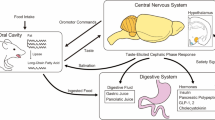
Abstract
The ingestion of dietary protein is of vital importance for the maintenance of fundamental physiological processes. The taste modality umami, with its prototype stimulus, glutamate, is considered to signal the protein content of food. Umami was thought to be mediated by the heterodimeric amino acid receptor, T1R1 + T1R3. Based on knockout studies, additional umami receptors are likely to exist. In addition to amino acids, certain peptides can also elicit and enhance umami taste suggesting that protein breakdown products may contribute to umami taste. The recently deorphanized peptone receptor, GPR92 (also named GPR93; LPAR5), is expressed in gastric enteroendocrine cells where it responds to protein hydrolysates. Therefore, it was of immediate interest to investigate if the receptor GPR92 is expressed in gustatory sensory cells. Using immunohistochemical approaches we found that a large population of cells in murine taste buds was labeled with an GPR92 antibody. A molecular phenotyping of GPR92 cells revealed that the vast majority of GPR92-immunoreactive cells express PLCβ2 and can therefore be classified as type II cells. More detailed analyses have shown that GPR92 is expressed in the majority of T1R1-positive taste cells. These results indicate that umami cells may respond not only to amino acids but also to peptides in protein hydrolysates.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- GPR92:
-
G protein-coupled receptor 92 (GPR93; LPAR5)
- mGluR4:
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 4
- T1R:
-
Taste receptor type 1
- T2R:
-
Taste receptor type 2
- T1R1:
-
Taste receptor type 1, member 1
- T1R3:
-
Taste receptor type 1, member 3
References
Bernhardt SJ, Naim M, Zehavi U, Lindemann B (1996) Changes in IP3 and cytosolic Ca2+ in response to sugars and non-sugar sweeteners in transduction of sweet taste in the rat. J Physiol 490(Pt 2):325–336
Breer H, Eberle J, Frick C, Haid D, Widmayer P (2012) Gastrointestinal chemosensation: chemosensory cells in the alimentary tract. Histochem Cell Biol 138(1):13–24. doi:10.1007/s00418-012-0954-z
Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2010) The cell biology of taste. J Cell Biol 190(3):285–296
Chaudhari N, Pereira E, Roper SD (2009) Taste receptors for umami: the case for multiple receptors. Am J Clin Nutr 90(3):738S–742S
Choi S, Lee M, Shiu AL, Yo SJ, Aponte GW (2007a) Identification of a protein hydrolysate responsive G protein-coupled receptor in enterocytes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(1):G98–G112
Choi S, Lee M, Shiu AL, Yo SJ, Halldén G, Aponte GW (2007b) GPR93 activation by protein hydrolysate induces CCK transcription and secretion in STC-1 cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(5):G1366–G1375
Clapp TR, Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon SC, Kinnamon JC (2004) Morphologic characterization of rat taste receptor cells that express components of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Comp Neurol 468(3):311–321
Cuber JC, Bernard G, Fushiki T, Bernard C, Yamanishi R, Sugimoto E, Chayvialle JA (1990) Luminal CCK-releasing factors in the isolated vascularly perfused rat duodenojejunum. Am J Physiol 259(2 Pt 1):G191–G197
Damak S, Rong M, Yasumatsu K, Kokrashvili Z, Varadarajan V, Zou S, Jiang P, Ninomiya Y, Margolskee RF (2003) Detection of sweet and umami taste in the absence of taste receptor T1r3. Science 301(5634):850–853
DeFazio RA, Dvoryanchikov G, Maruyama Y, Kim JW, Pereira E, Roper SD, Chaudhari N (2006) Separate populations of receptor cells and presynaptic cells in mouse taste buds. J Neurosci 26(15):3971–3980
Haid D, Jordan-Biegger C, Widmayer P, Breer H (2012) Receptors responsive to protein breakdown products in g-cells and d-cells of mouse, swine and human. Front Physiol 3:65. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00065
Ikeda K (1909) New seasonings. J Tokyo Chem Soc 30:820–836 (in Japanese)
Ikeda K (2002) New seasonings. Chem Sense 27(9):847–849
Iwatsuki K, Uneyama H (2012) Sense of taste in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharmacol Sci 118(2):123–128
Jahan-Mihan A, Luhovyy BL, El Khoury D, Anderson GH (2011) Dietary proteins as determinants of metabolic and physiologic functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Nutrients 3(5):574–603
Kim MR, Kusakabe Y, Miura H, Shindo Y, Ninomiya Y, Hino A (2003) Regional expression patterns of taste receptors and gustducin in the mouse tongue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312(2):500–506
Kim JW, Roberts C, Maruyama Y, Berg S, Roper S, Chaudhari N (2006) Faithful expression of GFP from the PLCbeta2 promoter in a functional class of taste receptor cells. Chem Senses 31(3):213–219
