rats on a high cholesterol and fructose diet by decreasing hepatic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 160(8):1892–1902
Leclercq IA, Sempoux C, Starkel P, Horsmans Y (2006) Limited therapeutic efficacy of pioglitazone on progression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut 55(7):1020–1029
Da Silva Morais A, Abarca-Quinones J, Horsmans Y, Starkel P, Leclercq IA (2007) Peroxisome proliferated-activated receptor gamma ligand, Pioglitazone, does not prevent hepatic fibrosis in mice. Int J Mol Med 19(1):105–112
Bae MA, Rhee SD, Jung WH, Ahn JH, Song BJ, Cheon HG (2010) Selective inhibition of activated stellate cells and protection from carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats by a new PPARgamma agonist KR62776. Arch Pharm Res 33(3):433–442
Yang L, Stimpson SA, Chen L, Wallace Harrington W, Rockey DC (2010) Effectiveness of the PPARgamma agonist, GW570, in liver fibrosis. Inflamm Res 59(12):1061–1071
Ahn JH, Shin MS, Jung SH, Kang SK, Kim KR, Rhee SD, Jung WH, Yang SD, Kim SJ, Woo JR, Lee JH, Cheon HG, Kim SS (2006) Indenone derivatives: a novel template for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) agonists. J Med Chem 49(15):4781–4784
Zheng S, Chen A (2004) Activation of PPARgamma is required for curcumin to induce apoptosis and to inhibit the expression of extracellular matrix genes in hepatic stellate cells in vitro. Biochem J 384(Pt 1):149–157
Zheng S, Chen A (2007) Disruption of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by curcumin induces gene expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in rat hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(1):G113–G123
Fu Y, Zheng S, Lin J, Ryerse J, Chen A (2008) Curcumin protects the rat liver from CCl4-caused injury and fibrogenesis by attenuating oxidative stress and suppressing inflammation. Mol Pharmacol 73(2):399–409
Argo CK, Caldwell SH (2009) Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis 13(4):511–531
Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA (2010) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology 51(5):1820–1832
Cohen JC, Horton JD, Hobbs HH (2011) Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science 332(6037):1519–1523
Caldwell SH, Hespenheide EE, Redick JA, Iezzoni JC, Battle EH, Sheppard BL (2001) A pilot study of a thiazolidinedione, troglitazone, in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 96(2):519–525
Argo CK, Iezzoni JC, Al-Osaimi AM, Caldwell SH (2009) Thiazolidinediones for the treatment in NASH: sustained benefit after drug discontinuation? J Clin Gastroenterol 43(6):565–568
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Wehmeier KR, Sponseller CA, Hampton K, Bacon BR (2003) Interim results of a pilot study demonstrating the early effects of the PPAR-gamma ligand rosiglitazone on insulin sensitivity, aminotransferases, hepatic steatosis and body weight in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 38(4):434–440
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Wehmeier KR, Oliver D, Bacon BR (2003) Improved nonalcoholic steatohepatitis after 48 weeks of treatment with the PPAR-gamma ligand rosiglitazone. Hepatology 38(4):1008–1017
Idilman R, Mizrak D, Corapcioglu D, Bektas M, Doganay B, Sayki M, Coban S, Erden E, Soykan I, Emral R, Uysal AR, Ozden A (2008) Clinical trial: insulin-sensitizing agents may reduce consequences of insulin resistance in individuals with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28(2):200–208
Caldwell SH, Patrie JT, Brunt EM, Redick JA, Davis CA, Park SH, Neuschwander-Tetri BA (2007) The effects of 48 weeks of rosiglitazone on hepatocyte mitochondria in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 46(4):1101–1107
Wang CH, Leung CH, Liu SC, Chung CH (2006) Safety and effectiveness of rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. J Formos Med Assoc 105(9):743–752
Saryusz-Wolska M, Szymanska-Garbacz E, Jablkowski M, Bialkowska J, Pawlowski M, Kwiecinska E, Omulecka A, Borkowska A, Ignaczak A, Loba J, Czupryniak L (2011) Rosiglitazone treatment in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pol Arch Med Wewn 121(3):61–66
