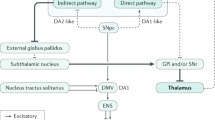
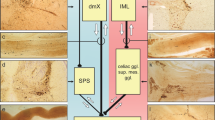
Abstract
Apart from the characteristic and progressive motor- and movement-related problems, Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients also suffer from several non-motor symptoms, including gastrointestinal dysfunction. The fact that the enteric nervous system (ENS) controls motility and that one of the typical PD hallmarks, α-synuclein-positive deposits, has also been found in the intestinal wall have rendered the ENS and the gut a popular subject of study in the context of PD. The possibility that these deposits could serve as an early biomarker is obviously of tremendous medical benefit but also the idea that the gut may possibly be a gateway via which the disease is initiated and progressively makes its way via the peripheral nerves to the central nervous system has increased the interest in the ENS–PD link. Furthermore, the fact that gastrointestinal symptoms are present in PD suggests that the ENS might be affected as well. However, despite a large body of literature on the topic, the actual role or the magnitude of involvement of the ENS in PD remains elusive. The multitudes of experimental approaches and animal models have complicated the interpretation of results and the outcome of different studies does not necessarily align well. In this review, we chose to highlight some elements of interest and some items of confusion, particularly those where research should be focusing. We also list a number of open questions in the field that could serve as a guideline for future, preferably concerted research.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
α-Synuclein
- α-synGFP:
-
α-Synuclein green fluorescent protein
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- DAT:
-
Dopamine transporter
- DBH:
-
Dopamine β-hydroxylase
- D2:
-
Dopamine receptor subtype 2
- DMV:
-
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve
- ENS:
-
Enteric nervous system
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- h-AS:
-
Human α-synuclein
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- kD:
-
Kilodalton
- P-AS:
-
Phosphorylated α-synuclein
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s Disease
- P-specific:
-
Phosphorylated specific
- NFM:
-
Neurofilament M (medium)
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SNARE:
-
Soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor) attachment protein receptor
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
- Thy1-AS:
-
Thy1 promoter induced α-synuclein
- VIP:
-
Vasointestinal peptide
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Anselmi L, Toti L, Bove C, Hampton J, Travagli RA (2017) A nigro-vagal pathway controls gastric motility and is affected in a rat model of parkinsonism. Gastroenterology 153(6):1581–1593
Barrenschee M, Zorenkov D, Böttner M, Lange C, Cossais F, Scharf AB, Deuschl G, Schneider SA, Ellrichmann M, Fritscher-Ravens A, Wedel T (2017 Jan 5) Distinct pattern of enteric phospho-alpha-synuclein aggregates and gene expression profiles in patients with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5(1):1
Baumuratov AS, Antony PM, Ostaszewski M, He F, Salamanca L, Antunes L et al (2016) Enteric neurons from Parkinson’s disease patients display ex vivo aberrations in mitochondrial structure. Sci Rep 6:33117
Beach TG et al (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):613–634
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG, Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium (2010) Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):689–702
Beach TG et al (2016) Multicenter assessment of immunohistochemical methods for pathological alpha-synuclein in sigmoid colon of autopsied Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. J Parkinsons Dis 6(4):761–770
Berthoud HR, Carlson NR, Powley TL (1991) Topography of efferent vagal innervation of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol260(1 Pt 2):R200-7. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.1.R200
Borghammer P (2018) How does Parkinson’s disease begin? Perspectives on neuroanatomical pathways, prions, and histology. Mov Disord 33(1):48–57
Böttner M, Fricke T, Müller M, Barrenschee M, Deuschl G, Schneider SA, Egberts JH, Becker T, Fritscher-Ravens A, Ellrichmann M, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Wedel T (2015) Alpha-synuclein is associated with the synaptic vesicle apparatus in the human and rat enteric nervous system. Brain Res 1614:51–59
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2017) Neuropathological staging of brain pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: separating the wheat from the chaff. J Parkinsons Dis 7(s1):S73–S87
