Abstract
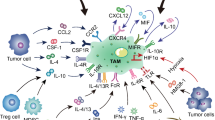
Inflammation is now a well-recognized hallmark of cancer progression. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are one of the major inflammatory cells that infiltrate murine and human tumors. While epidemiological studies indicate a clear correlation between TAM density and poor prognosis in a number of human cancers, transgenic studies and transcriptome profiling of TAMs in mice have established their crucial role in cancer progression. In fact, TAMs affect diverse aspects of cancer progression including tumor cell growth and survival, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and immunoregulation. New evidences have extended the repertoire of these cells to other tumor promoting activities like interactions with cancer stem cells, response to chemotherapy, and tumor relapse. These findings have triggered efforts to target TAMs and their associated molecules to modulate tumor progression. In particular, “re-education” to activate their anti-tumor potential or elimination of tumor promoting TAMs are strategies undergoing preclinical and clinical evaluation. Proof-of-principle studies indicate that TAM-centered therapeutic strategies may contribute to cancer therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357(9255):539–545
Mantovani A, Romero P, Palucka AK, Marincola FM (2008) Tumour immunity: effector response to tumour and role of the microenvironment. Lancet 371(9614):771–783. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60241-XS01406736(08)60241-X
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Price JF, Belch JF, Meade TW, Mehta Z (2012) Effect of daily aspirin on risk of cancer metastasis: a study of incident cancers during randomised controlled trials. Lancet 379(9826):1591–1601. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60209-8
Rothwell PM, Price JF, Fowkes FG, Zanchetti A, Roncaglioni MC, Tognoni G, Lee R, Belch JF, Wilson M, Mehta Z, Meade TW (2012) Short-term effects of daily aspirin on cancer incidence, mortality, and non-vascular death: analysis of the time course of risks and benefits in 51 randomised controlled trials. Lancet 379(9826):1602–1612. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61720-0
Chan AT, Cook NR (2012) Are we ready to recommend aspirin for cancer prevention? Lancet 379(9826):1569–1571. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61654-1
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454(7203):436–444
Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A (2005) Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell 7(3):211–217
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420(6917):860–867
Zhang QW, Liu L, Gong CY, Shi HS, Zeng YH, Wang XZ, Zhao YW, Wei YQ (2012) Prognostic significance of tumor-associated macrophages in solid tumor: a meta-analysis of the literature. PLoS One 7(12):e50946. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050946PONE-D-12-17794
Bingle L, Brown NJ, Lewis CE (2002) The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. The Journal of Pathology 196(3):254–265. doi:10.1002/path.1027
Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han G, Nayar T, Delaney A, Jones SJ, Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, Bast MA, Rosenwald A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Rimsza LM, Campo E, Delabie J, Braziel RM, Cook JR, Tubbs RR, Jaffe ES, Lenz G, Connors JM, Staudt LM, Chan WC, Gascoyne RD (2010) Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin's lymphoma. The New England Journal of Medicine 362(10):875–885
Biswas SK, Mantovani A (2010) Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nature Immunology 11(10):889–896. doi:10.1038/ni.1937
Gordon S, Taylor PR (2005) Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nature Reviews Immunology 5(12):953–964
Adams DO, Hamilton TA (1984) The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annual Review of Immunology 2:283–318. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N, Gordon S (1992) Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor activity: a marker of alternative immunologic macrophage activation. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 176(1):287–292
Loke P, Nair MG, Parkinson J, Guiliano D, Blaxter M, Allen JE (2002) IL-4 dependent alternatively-activated macrophages have a distinctive in vivo gene expression phenotype. BMC Immunology 3:7
Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM (2000) M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Journal of Immunology 164(12):6166–6173
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A (2002) Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends in Immunology 23(11):549–555
