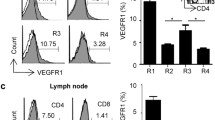
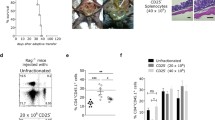
Abstract
Suppression of chronic intestinal inflammation by different subtypes of T cells has been described in recent years. In particular, naturally arising CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and IL-10-producing regulatory T cell type 1 CD4+ T lymphocytes have been implicated in the regulation of intestinal inflammation. Here we focus on the ability of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells to suppress innate and T-cell responses and discuss implications for immunoregulation in human inflammatory bowel disease. Besides the modulation of lymphoproliferation, a role for CD4+CD25+ T cells in down-modulation of innate immune responses is emerging and the immunoregulatory activities of regulatory T cells in vivo may be mediated via effects on dendritic cells. Considering the extraordinary regenerative potential of the intestinal mucosa, the ability to impede pathogenic T-cell responses by active regulation might be of particular therapeutic benefit for the treatment of chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Tr1:
-
regulatory T cell type 1
- TR:
-
regulatory T cell
- IBD:
-
inflammatory bowel disease
- DC:
-
dendritic cell
References
Aithal GP, Craggs A, Day CP et al (2001) Role of polymorphisms in the interleukin-10 gene in determining disease susceptibility and phenotype in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 46:1520
Annacker O, Pimenta-Araujo R, Burlen-Defranoux O et al (2001) CD25+ CD4+ T cells regulate the expansion of peripheral CD4 T cells through the production of IL-10. J Immunol 166:3008
Apostolou I, Sarukhan A, Klein L et al (2002) Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for antigen. Nat Immunol 3:756
Asseman C, Mauze S, Leach MW et al (1999) An essential role for interleukin 10 in the function of regulatory T cells that inhibit intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 190:995
Asseman C, Read S, Powrie F (2003) Colitogenic Th1 cells are present in the antigen-experienced T cell pool in normal mice: control by CD4+ regulatory T cells and IL-10. J Immunol 171:971
Banz A, Peixoto A, Pontoux C et al (2003) A unique subpopulation of CD4+ regulatory T cells controls wasting disease, IL-10 secretion and T cell homeostasis. Eur J Immunol 33:2419
Barrat FJ, Cua DJ, Boonstra A et al (2002) In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4(+) T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J Exp Med 195:603
Belkaid Y (2003) The role of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in Leishmania infection. Expert Opin Biol Ther 3:875
Bennett CL, Brunkow ME, Ramsdell F et al (2001) A rare polyadenylation signal mutation of the FOXP3 gene (AAUAAA→AAUGAA) leads to the IPEX syndrome. Immunogenetics 53:435
Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F et al (2001) The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 27:20
Berg DJ, Davidson N, Kuhn R et al (1996) Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4(+) TH1-like responses. J Clin Invest 98:1010
Bode U, Wonigeit K, Pabst R et al (1997) The fate of activated T cells migrating through the body: rescue from apoptosis in the tissue of origin. Eur J Immunol 27:2087
Bruder D, Probst-Kepper M, Westendorf AM et al (2004) Neuropilin-1: a surface marker of regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol 34:623
Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA et al (2001) Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet 27:68
Cao D, van Vollenhoven R, Klareskog L et al (2004) CD25brightCD4+ regulatory T cells are enriched in inflamed joints of patients with chronic rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R335
Cederbom L, Hall H, Ivars F (2000) CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells down-regulate co-stimulatory molecules on antigen-presenting cells. Eur J Immunol 30:1538
Coombes JL, Robinson NJ, Maloy KJ et al (2005) Regulatory T cells and intestinal homeostasis. Immunol Rev 204:184
Cozzo C, Larkin J III, Caton AJ (2003) Self-peptides drive the peripheral expansion of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 171:5678
Davidson NJ, Leach MW, Fort MM et al (1996) T helper cell 1-type CD4+ T cells, but not B cells, mediate colitis in interleukin 10-deficient mice. J Exp Med 184:241