Braak H et al (2002) Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages). J Neurol 249(Suppl 3):III/1–III/5
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rüb U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318(1):121–134
Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396(1):67–72
Braak H, Sastre M, Bohl JR, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2007) Parkinson’s disease: lesions in dorsal horn layer I, involvement of parasympathetic and sympathetic pre- and postganglionic neurons. Acta Neuropathol 113(4):421–429
Brookes SJ, Spencer NJ, Costa M, Zagorodnyuk VP (2013) Extrinsic primary afferent signalling in the gut. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(5):286–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.29. Epub 2013 Feb 26 Review
Burré J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Südhof TC (2010) Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329(5999):1663–1667
Cersosimo MG (2015) Gastrointestinal biopsies for the diagnosis of alpha-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2015:476041
Cersosimo MG, Benarroch EE (2008) Neural control of the gastrointestinal tract: implications for Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 23(8):1065–1075
Chalazonitis A, Rao M (2018) Enteric nervous system manifestations of neurodegenerative disease. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.201801.011
Chesselet MF, Fleming S, Mortazavi F, Meurers B (2008) Strengths and limitations of genetic mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(Suppl 2):S84–SS7
Chung SJ et al (2016) Alpha-synuclein in gastric and colonic mucosa in Parkinson’s disease: limited role as a biomarker. Mov Disord 31(2):241–249
Cirillo C, Tack J, Vanden Berghe P (2013) Nerve activity recordings in routine human intestinal biopsies. Gut 62(2):227–235
Comi C et al (2014) Peripheral nervous system involvement in Parkinson’s disease: evidence and controversies. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(12):1329–1334
Corbille AG et al (2016) What a gastrointestinal biopsy can tell us about Parkinson’s disease? Neurogastroenterol Motil 28(7):966–974
Del Tredici K, Braak H (2016) Review: sporadic Parkinson’s disease: development and distribution of alpha-synuclein pathology. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 42(1):33–50
Depoortere I (2015) Taste receptors in the gut tune the release of peptides in response to nutrients. Peptides 66:9–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2015.01.013
Derkinderen P (2017) LRRK2 expression in the enteric nervous system: ensuring its significance. Dig Dis Sci 62(4):826–827
Derkinderen P, Rouaud T, Lebouvier T, Bruley d, Varannes S, Neunlist M, De Giorgio R (2011) Parkinson disease: the enteric nervous system spills its guts. Neurology 77(19):1761–1767
Desmet AS, Cirillo C, Tack J, Vandenberghe W, Vanden Berghe P (2017) Live calcium and mitochondrial imaging in the enteric nervous system of Parkinson patients and controls. Elife
Desplats P, Lee HJ, Bae EJ, Patrick C, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Spencer B, Masliah E, Lee SJ (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(31):13010–13015
Devos D, Lebouvier T, Lardeux B, Biraud M, Rouaud T, Pouclet H, Coron E, Bruley d, Varannes S, Naveilhan P, Nguyen JM, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2013) Colonic inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 50:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2012.09.007
Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LW, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF (2015) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14(6):625–639
Forsyth CB et al (2011) Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 6(12):e28032
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) Alpha-synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4(2):160–164
Furness JB (2012) The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(5):286–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.32
Gershon MD (1998) The second brain: the scientific basis of gut instinct and a groundbreaking new understanding of nervous disorders of the stomach and intestine. HarperCollinsPublishers, New York
Giancola F, Torresan F, Repossi R, Bianco F, Latorre R, Ioannou A, Guarino M, Volta U, Clavenzani P, Mazzoni M, Chiocchetti R, Bazzoli F, Travagli RA, Sternini C, De Giorgio R (2017) Downregulation of neuronal vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in Parkinson’s disease and chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29(5).