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M (2004) The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends in Immunology 25(12):677–686
Mosser DM, Edwards JP (2008) Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nature Reviews Immunology 8(12):958–969
Murray PJ, Wynn TA (2011) Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nature Reviews Immunology 11(11):723–737. doi:10.1038/nri3073
Gerber JS, Mosser DM (2001) Reversing lipopolysaccharide toxicity by ligating the macrophage Fc gamma receptors. Journal of Immunology 166(11):6861–6868
Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M, Mantovani A (2006) Transcriptional profiling of the human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new molecules and patterns of gene expression. Journal of Immunology 177(10):7303–7311
Strassmann G, Patil-Koota V, Finkelman F, Fong M, Kambayashi T (1994) Evidence for the involvement of interleukin 10 in the differential deactivation of murine peritoneal macrophages by prostaglandin E2. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 180(6):2365–2370
Biswas SK, Mantovani A (2012) Orchestration of metabolism by macrophages. Cell Metabolism 15(4):432–437. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.11.013
Biswas SK, Lopez-Collazo E (2009) Endotoxin tolerance: new mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance. Trends in Immunology 30(10):475–487
Biswas SK, Sica A, Lewis CE (2008) Plasticity of macrophage function during tumor progression: regulation by distinct molecular mechanisms. Journal of Immunology 180(4):2011–2017
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 117(1):175–184
Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G, Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G, Geissmann F (2007) Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science 317(5838):666–670
Sica A, Mantovani A (2012) Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 122(3):787–795. doi:10.1172/JCI5964359643
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, Samokhvalov IM, Merad M (2010) Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 330(6005):841–845. doi:10.1126/science.1194637science.1194637
Schulz C, Gomez Perdiguero E, Chorro L, Szabo-Rogers H, Cagnard N, Kierdorf K, Prinz M, Wu B, Jacobsen SE, Pollard JW, Frampton J, Liu KJ, Geissmann F (2012) A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science 336(6077):86–90. doi:10.1126/science.1219179science.1219179
Yona S, Kim KW, Wolf Y, Mildner A, Varol D, Breker M, Strauss-Ayali D, Viukov S, Guilliams M, Misharin A, Hume DA, Perlman H, Malissen B, Zelzer E, Jung S (2013) Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity 38(1):79–91. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.12.001S1074-7613(12)00548-1
Rivollier A, He J, Kole A, Valatas V, Kelsall BL (2012) Inflammation switches the differentiation program of Ly6Chi monocytes from antiinflammatory macrophages to inflammatory dendritic cells in the colon. Journal of Experimental Medicine 209(1):139–155. doi:10.1084/jem.20101387
Varol C, Vallon-Eberhard A, Elinav E, Aychek T, Shapira Y, Luche H, Fehling HJ, Hardt WD, Shakhar G, Jung S (2009) Intestinal lamina propria dendritic cell subsets have different origin and functions. Immunity 31(3):502–512. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.025S1074-7613(09)00362-8
Swirski FK, Libby P, Aikawa E, Alcaide P, Luscinskas FW, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2007) Ly-6Chi monocytes dominate hypercholesterolemia-associated monocytosis and give rise to macrophages in atheromata. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 117(1):195–205. doi:10.1172/JCI29950
Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton A, Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A, Berger C, Ryan RJ, Iwamoto Y, Marinelli B, Gorbatov R, Forghani R, Novobrantseva TI, Koteliansky V, Figueiredo JL, Chen JW, Anderson DG, Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2012) Origins of tumor-associated macrophages and neutrophils. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109(7):2491–2496. doi:10.1073/pnas.11137441091113744109
Jenkins SJ, Ruckerl D, Cook PC, Jones LH, Finkelman FD, van Rooijen N, MacDonald AS, Allen JE (2011) Local macrophage proliferation, rather than recruitment from the blood, is a signature of TH2 inflammation. Science 332(6035):1284–1288. doi:10.1126/science.1204351
Davies LC, Rosas M, Smith PJ, Fraser DJ, Jones SA, Taylor PR (2011) A quantifiable proliferative burst of tissue macrophages restores homeostatic macrophage populations after acute inflammation. European Journal of Immunology 41(8):2155–2164. doi:10.1002/eji.201141817
