Abstract
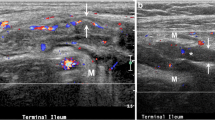
The purpose of this study was to assess the accuracy of MR enteroclysis in patients with Crohn’s disease recurrence after ileocolic resection and to establish an MR scoring sytem. MR enteroclysis and endoscopy were performed in 30 patients with suspected Crohn’s disease recurrence after ileocolic resection. Findings were evaluated by three radiologists, using an MR score based on image quality, contrast enhancement, and mural and extramural bowel-wall changes: MR0 (no abnormal features), MR1 (minimal mucosal changes), MR2 (diffuse aphtoid ileitis, moderate recurrence), and MR3 (severe recurrence with trans- and extramural changes). The endoscopic Rutgeerts score defines changes at the ileum on a scale from I0 to I4. In 3/30 (10%) patients, evaluation was not possible. The mean overall image quality was rated as 1.7 (kappa 0.78). Comparing MR and Rutgeerts score, the mean observer agreement for the total score rating was 77.8% (kappa 0.67). When comparing only scores below or above MR2—the threshold indicative of the necessity of medical treatment—there was a total agreement of 95.1% (kappa 0.84). MR enteroclysis allows assessment of Crohn’s disease recurrence after ileocolic resection. The MR score is reproducible and shows high agreement with the approved endoscopic Rutgeerts score.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Przemioslo RT, Ciclitira PJ (1995) Pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Q J Med 88:525–527
Daperno M, D’Haens G, Van Assche G et al (2004) Development and validation of a new, simplified endoscopic activity score for Crohn’s disease: the SES-CD. Gastrointest Endosc 60:505–512
Becker JM (1999) Surgical therapy for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 28:371–390
D’Haens GR, Geboes K, Peeters M, Baert F, Penninck F, Rutgeerts P (1998) Early lesions of recurrent Crohn’s disease caused by infusion of intestinal excluded ileum. Gastroenterology 114:262–267
Rutgeerts P, Geboes K, Vantrappen G, Beyls J, Kerremans R, Hiele M (1990) Predictability of the postoperative course of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 99:956–963
Ollendorf DA, Massarotti E, Birbara C, Burgess SM (2005) Frequency, predictors, and economic impact of upward dose adjustment of infliximab in managed care patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Manag Care Pharm 11:383–393
Korzenik JR, Dieckgraefe BK, Valentine JF, Hausman DF, Gilbert MJ (2005) Sargramostim in Crohn’s disease study group. Sargramostim for active Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med 352:2193–2201
Rutgeerts P, Van Assche G, Vermeire S et al (2005) Ornidazole for prophylaxis of postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 128:856–861
Prassopoulos P, Papanikolaou N, Grammatikakis J, Rousomoustakaki M, Maris T, Gourtsoyiannis N (2001) MR enteroclysis imaging of Crohn disease. Radiographics 21:161–172
Masselli G, Casciani E, Polettini E et al (2006) Assessment of Crohn’s disease in the small bowel: prospective comparison of magnetic resonance enteroclysis with conventional enteroclysis. Eur Radiol 16:2817–2827
Gourtsoyiannis N, Papanikolaou N, Grammatikakis J, Prassopoulos P (2002) MR enteroclysis: technical considerations and clinical applications. Eur Radiol 12:2651–2658
Masselli G, Brizi GM, Parrella A, Minordi LM, Vecchioli A, Marano P (2004) Crohn disease: magnetic resonance enteroclysis. Abdom Imaging 29:326–334
Maccioni F, Bruni A, Viscido A et al (2006) MR imaging in patients with Crohn’s disease: value of T2- versus T1-weighted gadolinium- enhanced MR sequences with use of an oral superparamagnetic contrast agent. Radiology 238:517–530
Meyers MA, McGuire PV (1995) Spiral CT demonstration of hypervascularity in Crohn’s disease: “vascular jejunization of the ileum” of the “comb sign”. Abdom Imaging 20:327–332
Gourtsoyiannis N, Papanikolaou N, Grammatikakis J et al (2004) Assessment of Crohn’s disease activity in the small bowel with MR and conventional enteroclysis: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 14:1017–1024
Chiorean MV, Sandrasegaran K, Saxena R et al (2007) Correlation of CT enteroclysis with surgical pathology in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterology 102:2541–2550
Maselli G, Vecchioli A, Gualdi GF (2006) Crohn disease of the small bowel: MR enteroclysis versus conventional enteroclysis. Abdom Imaging 31:400–409
Wiarda BM, Kuipers EJ, Heitbrink MA, van Oijen SA, Stoker J (2006) MR enteroclysis of inflammatory small-bowel diseases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:522–531
Paulsen SR, Huprich JE, Fletscher JG et al (2006) CT enterography as a diagnostic tool in evaluating small bowel disorders: review of clinical experience with over 700 cases. Radiographics 26:641–657
Sailer J, Peloschek P, Schober E et al (2005) Diagnostic value of CT enteroclysis compared with conventional enteroclysis in patients with Crohn’s disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:1575–1581
Maglinte DD, Siegelsmann EF, Kelvin FM (2000) MR enteroclysis: the future of small-bowel imaging? Radiology 215:639–641
Maccioni F, Viscido A, Broglia L et al (2000) Evaluation of Crohn disease activity with magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 25:219–228
Pauls S, Gabelmann A, Schmidt SA, Rieber A et al (2006) Evaluating bowel wall vascularity in Crohn’s disease: a comparison of dynamic MRI and wideband harmonic imaging contrast-enhanced low MI ultrasound. Eur Radiol 16:2410–2417
May A, Nachbar L, Schneider M, Ell C (2005) Double−balloon enteroscopy (push−and−pull enteroscopy) of the small bowel: feasibility, diagnostic and therapeutic yield in patients with suspected small bowel disease. Gastrointest Endoscopy 62:62–70
Laghi A, Carbone I, Catalano C et al (2001) Polyethylene glycol solution as an oral contrast agent for MR imaging of the small bowel. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:1333–1334
Patak MA, Froehlich JM, Weymann C, Ritz MA, Zollikofer CL, Wentz KU (2001) Non invasive distension of the small bowel for magnetic resonance imaging. Lancet 258:987–988
Colombel JF, Solem CA, Sandborn WJ et al (2006) Quantitative measurement and visual assessment of ileal Crohn’s disease activity by computed tomography enterography: correlation with endoscopic severity an C reactive protein. Gut 55:1561–1567
Rieber A, Nüssle K, Reinshagen M, Brambs HJ, Gabelmann A (2002) MRI of the abdomen with positive oral contrast agents for the diagnosis of inflammatory small bowel disease. Abdom Imaging 27:395–399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sailer, J., Peloschek, P., Reinisch, W. et al. Anastomotic recurrence of Crohn’s disease after ileocolic resection: comparison of MR enteroclysis with endoscopy. Eur Radiol 18, 2512–2521 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1034-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1034-6