Ratziu V, Giral P, Jacqueminet S, Charlotte F, Hartemann-Heurtier A, Serfaty L, Podevin P, Lacorte JM, Bernhardt C, Bruckert E, Grimaldi A, Poynard T (2008) Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled fatty liver improvement with rosiglitazone therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 135(1):100–110
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41(6):1313–1321
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Bernhardt C, Giral P, Halbron M, Lenaour G, Hartmann-Heurtier A, Bruckert E, Poynard T (2010) Long-term efficacy of rosiglitazone in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: results of the fatty liver improvement by rosiglitazone therapy (FLIRT 2) extension trial. Hepatology 51(2):445–453
Omer Z, Cetinkalp S, Akyildiz M, Yilmaz F, Batur Y, Yilmaz C, Akarca U (2010) Efficacy of insulin-sensitizing agents in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(1):18–23
Torres DM, Jones FJ, Shaw JC, Williams CD, Ward JA, Harrison SA (2011) Rosiglitazone versus rosiglitazone and metformin versus rosiglitazone and losartan in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in humans: a 12-month randomized, prospective, open- label trial. Hepatology 54(5):1631–1639
Shadid S, Jensen MD (2003) Effect of pioglitazone on biochemical indices of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in upper body obesity. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 1(5):384–387
Promrat K, Lutchman G, Uwaifo GI, Freedman RJ, Soza A, Heller T, Doo E, Ghany M, Premkumar A, Park Y, Liang TJ, Yanovski JA, Kleiner DE, Hoofnagle JH (2004) A pilot study of pioglitazone treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 39(1):188–196
Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, Darland C, Finch J, Hardies J, Balas B, Gastaldelli A, Tio F, Pulcini J, Berria R, Ma JZ, Dwivedi S, Havranek R, Fincke C, DeFronzo R, Bannayan GA, Schenker S, Cusi K (2006) A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 355(22):2297–2307
Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, Lawson A, Ryder SD, Spendlove I, Austin AS, Freeman JG, Morgan L, Webber J (2008) Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 135(4):1176–1184
Lutchman G, Modi A, Kleiner DE, Promrat K, Heller T, Ghany M, Borg B, Loomba R, Liang TJ, Premkumar A, Hoofnagle JH (2007) The effects of discontinuing pioglitazone in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 46(2):424–429
Lutchman G, Promrat K, Kleiner DE, Heller T, Ghany MG, Yanovski JA, Liang TJ, Hoofnagle JH (2006) Changes in serum adipokine levels during pioglitazone treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: relationship to histological improvement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4(8):1048–1052
Gastaldelli A, Harrison SA, Belfort-Aguilar R, Hardies LJ, Balas B, Schenker S, Cusi K (2009) Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 50(4):1087–1093
Urtasun R, Conde de la Rosa L, Nieto N (2008) Oxidative and nitrosative stress and fibrogenic response. Clin Liver Dis 12(4):769–790, viii
Sanyal AJ, Mofrad PS, Contos MJ, Sargeant C, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Shiffman ML, Clore J, Mills AS (2004) A pilot study of vitamin E versus vitamin E and pioglitazone for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2(12):1107–1115
Chalasani NP, Sanyal AJ, Kowdley KV, Robuck PR, Hoofnagle J, Kleiner DE, Unalp A, Tonascia J (2009) Pioglitazone versus vitamin E versus placebo for the treatment of non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: PIVENS trial design. Contemp Clin Trials 30(1):88–96
Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, McCullough A, Diehl AM, Bass NM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Lavine JE, Tonascia J, Unalp A, Van Natta M, Clark J, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Hoofnagle JH, Robuck PR (2010) Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 362(18):1675–1685
McHutchison J, Goodman Z, Patel K, Makhlouf H, Rodriguez-Torres M, Shiffman M, Rockey D, Husa P, Chuang WL, Levine R, Jonas M, Theodore D, Brigandi R, Webster A, Schultz M, Watson H, Stancil B, Gardner S (2010) Farglitazar lacks antifibrotic activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology 138(4):1365–1373
Iredale JP (2007) Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ. J Clin Invest 117(3):539–548
Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G (2010) A meta-analysis of randomized trials for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 52(1):79–104
Mahady SE, Webster AC, Walker S, Sanyal A, George J (2011) The role of thiazolidinediones in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis—a systematic review and meta analysis. J Hepatol 55(6):1383–1390
Rakoski MO, Singal AG, Rogers MA, Conjeevaram H (2010) Meta-analysis: insulin sensitizers for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 32(10):1211–1221
Boettcher E, Csako G, Pucino F, Wesley R, Loomba R (2012) Meta-analysis: pioglitazone improves liver histology and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35(1):66–75
Gavrilova O, Haluzik M, Matsusue K, Cutson JJ, Johnson L, Dietz KR, Nicol CJ, Vinson C, Gonzalez FJ, Reitman ML (2003) Liver peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma contributes to hepatic steatosis, triglyceride clearance, and regulation of body fat mass. J Biol Chem 278(36):34268–34276
Gluud C, Brok J, Gong Y, Koretz RL (2007) Hepatology may have problems with putative surrogate outcome measures. J Hepatol 46(4):734–742
Hannivoort RA, Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL (2012) Genomics and proteomics in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5(1):1
Constantinou MA, Theocharis SE, Mikros E (2007) Application of metabonomics on an experimental model of fibrosis and cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 218(1):11–19
Verreth W, De Keyzer D, Pelat M, Verhamme P, Ganame J, Bielicki JK, Mertens A, Quarck R, Benhabiles N, Marguerie G, Mackness B, Mackness M, Ninio E, Herregods MC, Balligand JL, Holvoet P (2004) Weight-loss-associated induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma correlate with reduced atherosclerosis and improved cardiovascular function in obese insulin-resistant mice. Circulation 110(20):3259–3269
Gastaldi G, Russell A, Golay A, Giacobino JP, Habicht F, Barthassat V, Muzzin P, Bobbioni-Harsch E (2007) Upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator gene (PGC1A) during weight loss is related to insulin sensitivity but not to energy expenditure. Diabetologia 50(11):2348–2355
Tolman KG (2011) The safety of thiazolidinediones. Expert Opin Drug Saf 10(3):419–428
Blind E, Dunder K, de Graeff PA, Abadie E (2011) Rosiglitazone: a European regulatory perspective. Diabetologia 54(2):213–218
Woodcock J, Sharfstein JM, Hamburg M (2010) Regulatory action on rosiglitazone by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. N Engl J Med 363(16):1489–1491
Marcy TR, Britton ML, Blevins SM (2004) Second-generation thiazolidinediones and hepatotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother 38(9):1419–1423
Lewis JD, Ferrara A, Peng T, Hedderson M, Bilker WB, Quesenberry CP Jr, Vaughn DJ, Nessel L, Selby J, Strom BL (2011) Risk of bladder cancer among diabetic patients treated with pioglitazone: interim report of a longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Care 34(4):916–922
Piccinni C, Motola D, Marchesini G, Poluzzi E (2011) Assessing the association of pioglitazone use and bladder cancer through drug adverse event reporting. Diabetes Care 34(6):1369–1371
Tian L, Zhou J, Casimiro MC, Liang B, Ojeifo JO, Wang M, Hyslop T, Wang C, Pestell RG (2009) Activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma mutant promotes tumor growth in vivo by enhancing angiogenesis. Cancer Res 69(24):9236–9244
Schadinger SE, Bucher NL, Schreiber BM, Farmer SR (2005) PPARgamma2 regulates lipogenesis and lipid accumulation in steatotic hepatocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288(6):E1195–E1205
Wobser H, Dorn C, Weiss TS, Amann T, Bollheimer C, Buttner R, Scholmerich J, Hellerbrand C (2009) Lipid accumulation in hepatocytes induces fibrogenic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Cell Res 19(8):996–1005
Sharma C, Pradeep A, Pestell RG, Rana B (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation modulates cyclin D1 transcription via beta-catenin-independent and cAMP-response element-binding protein-dependent pathways in mouse hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 279(17):16927–16938
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Bostrom P, Laznik D, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Bluher M, Griffin PR, Spiegelman BM (2010) Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5. Nature 466(7305):451–456