Frankenberger M, Hofer TP, Marei A, Dayyani F, Schewe S, Strasser C, Aldraihim A, Stanzel F, Lang R, Hoffmann R, Prazeres da Costa O, Buch T, Ziegler-Heitbrock L (2012) Transcript profiling of CD16-positive monocytes reveals a unique molecular fingerprint. European Journal of Immunology 42(4):957–974. doi:10.1002/eji.201141907
Chitu V, Stanley ER (2006) Colony-stimulating factor-1 in immunity and inflammation. Current Opinion in Immunology 18(1):39–48. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2005.11.006
Hamilton JA, Achuthan A (2013) Colony stimulating factors and myeloid cell biology in health and disease. Trends in Immunology 34(2):81–89. doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.08.006S1471-4906(12)00144-5
Lin H, Lee E, Hestir K, Leo C, Huang M, Bosch E, Halenbeck R, Wu G, Zhou A, Behrens D, Hollenbaugh D, Linnemann T, Qin M, Wong J, Chu K, Doberstein SK, Williams LT (2008) Discovery of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of the extracellular proteome. Science 320(5877):807–811. doi:10.1126/science.1154370320/5877/807
DeNardo DG, Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E, Ruffell B, Shiao SL, Madden SF, Gallagher WM, Wadhwani N, Keil SD, Junaid SA, Rugo HS, Hwang ES, Jirstrom K, West BL, Coussens LM (2011) Leukocyte complexity predicts breast cancer survival and functionally regulates response to chemotherapy. Cancer Discovery 1(1):54–67. doi:10.1158/2159-8274.CD-10-00282159-8274.CD-10-0028
Mantovani A, Ming WJ, Balotta C, Abdeljalil B, Bottazzi B (1986) Origin and regulation of tumor-associated macrophages: the role of tumor-derived chemotactic factor. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 865(1):59–67
Aharinejad S, Sioud M, Lucas T, Abraham D (2007) Target validation using RNA interference in solid tumors. Methods in Molecular Biology 361:227–238
Lin EY, Nguyen AV, Russell RG, Pollard JW (2001) Colony-stimulating factor 1 promotes progression of mammary tumors to malignancy. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 193(6):727–740
Bottazzi B, Walter S, Govoni D, Colotta F, Mantovani A (1992) Monocyte chemotactic cytokine gene transfer modulates macrophage infiltration, growth, and susceptibility to IL-2 therapy of a murine melanoma. Journal of Immunology 148(4):1280–1285
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang J, Campion LR, Kaiser EA, Snyder LA, Pollard JW (7355) CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature 475:222–225. doi:10.1038/nature10138nature10138
Bottazzi B, Nobili N, Mantovani A (1990) Expression of c-fos proto-oncogene in tumor-associated macrophages. Journal of Immunology 144(12):4878–4882
Ko JS, Rayman P, Ireland J, Swaidani S, Li G, Bunting KD, Rini B, Finke JH, Cohen PA (2010) Direct and differential suppression of myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets by sunitinib is compartmentally constrained. Cancer Research 70(9):3526–3536. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-32780008-5472.CAN-09-3278
Sawanobori Y, Ueha S, Kurachi M, Shimaoka T, Talmadge JE, Abe J, Shono Y, Kitabatake M, Kakimi K, Mukaida N, Matsushima K (2008) Chemokine-mediated rapid turnover of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Blood 111(12):5457–5466. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-01-136895blood-2008-01-136895
Movahedi K, Laoui D, Gysemans C, Baeten M, Stange G, Van den Bossche J, Mack M, Pipeleers D, In't Veld P, De Baetselier P, Van Ginderachter JA (2010) Different tumor microenvironments contain functionally distinct subsets of macrophages derived from Ly6C(high) monocytes. Cancer Research 70:5728–5739. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4672
Mazzieri R, Pucci F, Moi D, Zonari E, Ranghetti A, Berti A, Politi LS, Gentner B, Brown JL, Naldini L, De Palma M (2011) Targeting the ANG2/TIE2 axis inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by impairing angiogenesis and disabling rebounds of proangiogenic myeloid cells. Cancer Cell 19(4):512–526. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.005S1535-6108(11)00081-X
Venneri MA, De Palma M, Ponzoni M, Pucci F, Scielzo C, Zonari E, Mazzieri R, Doglioni C, Naldini L (2007) Identification of proangiogenic TIE2-expressing monocytes (TEMs) in human peripheral blood and cancer. Blood 109(12):5276–5285. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-053504
Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton A, Ryan R, Pucci F, Sio SW, Kuswanto W, Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A, Iwamoto Y, Kohler R, Marinelli B, Gorbatov R, Wojtkiewicz G, Panizzi P, Mino-Kenudson M, Forghani R, Figueiredo JL, Chen JW, Xavier R, Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2013) Angiotensin II drives the production of tumor-promoting macrophages. Immunity. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.015