Greene JG, Noorian AR, Srinivasan S (2009) Delayed gastric emptying and enteric nervous system dysfunction in the rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 218(1):154–161
Hao MM, Foong JP, Bornstein JC, Li ZL, Vanden Berghe P, Boesmans W (2016) Enteric nervous system assembly: functional integration within the developing gut. Dev Biol 417(2):168–181
Heintz-Buschart A et al (2018) The nasal and gut microbiome in Parkinson’s disease and idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Mov Disord 33(1):88–98
Hill-Burns EM et al (2017) Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Mov Disord 32(5):739–749
Holmqvist S, Chutna O, Bousset L, Aldrin-Kirk P, Li W, Björklund T, Wang ZY, Roybon L, Melki R, Li JY (2014) Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol 128(6):805–820
Hopfner F et al (2017) Gut microbiota in Parkinson disease in a northern German cohort. Brain Res 1667:41–45
Houser MC, Tansey MG (2017) The gut-brain axis: is intestinal inflammation a silent driver of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis? NPJ Parkinsons Dis 3:3
Jellinger KA (2009) A critical evaluation of current staging of alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(7):730–740
Jellinger KA (2015) Neuropathobiology of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 122(10):1429–1440
Jennings D et al (2014) Imaging prodromal Parkinson disease: the Parkinson Associated Risk Syndrome Study. Neurology 83(19):1739–1746
Joseph NM, He S, Quintana E, Kim YG, Núñez G, Morrison SJ (2011) Enteric glia are multipotent in culture but primarily form glia in the adult rodent gut. J Clin Invest 121(9):3398–3411
Jucker M (2010) The benefits and limitations of animal models for translational research in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med 16(11):1210–1214. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2224
Kalaitzakis ME et al (2008) The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is not an obligatory trigger site of Parkinson’s disease: a critical analysis of alpha-synuclein staging. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34(3):284–295
Keshavarzian A, Green SJ, Engen PA, Voigt RM, Naqib A, Forsyth CB, Mutlu E, Shannon KM (2015) Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(10):1351–1360. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26307
Klingelhoefer L, Reichmann H (2015) Pathogenesis of Parkinson disease—the gut-brain axis and environmental factors. Nat Rev Neurol 11(11):625–636
Kordower JH et al (2008) Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 14(5):504–506
Kulkarni S, Micci MA, Leser J, Shin C, Tang SC, Fu YY, Liu L, Li Q, Saha M, Li C, Enikolopov G, Becker L, Rakhilin N, Anderson M, Shen X, Dong X, Butte MJ, Song H, Southard-Smith EM, Kapur RP, Bogunovic M, Pasricha PJ (2017) Adult enteric nervous system in health is maintained by a dynamic balance between neuronal apoptosis and neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(18):E3709–E3718. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1619406114
Kuo YM, Li Z, Jiao Y, Gaborit N, Pani AK, Orrison BM, Bruneau BG, Giasson BI, Smeyne RJ, Gershon MD, Nussbaum RL (2010) Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson disease-associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central nervous system changes. Hum Mol Genet 19(9):1633–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq038
Kupsky WJ, Grimes MM, Sweeting J, Bertsch R, Cote LJ (1987) Parkinson’s disease and megacolon: concentric hyaline inclusions (Lewy bodies) in enteric ganglion cells. Neurology 37:1253–1255
Langston JW (2017) The MPTP story. J Parkinsons Dis 7(s1):S11–S22
Laranjeira C, Sandgren K, Kessaris N, Richardson W, Potocnik A, Vanden Berghe P, Pachnis V (2011) Glial cells in the mouse enteric nervous system can undergo neurogenesis in response to injury. J Clin Invest 121(9):3412–3424
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Damier P, Coron E, Touchefeu Y, Vrignaud S et al (2008) Pathological lesions in colonic biopsies during Parkinson’s disease. Gut 57(12):1741–1743
Lebouvier T et al (2010) Colonic biopsies to assess the neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease and its relationship with symptoms. PLoS One 5(9):e12728
Leclair-Visonneau L et al (2017) REM sleep behavior disorder is related to enteric neuropathology in Parkinson disease. Neurology 89(15):1612–1618
Lee HJ, Patel S, Lee SJ (2005) Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J Neurosci 25(25):6016–6024
Lewy FH (1914) Zur pathologischen Anatomie der Paralysis agitans. Dtsch Ztschr Nervenheilkunde 50:50–55
Li ZS, Pham TD, Tamir H, Chen JJ, Gershon MD (2004) Enteric dopaminergic neurons: definition, developmental lineage, and effects of extrinsic denervation. J Neurosci 24(6):1330–1339
Li ZS, Schmauss C, Cuenca A, Ratcliffe E, Gershon MD (2006) Physiological modulation of intestinal motility by enteric dopaminergic neurons and the D2 receptor: analysis of dopamine receptor expression, location, development, and function in wild-type and knock-out mice. J Neurosci 26(10):2798–2807
Li W et al (2017) Structural changes of gut microbiota in Parkinson’s disease and its correlation with clinical features. Sci China Life Sci 60(11):1223–1233