Donnelly RP, Dickensheets H, Finbloom DS (1999) The interleukin-10 signal transduction pathway and regulation of gene expression in mononuclear phagocytes. J Interferon Cytokine Res 19:563
Ermann J, Szanya V, Ford GS et al (2001) CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells facilitate the induction of T cell anergy. J Immunol 167:4271
Fahlen L, Read S, Gorelik L et al (2005) T cells that cannot respond to TGF-{beta} escape control by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 201:737
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM et al (2005) Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity 22:329
Fort MM, Leach MW, Rennick DM (1998) A role for NK cells as regulators of CD4+ T cells in a transfer model of colitis. J Immunol 161:3256
Foussat A, Cottrez F, Brun V et al (2003) A comparative study between T regulatory type 1 and CD4+CD25+ T cells in the control of inflammation. J Immunol 171:5018
Gavin MA, Clarke SR, Negrou E et al (2002) Homeostasis and anergy of CD4(+)CD25(+) suppressor T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 3:33
Gebbers JO, Kennel I, Laissue JA (1992) Lymphoid follicles of the human large bowel mucosa: structure and function. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 76:126
Gershon RK (1975) A disquisition on suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev 26:170
Gorelik L, Flavell RA (2000) Abrogation of TGFbeta signaling in T cells leads to spontaneous T cell differentiation and autoimmune disease. Immunity 12:171
Gorelik L, Flavell RA (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol 2:46
Graca L, Cobbold SP, Waldmann H (2002) Identification of regulatory T cells in tolerated allografts. J Exp Med 195:1641
Groux H, O’Garra A, Bigler M et al (1997) A CD4+ T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature 389:737
Herfarth H, Scholmerich J (2002) IL-10 therapy in Crohn’s disease: at the crossroads. Treatment of Crohn’s disease with the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 10. Gut 50:146
Hori S, Carvalho TL, Demengeot J (2002) CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells suppress CD4+ T cell-mediated pulmonary hyperinflammation driven by Pneumocystis carinii in immunodeficient mice. Eur J Immunol 32:1282
Hori S, Haury M, Coutinho A et al (2002) Specificity requirements for selection and effector functions of CD25+4+ regulatory T cells in anti-myelin basic protein T cell receptor transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8213
Itano AA, Jenkins MK (2003) Antigen presentation to naive CD4 T cells in the lymph node. Nat Immunol 4:733
Ito S, Ansari P, Sakatsume M et al (1999) Interleukin-10 inhibits expression of both interferon alpha- and interferon gamma-induced genes by suppressing tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT1. Blood 93:1456
Itoh M, Takahashi T, Sakaguchi N et al (1999) Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunologic self-tolerance. J Immunol 162:5317
Jordan MS, Boesteanu A, Reed AJ et al (2001) Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat Immunol 2:301
Khattri R, Kasprowicz D, Cox T et al (2001) The amount of scurfin protein determines peripheral T cell number and responsiveness. J Immunol 167:6312
Kim JD, Choi BK, Bae JS et al (2003) Cloning and characterization of GITR ligand. Genes Immun 4:564
Kitani A, Fuss I, Nakamura K et al (2003) Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-producing regulatory T cells induce Smad-mediated interleukin 10 secretion that facilitates coordinated immunoregulatory activity and amelioration of TGF-beta1-mediated fibrosis. J Exp Med 198:1179
Kobayashi M, Kweon MN, Kuwata H et al (2003) Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 111:1297
Kullberg MC, Jankovic D, Gorelick PL et al (2002) Bacteria-triggered CD4(+) T regulatory cells suppress Helicobacter hepaticus-induced colitis. J Exp Med 196:505
Kullberg MC, Ward JM, Gorelick PL et al (1998) Helicobacter hepaticus triggers colitis in specific-pathogen-free interleukin-10 (IL-10)-deficient mice through an IL-12- and gamma interferon-dependent mechanism. Infect Immun 66:5157
Lehmann J, Huehn J, de la Rosa M et al (2002) Expression of the integrin alpha Ebeta 7 identifies unique subsets of CD25+ as well as CD25− regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13031