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21(3):309–322. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.022S1535-6108(12)00082-7
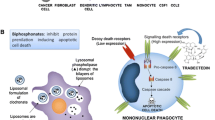
Zeisberger SM, Odermatt B, Marty C, Zehnder-Fjallman AH, Ballmer-Hofer K, Schwendener RA (2006) Clodronate-liposome-mediated depletion of tumour-associated macrophages: a new and highly effective antiangiogenic therapy approach. British Journal of Cancer 95(3):272–281
Karin M, Lawrence T, Nizet V (2006) Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell 124(4):823–835
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF, Karin M (2004) IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 118(3):285–296
Maeda S, Kamata H, Luo JL, Leffert H, Karin M (2005) IKKbeta couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 121(7):977–990
Grivennikov SI, Wang K, Mucida D, Stewart CA, Schnabl B, Jauch D, Taniguchi K, Yu GY, Osterreicher CH, Hung KE, Datz C, Feng Y, Fearon ER, Oukka M, Tessarollo L, Coppola V, Yarovinsky F, Cheroutre H, Eckmann L, Trinchieri G, Karin M (2012) Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature 491(7423):254–258. doi:10.1038/nature11465nature11465
Lin EY, Li JF, Gnatovskiy L, Deng Y, Zhu L, Grzesik DA, Qian H, Xue XN, Pollard JW (2006) Macrophages regulate the angiogenic switch in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Research 66(23):11238–11246
Fantin A, Vieira JM, Gestri G, Denti L, Schwarz Q, Prykhozhij S, Peri F, Wilson SW, Ruhrberg C (2010) Tissue macrophages act as cellular chaperones for vascular anastomosis downstream of VEGF-mediated endothelial tip cell induction. Blood 116:829–840
De Palma M, Venneri MA, Galli R, Sergi Sergi L, Politi LS, Sampaolesi M, Naldini L (2005) Tie2 identifies a hematopoietic lineage of proangiogenic monocytes required for tumor vessel formation and a mesenchymal population of pericyte progenitors. Cancer Cell 8(3):211–226
Pucci F, Venneri MA, Biziato D, Nonis A, Moi D, Sica A, Di Serio C, Naldini L, De Palma M (2009) A distinguishing gene signature shared by tumor-infiltrating Tie2-expressing monocytes, blood “resident” monocytes, and embryonic macrophages suggests common functions and developmental relationships. Blood 114(4):901–914
Coffelt SB, Tal AO, Scholz A, De Palma M, Patel S, Urbich C, Biswas SK, Murdoch C, Plate KH, Reiss Y, Lewis CE (2010) Angiopoietin-2 regulates gene expression in TIE2-expressing monocytes and augments their inherent proangiogenic functions. Cancer Research 70(13):5270–5280. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-00120008-5472.CAN-10-0012
Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Stockl J, Kalt R, Ullrich R, Caucig C, Kriehuber E, Nagy K, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D (2002) Tumor-associated macrophages express lymphatic endothelial growth factors and are related to peritumoral lymphangiogenesis. American Journal of Pathology 161(3):947–956
Condeelis J, Pollard JW (2006) Macrophages: obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell 124(2):263–266
Andreu P, Johansson M, Affara NI, Pucci F, Tan T, Junankar S, Korets L, Lam J, Tawfik D, DeNardo DG, Naldini L, de Visser KE, De Palma M, Coussens LM (2010) FcRgamma activation regulates inflammation-associated squamous carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 17(2):121–134
Gocheva V, Wang HW, Gadea BB, Shree T, Hunter KE, Garfall AL, Berman T, Joyce JA (2010) IL-4 induces cathepsin protease activity in tumor-associated macrophages to promote cancer growth and invasion. Genes & Development 24(3):241–255. doi:10.1101/gad.1874010gad.1874010
Qian BZ, Pollard JW (2010) Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 141(1):39–51
Biswas SK, Gangi L, Paul S, Schioppa T, Saccani A, Sironi M, Bottazzi B, Doni A, Vincenzo B, Pasqualini F, Vago L, Nebuloni M, Mantovani A, Sica A (2006) A distinct and unique transcriptional program expressed by tumor-associated macrophages (defective NF-kappaB and enhanced IRF-3/STAT1 activation). Blood 107(5):2112–2122
Sica A, Saccani A, Bottazzi B, Polentarutti N, Vecchi A, van Damme J, Mantovani A (2000) Autocrine production of IL-10 mediates defective IL-12 production and NF-kappa B activation in tumor-associated macrophages. Journal of Immunology 164(2):762–767
Hagemann T, Lawrence T, McNeish I, Charles KA, Kulbe H, Thompson RG, Robinson SC, Balkwill FR (2008) “Re-educating” tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-kappaB. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(6):1261–1268