Choi JH, Banks AS, Kamenecka TM, Busby SA, Chalmers MJ, Kumar N, Kuruvilla DS, Shin Y, He Y, Bruning JB, Marciano DP, Cameron MD, Laznik D, Jurczak MJ, Schurer SC, Vidovic D, Shulman GI, Spiegelman BM, Griffin PR (2011) Antidiabetic actions of a non-agonist PPARgamma ligand blocking Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation. Nature 477(7365):477–481
Steiling H, Muhlbauer M, Bataille F, Scholmerich J, Werner S, Hellerbrand C (2004) Activated hepatic stellate cells express keratinocyte growth factor in chronic liver disease. Am J Pathol 165(4):1233–1241
Tailleux A, Wouters K, Staels B (2012) Roles of PPARs in NAFLD: Potential therapeutic targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821(5):809–818
Ip E, Farrell G, Hall P, Robertson G, Leclercq I (2004) Administration of the potent PPARalpha agonist, Wy-14,643, reverses nutritional fibrosis and steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 39(5):1286–1296
Stienstra R, Mandard S, Patsouris D, Maass C, Kersten S, Muller M (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha protects against obesity-induced hepatic inflammation. Endocrinology 148(6):2753–2763
Kondo K, Sugioka T, Tsukada K, Aizawa M, Takizawa M, Shimizu K, Morimoto M, Suematsu M, Goda N (2010) Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonist, improves hepatic microcirculatory patency and oxygen availability in a high-fat-diet-induced fatty liver in mice. Adv Exp Med Biol 662:77–82
Abdelmegeed MA, Yoo SH, Henderson LE, Gonzalez FJ, Woodcroft KJ, Song BJ (2011) PPARalpha expression protects male mice from high fat-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver. J Nutr 141(4):603–610
Fernandez-Miranda C, Perez-Carreras M, Colina F, Lopez-Alonso G, Vargas C, Solis-Herruzo JA (2008) A pilot trial of fenofibrate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis 40(3):200–205
Thulin P, Rafter I, Stockling K, Tomkiewicz C, Norjavaara E, Aggerbeck M, Hellmold H, Ehrenborg E, Andersson U, Cotgreave I, Glinghammar B (2008) PPARalpha regulates the hepatotoxic biomarker alanine aminotransferase (ALT1) gene expression in human hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 231(1):1–9
Sanwald-Ducray P, Liogier D’ardhuy X, Jamois C, Banken L (2010) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of aleglitazar in patients with type 2 diabetes: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study. Clin Pharmacol Ther 88(2):197–203
Hansen BC, Tigno XT, Benardeau A, Meyer M, Sebokova E, Mizrahi J (2011) Effects of aleglitazar, a balanced dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma agonist on glycemic and lipid parameters in a primate model of the metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:7
Lindblom P, Berg AL, Zhang H, Westerberg R, Tugwood J, Lundgren H, Marcusson-Stahl M, Sjogren N, Blomgren B, Ohman P, Skanberg I, Evans J, Hellmold H (2012) Tesaglitazar, a dual PPAR-alpha/gamma agonist, hamster carcinogenicity, investigative animal and clinical studies. Toxicol Pathol 40(1):18–32
Acknowledgments
We thank the financial support from the Open Project Program of National First-Class Key Discipline for Traditional Chinese Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (2011ZYX4-008), Doctoral Discipline Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20103237110010), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30873424), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (BK2008456), Project for Supporting Jiangsu Provincial Talents in Six Fields (2009112), Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (ysxk-2010), and “Eleven-Five” National Science and Technology Supporting Program (2008BAI51B02). We are grateful to Dr. Shile Huang, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, USA, for his critical reading and reversion of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Kong, D., Lu, Y. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ as a therapeutic target for hepatic fibrosis: from bench to bedside. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 259–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1046-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1046-x