Lin JC, Lin CS, Hsu CW, Lin CL, Kao CH (2016) Association between Parkinson’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease: a nationwide Taiwanese retrospective cohort study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 22(5):1049–1055
Linazasoro G (2007) Classical Parkinson disease versus Parkinson complex—reflections against staging and in favour of heterogeneity. Eur J Neurol 14(7):721–728
Lionnet A et al (2018) Does Parkinson’s disease start in the gut? Acta Neuropathol 135(1):1–12
Liu B et al (2017) Vagotomy and Parkinson disease: a Swedish register-based matched-cohort study. Neurology 88(21):1996–2002
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338(6109):949–953
Malek N et al (2014) Alpha-synuclein in peripheral tissues and body fluids as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease—a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand 130(2):59–72
Meredith GE, Sonsalla PK, Chesselet MF (2008) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease progression. Acta Neuropathol 115(4):385–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0350-x. Epub 2008 Feb 14 Review
Moretto A, Colosio C (2013) The role of pesticide exposure in the genesis of Parkinson’s disease: epidemiological studies and experimental data. Toxicology 307:24–34
Mukherjee A, Biswas A, Das SK (2016) Gut dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 22(25):5742–5752. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5742 Review
Mulak A, Bonaz B (2015) Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Parkinson’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 21(37):10609–10620
Narayan S et al (2017) Occupational pesticide use and Parkinson’s disease in the Parkinson Environment Gene (PEG) study. Environ Int 107:266–273
Natale G, Pasquali L, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008) Parkinson’s disease and the gut: a well known clinical association in need of an effective cure and explanation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20(7):741–749
Neunlist M et al (2013) The digestive neuronal-glial-epithelial unit: a new actor in gut health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(2):90–100
Obeso JA et al (2017) Past, present, and future of Parkinson’s disease: a special essay on the 200th anniversary of the shaking palsy. Mov Disord 32(9):1264–1310
Pan-Montojo F, Anichtchik O, Dening Y, Knels L, Pursche S, Jung R et al (2010) Progression of Parkinson’s disease pathology is reproduced by intragastric administration of rotenone in mice. PLoS One 5(1):e8762
Pan-Montojo F, Schwarz M, Winkler C, Arnhold M, O'Sullivan GA, Pal A et al (2012) Environmental toxins trigger Parkinson’s disease-like progression via increased alpha-synuclein release from enteric neurons in mice. Sci Rep 2:898
Parashar A, Udayabanu M (2017) Gut microbiota: implications in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 38:1–7
Peelaerts W, Baekelandt V (2016) α-Synuclein folds: the cards are on the table. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23(5):359–360
Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, Moskalyuk A, Pulizzi R, Giugliano M, Van den Haute C, Melki R, Baekelandt V (2015) α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 522(7556):340–344
Pellegrini C et al (2016) Intestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: lessons learned from translational studies and experimental models. Neurogastroenterol Motil 28(12):1781–1791
Pereira PAB et al (2017) Oral and nasal microbiota in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 38:61–67
Petrov VA et al (2017) Analysis of gut microbiota in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 162(6):734–737
Petrovitch H et al (2009) Bowel movement frequency in late-life and substantia nigra neuron density at death. Mov Disord 24(3):371–376
Phillips RJ, Kieffer EJ, Powley TL (2003) Aging of the myenteric plexus: neuronal loss is specific to cholinergic neurons. Auton Neurosci 106(2):69–83
Phillips RJ, Martin FN, Billingsley CN, Powley TL (2013) Alpha-synuclein expression patterns in the colonic submucosal plexus of the aging Fischer 344 rat: implications for biopsies in aging and neurodegenerative disorders? Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(9):e621–e633
Pouchieu C et al (2018) Pesticide use in agriculture and Parkinson’s disease in the AGRICAN cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 47(1):299–310
Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2012) Lewy pathology in gastric and duodenal biopsies in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(6):708
Powley TL, Spaulding RA, Haglof SA (2011) Vagal afferent innervation of the proximal gastrointestinal tract mucosa: chemoreceptor and mechanoreceptor architecture. J Comp Neurol 519(4):644–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.22541
Qualman SJ, Haupt HM, Yang P, Hamilton SR (1984) Esophageal Lewy bodies associated with ganglion cell loss in achalasia. Similarity to Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterology 87(4):848–856
Rao M, Gershon MD (2016) The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13(9):517–528
Rao M, Gershon MD (2017) Neurogastroenterology: the dynamic cycle of life in the enteric nervous system. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):453–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.85