Torroella-Kouri M, Ma X, Perry G, Ivanova M, Cejas PJ, Owen JL, Iragavarapu-Charyulu V, Lopez DM (2005) Diminished expression of transcription factors nuclear factor kappaB and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein underlies a novel tumor evasion mechanism affecting macrophages of mammary tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Research 65(22):10578–10584
DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N, Coussens LM (2009) CD4(+) T cells regulate pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell 16(2):91–102
Kuang DM, Zhao Q, Peng C, Xu J, Zhang JP, Wu C, Zheng L (2009) Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma foster immune privilege and disease progression through PD-L1. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 206(6):1327–1337
Rius J, Guma M, Schachtrup C, Akassoglou K, Zinkernagel AS, Nizet V, Johnson RS, Haddad GG, Karin M (2008) NF-kappaB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1alpha. Nature 453(7196):807–811
Rodriguez-Prados JC, Traves PG, Cuenca J, Rico D, Aragones J, Martin-Sanz P, Cascante M, Bosca L (2010) Substrate fate in activated macrophages: a comparison between innate, classic, and alternative activation. Journal of Immunology 185(1):605–614
Sica A, Bronte V (2007) Altered macrophage differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 117(5):1155–1166
Srivastava MK, Sinha P, Clements VK, Rodriguez P, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (2010) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T-cell activation by depleting cystine and cysteine. Cancer Research 70(1):68–77. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2587
Paulus P, Stanley ER, Schafer R, Abraham D, Aharinejad S (2006) Colony-stimulating factor-1 antibody reverses chemoresistance in human MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Research 66(8):4349–4356. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3523
Shree T, Olson OC, Elie BT, Kester JC, Garfall AL, Simpson K, Bell-McGuinn KM, Zabor EC, Brogi E, Joyce JA (2011) Macrophages and cathepsin proteases blunt chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer. Genes & Development 25(23):2465–2479. doi:10.1101/gad.180331.11125/23/2465
Nakasone ES, Askautrud HA, Kees T, Park JH, Plaks V, Ewald AJ, Fein M, Rasch MG, Tan YX, Qiu J, Park J, Sinha P, Bissell MJ, Frengen E, Werb Z, Egeblad M (2012) Imaging tumor-stroma interactions during chemotherapy reveals contributions of the microenvironment to resistance. Cancer Cell 21(4):488–503. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.017S1535-6108(12)00079-7
Rolny C, Mazzone M, Tugues S, Laoui D, Johansson I, Coulon C, Squadrito ML, Segura I, Li X, Knevels E, Costa S, Vinckier S, Dresselaer T, Akerud P, De Mol M, Salomaki H, Phillipson M, Wyns S, Larsson E, Buysschaert I, Botling J, Himmelreich U, Van Ginderachter JA, De Palma M, Dewerchin M, Claesson-Welsh L, Carmeliet P (2011) HRG inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization and vessel normalization through downregulation of PlGF. Cancer Cell 19(1):31–44. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2010.11.009S1535-6108(10)00474-5
Stockmann C, Doedens A, Weidemann A, Zhang N, Takeda N, Greenberg JI, Cheresh DA, Johnson RS (2008) Deletion of vascular endothelial growth factor in myeloid cells accelerates tumorigenesis. Nature 456(7223):814–818. doi:10.1038/nature07445nature07445
Bruchard M, Mignot G, Derangere V, Chalmin F, Chevriaux A, Vegran F, Boireau W, Simon B, Ryffel B, Connat JL, Kanellopoulos J, Martin F, Rebe C, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F (2013) Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome and promotes tumor growth. Nature Medicine 19(1):57–64. doi:10.1038/nm.2999nm.2999
Kioi M, Vogel H, Schultz G, Hoffman RM, Harsh GR, Brown JM (2010) Inhibition of vasculogenesis, but not angiogenesis, prevents the recurrence of glioblastoma after irradiation in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 120(3):694–705. doi:10.1172/JCI4028340283
Welford AF, Biziato D, Coffelt SB, Nucera S, Fisher M, Pucci F, Di Serio C, Naldini L, De Palma M, Tozer GM, Lewis CE (2011) TIE2-expressing macrophages limit the therapeutic efficacy of the vascular-disrupting agent combretastatin A4 phosphate in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 121(5):1969–1973. doi:10.1172/JCI4456244562
Mantovani A (2012) MSCs, macrophages, and cancer: a dangerous menage-a-trois. Cell Stem Cell 11(6):730–732. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.11.016S1934-5909(12)00650-9
Ren G, Zhao X, Wang Y, Zhang X, Chen X, Xu C, Yuan ZR, Roberts AI, Zhang L, Zheng B, Wen T, Han Y, Rabson AB, Tischfield JA, Shao C, Shi Y (2012) CCR2-dependent recruitment of macrophages by tumor-educated mesenchymal stromal cells promotes tumor development and is mimicked by TNFalpha. Cell Stem Cell 11(6):812–824. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.08.013S1934-5909(12)00538-3