Leithauser F, Trobonjaca Z, Moller P et al (2001) Clustering of colonic lamina propria CD4(+) T cells to subepithelial dendritic cell aggregates precedes the development of colitis in a murine adoptive transfer model. Lab Invest 81:1339
Liu H, Hu B, Xu D et al (2003) CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells cure murine colitis: the role of IL-10, TGF-beta, and CTLA4. J Immunol 171:5012
Lohr J, Knoechel B, Jiang S et al (2003) The inhibitory function of B7 costimulators in T cell responses to foreign and self-antigens. Nat Immunol 4:664
Macpherson AJ, Harris NL (2004) Interactions between commensal intestinal bacteria and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 4:478
Makita S, Kanai T, Oshima S et al (2004) CD4+CD25 bright T cells in human intestinal lamina propria as regulatory cells. J Immunol 173:3119
Malmstrom V, Shipton D, Singh B et al (2001) CD134L expression on dendritic cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes drives colitis in T cell-restored SCID mice. J Immunol 166:6972
Maloy KJ, Antonelli LR, Lefevre M et al (2005) Cure of innate intestinal immune pathology by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Immunol Lett 97:189
Maloy KJ, Powrie F (2001) Regulatory T cells in the control of immune pathology. Nat Immunol 2:816
Maloy KJ, Salaun L, Cahill R et al (2003) CD4+CD25+ T(R) cells suppress innate immune pathology through cytokine-dependent mechanisms. J Exp Med 197:111
McGuirk P, Mills KH (2002) Pathogen-specific regulatory T cells provoke a shift in the Th1/Th2 paradigm in immunity to infectious diseases. Trends Immunol 23:450
McHugh RS, Whitters MJ, Piccirillo CA et al (2002) CD4(+)CD25(+) immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Immunity 16:311
Melgar S, Yeung MM, Bas A et al (2003) Over-expression of interleukin 10 in mucosal T cells of patients with active ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 134:127
Mellor AL, Munn DH (2004) IDO expression by dendritic cells: tolerance and tryptophan catabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 4:762
Meresse B, Rutgeerts P, Malchow H et al (2002) Low ileal interleukin 10 concentrations are predictive of endoscopic recurrence in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gut 50:25
Mizoguchi A, Mizoguchi E, Smith RN et al (1997) Suppressive role of B cells in chronic colitis of T cell receptor alpha mutant mice. J Exp Med 186:1749
Mizoguchi E, Mizoguchi A, Preffer FI et al (2000) Regulatory role of mature B cells in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunol 12:597
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL et al (2001) Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 19:683
Mottet C, Uhlig HH, Powrie F (2003) Cutting edge: cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 170:3939
Nakamura K, Kitani A, Fuss I et al (2004) TGF-beta1 plays an important role in the mechanism of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell activity in both humans and mice. J Immunol 172:834
O’Garra A, Barrat FJ (2003) In vitro generation of IL-10-producing regulatory CD4+ T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by Th1- and Th2-inducing cytokines. Immunol Lett 85:135
O’Garra A, Vieira PL, Vieira P et al (2004) IL-10-producing and naturally occurring CD4+ Tregs: limiting collateral damage. J Clin Invest 114:1372
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2004) Toll-dependent control mechanisms of CD4 T cell activation. Immunity 21:733
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll-like receptors: balancing host resistance with immune tolerance. Curr Opin Immunol 15:677
Piccirillo CA, Letterio JJ, Thornton AM et al (2002) CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells can mediate suppressor function in the absence of transforming growth factor beta1 production and responsiveness. J Exp Med 196:237
Piccirillo CA, Shevach EM (2001) Cutting edge: control of CD8+ T cell activation by CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory cells. J Immunol 167:1137
Poussier P, Ning T, Banerjee D et al (2002) A unique subset of self-specific intraintestinal T cells maintains gut integrity. J Exp Med 195:1491
Raghavan S, Fredriksson M, Svennerholm AM et al (2003) Absence of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is associated with a loss of regulation leading to increased pathology in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Clin Exp Immunol 132:393