Kretz O, Barbry P, Bock R, Lindemann B (1999) Differential expression of RNA and protein of the three pore-forming subunits of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel in taste buds of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 47(1):51–64
Kusakabe Y, Kim MR, Miura H, Shindo Y, Ninomiya Y, Hino A (2005) Regional expression patterns of T1r family in the mouse tongue. Chem Sense 30(Suppl 1):i23–i24
Li X, Staszewski L, Xu H, Durick K, Zoller M, Adler E (2002) Human receptors for sweet and umami taste. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(7):4692–4696
Maga JA (1983) Flavor potentiators. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 18(3):231–312
Maruyama Y, Pereira E, Margolskee RF, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2006) Umami responses in mouse taste cells indicate more than one receptor. J Neurosci 26(8):2227–2234
Nelson G, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Zhang Y, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2001) Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 106(3):381–390
Nelson G, Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, Feng L, Zhao G, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2002) An amino-acid taste receptor. Nature 14;416(6877):199–202
Raksakulthai N, Haard NF (1992) Correlation between the concentration of peptides and amino acids and the flavour of fish sauce. ASEAN Food J 7(2):86–90
Rössler P, Kroner C, Freitag J, Noè J, Breer H (1998) Identification of a phospholipase C beta subtype in rat taste cells. Eur J Cell Biol 77(3):253–261
Saffouri B, DuVal JW, Makhlouf GM (1984) Stimulation of gastrin secretion in vitro by intraluminal chemicals: regulation by intramural cholinergic and noncholinergic neurons. Gastroenterology 87:557–561
San Gabriel A, Uneyama H (2012) Amino acid sensing in the gastrointestinal tract. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1371-2
Schlichtherle-Cerny H, Amadò R (2002) Analysis of taste-active compounds in an enzymatic hydrolysate of deamidated wheat gluten. J Agric Food Chem 50(6):1515–1522
Striem BJ, Naim M, Lindemann B (1991) Generation of cyclic AMP in Taste Buds of the Rat Circumvallate Papilla in Response to Sucrose. Cell Physiol Biochem 1:46–54
Tamura M, Nakatsuka T, Tada M, Kawasaki Y, Kikuchi E, Okai A (1989) The relationship between taste and primary structure of “delicious peptide” (Lys-Gly-Asp-Glu-Glu-Ser-Leu-Ala) from beef soup. Agric Biol Chem 53:319–325
Tomchik SM, Berg S, Kim JW, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2007) Breadth of tuning and taste coding in mammalian taste buds. J Neurosci 27(40):10840–10848
Van Den Oord AHA, Van Wassenaar PD (1997) Umami peptides: assessment of their alleged taste properties. Eur Food Res Technol 205:25–130
Voigt A, Hübner S, Lossow K, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Boehm U, Meyerhof W (2012) Genetic Labeling of Tas1r1 and Tas2r131 Taste Receptor Cells in Mice. Chem Sense 37(9):897–911
Wu G (2009) Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 37(1):1–17
Yamaguchi S, Ninomiya K (2000) Umami and food palatability. J Nutr 130(4S Suppl):921S–926S
Yee CL, Yang R, Böttger B, Finger TE, Kinnamon JC (2001) “Type III” cells of rat taste buds: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies of neuron-specific enolase, protein gene product 9.5, and serotonin. J Comp Neurol 440(1):97–108
Yoshida R, Yasumatsu K, Shirosaki S, Jyotaki M, Horio N, Murata Y, Shigemura N, Nakashima K, Ninomiya Y (2009) Multiple receptor systems for umami taste in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1170:51–54
Zhang Y, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Mueller KL, Cook B, Wu D, Zuker CS, Ryba NJ (2003) Coding of sweet, bitter, and umami tastes: different receptor cells sharing similar signaling pathways. Cell 112(3):293–301
Zhang F, Klebansky B, Fine RM, Xu H, Pronin A, Liu H, Tachdjian C, Li X (2008) Molecular mechanism for the umami taste synergism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(52):20930–20934
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Kerstin Bach for excellent technical assistance and Prof. Meyerhof for providing the T1R1-mCherry mice. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, BR 712/25-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haid, D., Widmayer, P., Voigt, A. et al. Gustatory sensory cells express a receptor responsive to protein breakdown products (GPR92). Histochem Cell Biol 140, 137–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1080-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1080-2