Malanchi I, Santamaria-Martinez A, Susanto E, Peng H, Lehr HA, Delaloye JF, Huelsken J (2012) Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature 481(7379):85–89. doi:10.1038/nature10694nature10694
Jinushi M, Chiba S, Yoshiyama H, Masutomi K, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Yagita H, Takaoka A, Tahara H (2011) Tumor-associated macrophages regulate tumorigenicity and anticancer drug responses of cancer stem/initiating cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108(30):12425–12430. doi:10.1073/pnas.11066451081106645108
Mitchem JB, Brennan DJ, Knolhoff BL, Belt BA, Zhu Y, Sanford DE, Belaygorod L, Carpenter D, Collins L, Piwnica-Worms D, Hewitt S, Udupi GM, Gallagher WM, Wegner C, West BL, Wang-Gillam A, Goedegebuure P, Linehan DC, Denardo DG (2013) Targeting tumor-infiltrating macrophages decreases tumor-initiating cells, relieves immunosuppression, and improves chemotherapeutic responses. Cancer Research 73(3):1128–1141. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2731
Medrek C, Ponten F, Jirstrom K, Leandersson K (2012) The presence of tumor associated macrophages in tumor stroma as a prognostic marker for breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 12:306. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-3061471-2407-12-306
Tan KL, Scott DW, Hong F, Kahl BS, Fisher RI, Bartlett NL, Advani RH, Buckstein R, Rimsza LM, Connors JM, Steidl C, Gordon LI, Horning SJ, Gascoyne RD (2012) Tumor-associated macrophages predict inferior outcomes in classic Hodgkin lymphoma: a correlative study from the E2496 Intergroup trial. Blood 120(16):3280–3287. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-421057blood-2012-04-421057
Lee Y, Chittezhath M, Andre V, Zhao H, Poidinger M, Biondi A, D'Amico G, Biswas SK (2012) Protumoral role of monocytes in human B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: involvement of the chemokine CXCL10. Blood 119(1):227–237. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-06-357442blood-2011-06-357442
Negus RP, Stamp GW, Hadley J, Balkwill FR (1997) Quantitative assessment of the leukocyte infiltrate in ovarian cancer and its relationship to the expression of C–C chemokines. American Journal of Pathology 150(5):1723–1734
Sica A, Saccani A, Bottazzi B, Bernasconi S, Allavena P, Gaetano B, Fei F, LaRosa G, Scotton C, Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2000) Defective expression of the monocyte chemotactic protein-1 receptor CCR2 in macrophages associated with human ovarian carcinoma. Journal of Immunology 164(2):733–738
Hagemann T, Wilson J, Burke F, Kulbe H, Li NF, Pluddemann A, Charles K, Gordon S, Balkwill FR (2006) Ovarian cancer cells polarize macrophages toward a tumor-associated phenotype. Journal of Immunology 176(8):5023–5032
Hagemann T, Wilson J, Kulbe H, Li NF, Leinster DA, Charles K, Klemm F, Pukrop T, Binder C, Balkwill FR (2005) Macrophages induce invasiveness of epithelial cancer cells via NF-kappa B and JNK. Journal of Immunology 175(2):1197–1205
Charles KA, Kulbe H, Soper R, Escorcio-Correia M, Lawrence T, Schultheis A, Chakravarty P, Thompson RG, Kollias G, Smyth JF, Balkwill FR, Hagemann T (2009) The tumor-promoting actions of TNF-alpha involve TNFR1 and IL-17 in ovarian cancer in mice and humans. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 119(10):3011–3023
Zhou J, Ding T, Pan W, Zhu LY, Li L, Zheng L (2009) Increased intratumoral regulatory T cells are related to intratumoral macrophages and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. International Journal of Cancer 125(7):1640–1648. doi:10.1002/ijc.24556
Scholl SM, Pallud C, Beuvon F, Hacene K, Stanley ER, Rohrschneider L, Tang R, Pouillart P, Lidereau R (1994) Anti-colony-stimulating factor-1 antibody staining in primary breast adenocarcinomas correlates with marked inflammatory cell infiltrates and prognosis. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 86(2):120–126
Ueno T, Toi M, Saji H, Muta M, Bando H, Kuroi K, Koike M, Inadera H, Matsushima K (2000) Significance of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophage recruitment, angiogenesis, and survival in human breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 6(8):3282–3289
Ojalvo LS, King W, Cox D, Pollard JW (2009) High-density gene expression analysis of tumor-associated macrophages from mouse mammary tumors. American Journal of Pathology 174(3):1048–1064
Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, Yao H, Su F, Anderson KS, Liu Q, Ewen ME, Yao X, Song E (2011) CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer Cell 19(4):541–555. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.006S1535-6108(11)00082-1
Shimura S, Yang G, Ebara S, Wheeler TM, Frolov A, Thompson TC (2000) Reduced infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages in human prostate cancer: association with cancer progression. Cancer Research 60(20):5857–5861
Nonomura N, Takayama H, Nakayama M, Nakai Y, Kawashima A, Mukai M, Nagahara A, Aozasa K, Tsujimura A (2011) Infiltration of tumour-associated macrophages in prostate biopsy specimens is predictive of disease progression after hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. BJU International 107(12):1918–1922. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09804.x
Mizutani K, Sud S, McGregor NA, Martinovski G, Rice BT, Craig MJ, Varsos ZS, Roca H, Pienta KJ (2009) The chemokine CCL2 increases prostate tumor growth and bone metastasis through macrophage and osteoclast recruitment. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 11(11):1235–1242
Kim SW, Kim JS, Papadopoulos J, Choi HJ, He J, Maya M, Langley RR, Fan D, Fidler IJ, Kim SJ (2011) Consistent interactions between tumor cell IL-6 and macrophage TNF-alpha enhance the growth of human prostate cancer cells in the bone of nude mouse. International Immunopharmacology 11(7):862–872. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.004S1567-5769(11)00024-5
Eruslanov E, Stoffs T, Kim WJ, Daurkin I, Gilbert SM, Su LM, Vieweg J, Daaka Y, Kusmartsev S (2013) Expansion of CCR8+ inflammatory myeloid cells in cancer patients with urothelial and renal carcinomas. Clinical Cancer Research. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2091
Ong SM, Tan YC, Beretta O, Jiang D, Yeap WH, Tai JJ, Wong WC, Yang H, Schwarz H, Lim KH, Koh PK, Ling KL, Wong SC (2012) Macrophages in human colorectal cancer are pro-inflammatory and prime T cells towards an anti-tumour type-1 inflammatory response. European Journal of Immunology 42(1):89–100. doi:10.1002/eji.201141825
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, Berger A, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Pages F, Galon J (2011) Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Research 71(4):1263–1271. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-29070008-5472.CAN-10-2907
Ahn GO, Tseng D, Liao CH, Dorie MJ, Czechowicz A, Brown JM (2010) Inhibition of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) enhances tumor response to radiation by reducing myeloid cell recruitment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107(18):8363–8368. doi:10.1073/pnas.09113781070911378107
Karin M, Greten FR (2005) NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nature Reviews Immunology 5(10):749–759
Torroella-Kouri M, Silvera R, Rodriguez D, Caso R, Shatry A, Opiela S, Ilkovitch D, Schwendener RA, Iragavarapu-Charyulu V, Cardentey Y, Strbo N, Lopez DM (2009) Identification of a subpopulation of macrophages in mammary tumor-bearing mice that are neither M1 nor M2 and are less differentiated. Cancer Research 69(11):4800–4809
Kuang D-M, Zheng L (2012) Immunobiology of monocytes/macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Biswas SK (ed) Tumor microenvironment and myelomonocytic cells. InTech, Rijeka, pp 157–172
Schioppa T, Uranchimeg B, Saccani A, Biswas SK, Doni A, Rapisarda A, Bernasconi S, Saccani S, Nebuloni M, Vago L, Mantovani A, Melillo G, Sica A (2003) Regulation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by hypoxia. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 198(9):1391–1402
Wang B, Li Q, Qin L, Zhao S, Wang J, Chen X (2011) Transition of tumor-associated macrophages from MHC class II(hi) to MHC class II(low) mediates tumor progression in mice. BMC Immunology 12:43. doi:10.1186/1471-2172-12-431471-2172-12-43
Foucher ED, Blanchard S, Preisser L, Garo E, Ifrah N, Guardiola P, Delneste Y, Jeannin P (2013) IL-34 induces the differentiation of human monocytes into immunosuppressive macrophages. Antagonistic effects of GM-CSF and IFNgamma. PLoS One 8(2):e56045. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056045PONE-D-12-17596
Lepique AP, Daghastanli KR, Cuccovia IM, Villa LL (2009) HPV16 tumor associated macrophages suppress antitumor T cell responses. Clinical Cancer Research 15(13):4391–4400. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-04891078-0432.CCR-09-0489
Saccani A, Schioppa T, Porta C, Biswas SK, Nebuloni M, Vago L, Bottazzi B, Colombo MP, Mantovani A, Sica A (2006) p50 nuclear factor-kappaB overexpression in tumor-associated macrophages inhibits M1 inflammatory responses and antitumor resistance. Cancer Research 66(23):11432–11440