Read S, Malmstrom V, Powrie F (2000) Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 192:295
Roncarolo MG, Bacchetta R, Bordignon C et al (2001) Type 1 T regulatory cells. Immunol Rev 182:68
Sakaguchi S (2004) Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 22:531
Serra P, Amrani A, Yamanouchi J et al (2003) CD40 ligation releases immature dendritic cells from the control of regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells. Immunity 19:877
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Takahashi T et al (2002) Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nat Immunol 3:135
Shull MM, Ormsby I, Kier AB et al (1992) Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 359:693
Singh B, Read S, Asseman C et al (2001) Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev 182:190
Takeda K, Clausen BE, Kaisho T et al (1999) Enhanced Th1 activity and development of chronic enterocolitis in mice devoid of Stat3 in macrophages and neutrophils. Immunity 10:39
Thornton AM, Shevach EM (1998) CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med 188:287
Tivol EA, Borriello F, Schweitzer AN et al (1995) Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity 3:541
Tone M, Tone Y, Adams E et al (2003) From the cover: mouse glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor ligand is costimulatory for T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15059
Uhlig HH, Mottet C, Powrie F (2004) Homing of intestinal immune cells. Novartis Found Symp 263:179–188; discussion 188–192, 211
Uraushihara K, Kanai T, Ko K et al (2003) Regulation of murine inflammatory bowel disease by CD25+ and CD25− CD4+ glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family-related gene+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 171:708
van der Linde K, Boor PP, Sandkuijl LA et al (2003) A Gly15Arg mutation in the interleukin-10 gene reduces secretion of interleukin-10 in Crohn disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 38:611
Van Montfrans C, Hooijberg E, Rodriguez Pena MS et al (2002) Generation of regulatory gut-homing human T lymphocytes using ex vivo interleukin 10 gene transfer. Gastroenterology 123:1877
Van Montfrans C, Rodriguez Pena MS, Pronk I et al (2002) Prevention of colitis by interleukin 10-transduced T lymphocytes in the SCID mice transfer model. Gastroenterology 123:1865
Vieira PL, Christensen JR, Minaee S et al (2004) IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells do not express Foxp3 but have comparable regulatory function to naturally occurring CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 172:5986
Walker LS, Chodos A, Eggena M et al (2003) Antigen-dependent proliferation of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo. J Exp Med 198:249
Waterhouse P, Penninger JM, Timms E et al (1995) Lymphoproliferative disorders with early lethality in mice deficient in CTLA-4. Science 270:985
Wei B, Velazquez P, Turovskaya O et al (2005) Mesenteric B cells centrally inhibit CD4+ T cell colitis through interaction with regulatory T cell subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:2010
Weiner HL (2001) Induction and mechanism of action of transforming growth factor-beta-secreting Th3 regulatory cells. Immunol Rev 182:207
Wildin RS, Ramsdell F, Peake J et al (2001) X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat Genet 27:18
Wildin RS, Smyk-Pearson S, Filipovich AH (2002) Clinical and molecular features of the immunodysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X linked (IPEX) syndrome. J Med Genet 39:537
Yoshida M, Watanabe T, Usui T et al (2001) CD4 T cells monospecific to ovalbumin produced by Escherichia coli can induce colitis upon transfer to BALB/c and SCID mice. Int Immunol 13:1561
Acknowledgements
H.U. is supported by a University of Leipzig grant (F1-49) and F.P. by the Wellcome Trust. We would like to thank Kevin Maloy and Ana Izcue for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhlig, H.H., Powrie, F. The role of mucosal T lymphocytes in regulating intestinal inflammation. Springer Semin Immun 27, 167–180 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-005-0206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-005-0206-6