Ross GW et al (2012) Pre-motor features of Parkinson’s disease: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study experience. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl 1):S199–S202
Ruffmann C, Parkkinen L (2016) Gut feelings about α-synuclein in gastrointestinal biopsies: biomarker in the making? Mov Disord 31(2):193–202
Saffrey MJ (2013) Cellular changes in the enteric nervous system during ageing. Dev Biol 382(1):344–355
Sampson TR et al (2016) Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167(6):1469–1480 e12
Sanchez-Ferro A et al (2015) In vivo gastric detection of alpha-synuclein inclusions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(4):517–524
Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PA, Koskinen K, Paulin L, Pekkonen E et al (2015) Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Mov Disord 30(3):350–358
Schneider SA, Boettner M, Alexoudi A, Zorenkov D, Deuschl G, Wedel T (2016) Can we use peripheral tissue biopsies to diagnose Parkinson’s disease? A review of the literature. Eur J Neurol 23(2):247–261
Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2012) Neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease: moving Lewy bodies out of focus. Neurology 79(24):2298–2299
Schuurkes JA, Helsen LF, Van Nueten JM (1985) A comparative study on the effects of domperidone, metoclopramide, clebopride and trimebutine on the gastro-duodenal preparation of the guinea pig. Jpn J Pharmacol 39(2):123–130
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu E, Dodiya HB, Daian D, Jaglin JA et al (2012) Alpha-synuclein in colonic submucosa in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(6):709–715
Sharrad DF, Chen BN, Brookes SJ (2013) Neurochemical coding compared between varicose axons and cell bodies of myenteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Neurosci Lett 534:171–176
Sharrad DF, Chen BN, Gai WP, Vaikath N, El-Agnaf OM, Brookes SJ (2017) Rotenone and elevated extracellular potassium concentration induce cell-specific fibrillation of α-synuclein in axons of cholinergic enteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29(4)
Singaram C, Ashraf W, Gaumnitz EA, Torbey C, Sengupta A, Pfeiffer R, Quigley EM (1995) Dopaminergic defect of enteric nervous system in Parkinson’s disease patients with chronic constipation. Lancet 346(8979):861–864
Svensson E et al (2015) Vagotomy and subsequent risk of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 78(4):522–529
Tasselli M, Chaumette T, Paillusson S, Monnet Y, Lafoux A, Huchet-Cadiou C, Aubert P, Hunot S, Derkinderen P, Neunlist M (2013) Effects of oral administration of rotenone on gastrointestinal functions in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(3):e183–e193
Timmermans JP, Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Adriaensen D, De Groodt-Lasseel MH (1992) Functional morphology of the enteric nervous system with special reference to large mammals. Eur J Morphol 30(2):113–122 Review
Ulusoy A, Rusconi R, Pérez-Revuelta BI, Musgrove RE, Helwig M, Winzen-Reichert B, Di Monte DA (2013) Caudo-rostral brain spreading of α-synuclein through vagal connections. EMBO Mol Med 5(7):1119–1127
Ulusoy A, Phillips RJ, Helwig M, Klinkenberg M, Powley TL, Di Monte DA (2017) Brain-to-stomach transfer of α-synuclein via vagal preganglionic projections. Acta Neuropathol 133(3):381–393
Unger MM et al (2016) Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 32:66–72
Veiga-Fernandes H, Pachnis V (2017) Neuroimmune regulation during intestinal development and homeostasis. Nat Immunol 18(2):116–122
Villarán RF, Espinosa-Oliva AM, Sarmiento M, De Pablos RM, Argüelles S, Delgado-Cortés MJ, Sobrino V, Van Rooijen N, Venero JL, Herrera AJ, Cano J, Machado A (2010) Ulcerative colitis exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced damage to the nigral dopaminergic system: potential risk factor in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 114(6):1687–1700
Visanji NP, Marras C, Kern DS et al (2015) Colonic mucosal a-synuclein lacks specificity as a biomarker for Parkinson disease. Neurology 84:609–616
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1988) Parkinson’s disease: the presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol 76(3):217–221
Wedel T, Roblick U, Gleiss J, Schiedeck T, Bruch HP, Kühnel W, Krammer HJ (1999) Organization of the enteric nervous system in the human colon demonstrated by wholemount immunohistochemistry with special reference to the submucous plexus. Ann Anat 181(4):327–337
Zhong CB, Chen QQ, Haikal C, Li W, Svanbergsson A, Diepenbroek M, Li JY (2017) Age-dependent alpha-synuclein accumulation and phosphorylation in the enteric nervous system in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Bull 33(5):483–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-017-0179-1
Funding
FWO – G.0A44.13 (PVB)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shannon, K., Vanden Berghe, P. The enteric nervous system in PD: gateway, bystander victim, or source of solutions. Cell Tissue Res 373, 313–326 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2856-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2856-4