Guiducci C, Vicari AP, Sangaletti S, Trinchieri G, Colombo MP (2005) Redirecting in vivo elicited tumor infiltrating macrophages and dendritic cells towards tumor rejection. Cancer Research 65(8):3437–3446
Beatty GL, Chiorean EG, Fishman MP, Saboury B, Teitelbaum UR, Sun W, Huhn RD, Song W, Li D, Sharp LL, Torigian DA, O'Dwyer PJ, Vonderheide RH (2011) CD40 agonists alter tumor stroma and show efficacy against pancreatic carcinoma in mice and humans. Science 331(6024):1612–1616. doi:10.1126/science.1198443331/6024/1612
O'Sullivan T, Saddawi-Konefka R, Vermi W, Koebel CM, Arthur C, White JM, Uppaluri R, Andrews DM, Ngiow SF, Teng MW, Smyth MJ, Schreiber RD, Bui JD (2012) Cancer immunoediting by the innate immune system in the absence of adaptive immunity. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 209(10):1869–1882. doi:10.1084/jem.20112738
Watkins SK, Egilmez NK, Suttles J, Stout RD (2007) IL-12 rapidly alters the functional profile of tumor-associated and tumor-infiltrating macrophages in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Immunology 178(3):1357–1362
Watkins SK, Li B, Richardson KS, Head K, Egilmez NK, Zeng Q, Suttles J, Stout RD (2009) Rapid release of cytoplasmic IL-15 from tumor-associated macrophages is an initial and critical event in IL-12-initiated tumor regression. European Journal of Immunology 39(8):2126–2135. doi:10.1002/eji.200839010
Topalian SL, Drake CG, Pardoll DM (2012) Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Current Opinion in Immunology 24(2):207–212. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2011.12.009S0952-7915(11)00184-1
Park S, Jiang Z, Mortenson ED, Deng L, Radkevich-Brown O, Yang X, Sattar H, Wang Y, Brown NK, Greene M, Liu Y, Tang J, Wang S, Fu YX (2010) The therapeutic effect of anti-HER2/neu antibody depends on both innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Cell 18(2):160–170. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2010.06.014S1535-6108(10)00248-5
Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Tang C, Myklebust JH, Varghese B, Gill S, Jan M, Cha AC, Chan CK, Tan BT, Park CY, Zhao F, Kohrt HE, Malumbres R, Briones J, Gascoyne RD, Lossos IS, Levy R, Weissman IL, Majeti R (2010) Anti-CD47 antibody synergizes with rituximab to promote phagocytosis and eradicate non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell 142(5):699–713. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.044S0092-8674(10)00892-5
De Palma M, Mazzieri R, Politi LS, Pucci F, Zonari E, Sitia G, Mazzoleni S, Moi D, Venneri MA, Indraccolo S, Falini A, Guidotti LG, Galli R, Naldini L (2008) Tumor-targeted interferon-alpha delivery by Tie2-expressing monocytes inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Cell 14(4):299–311. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.09.004S1535-6108(08)00296-1
Muthana M, Rodrigues S, Chen YY, Welford A, Hughes R, Tazzyman S, Essand M, Morrow F, Lewis CE (2013) Macrophage delivery of an oncolytic virus abolishes tumor regrowth and metastasis after chemotherapy or irradiation. Cancer Research 73(2):490–495. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-30560008-5472.CAN-12-3056
Germano G, Frapolli R, Belgiovine C, Anselmo A, Pesce S, Liguori M, Erba E, Uboldi S, Zucchetti M, Pasqualini F, Nebuloni M, van Rooijen N, Mortarini R, Beltrame L, Marchini S, Fuso Nerini I, Sanfilippo R, Casali PG, Pilotti S, Galmarini CM, Anichini A, Mantovani A, D'Incalci M, Allavena P (2013) Role of macrophage targeting in the antitumor activity of trabectedin. Cancer Cell 23(2):249–262. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.01.008S1535-6108(13)00033-0
Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2008) The Yin-Yang of tumor-associated macrophages in neoplastic progression and immune surveillance. Immunology Reviews 222:155–161. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00607.xIMR607
Ruffell B, Affara NI, Coussens LM (2012) Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment. Trends in Immunology 33(3):119–126. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.12.001S1471-4906(11)00213-4
Acknowledgments
AM and PA are supported by AIRC (Investigators Grants and Grants 5x 1000). SKB is supported by funding from SIgN, A*STAR, Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the special issue on Macrophage Heterogeneity, Subsets and Human Disease - Guest Editor: Siamon Gordon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, S.K., Allavena, P. & Mantovani, A. Tumor-associated macrophages: functional diversity, clinical significance, and open questions. Semin Immunopathol 35, 585–600 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0367-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0367-7