Abstract
Background
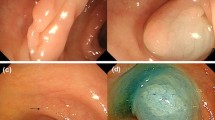
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is today the treatment of choice for flat and sessile colorectal lesion, the only concern being completeness of resection. One of the major issues is the choice of the infiltrating substance to enable a long-lasting cushion under the lesion. The aim of this study was to prospectively evaluate safety and efficacy of hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose (HPMC) injection for this purpose.
Patients
All flat and sessile lesions of the colon and rectum larger than 20 mm and considered suitable for EMR were included. In all cases 0.8% HPMC solution was injected through a 23G needle, in quantity according to the endoscopist’s indication. Primary endpoints of the study were: (1) ability to perform en bloc resection of the lesions by using this new injection means, (2) complete resection rate, and (3) early and late complication rate.
Results
We resected 27 flat, sessile, or laterally spreading lesions up to 60 mm (28 mm average). Mean dose of HPMC injected was 10.2 ml (range 8–40 ml). Median procedure time was 32 min (range 15–105 min). En bloc resection was achieved in up to 21 cases (78%). Histologically detected complete tumour removal was achieved in 23 lesions, whereas lateral margins could not be properly evaluated in 4 cases due to coagulation artefacts. No perforation was observed. Procedural spurting bleeding was managed by epinephrine injection in one case and clip application in the remaining. Two case of local recurrence of adenomatous tissue were observed at 3 and 12 months, and treated by EMR. No complication related to the use of HPMC was observed.
Conclusions
Injection of HPMC for EMR resulted safe and effective, allowing en bloc resection in the majority of cases with a limited number of complications. Continued progress in the field will include more outcomes research and techniques simplification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishiguro A, Uno Y, Ishiguro Y, Munakata A, Morita T (1999) Correlation of lifting versus non-lifting and microscopic depth of invasion in early colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 50:329–333
Kim MH, Lee SK, Seo DW, Won SY, Lee SS, Min YI (2001) Tumors of the major duodenal papilla. Gastrointest Endosc 54:609–620
Fleischer D (2000) Endoscopic mucosal resection: (not) made in the USA (so commonly). A dissection of the definition, technique, use, and controversies [editorial]. Gastrointest Endosc 52:440–444
Technology status report evaluation, Endoscopic mucosal resection (2000) Gastrointest Endosc 52:831–837
Sakai P, Maluf Filho F, Iryia K, Moura EG, Tomishigue T, Scabbia A et al (1996) An endoscopic technique for resection of small gastrointestinal carcinomas. Gastrointest Endosc 44:65–68
Fleischer DE, Wang GQ, Dawsey S, Tio TL, Newsome J, Kidwell J et al (1996) Tissue band ligation followed by snare resection (band and snare): a new technique for tissue acquisition in the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 44:68–72
Torii A, Sakai M, Kajiyama T, Kishimoto H, Kin G, Inoue K et al (1995) Endoscopic aspiration mucosectomy as curative endoscopic surgery; analysis of 24 cases of early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 42:475–479
Yamamoto H, Yube T, Isoda N, Sato Y, Sekine Y, Higashizawa T et al (1999) A novel method of endoscopic mucosal resection using sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc 50:251–256
Yamamoto H (1999) A successful single-step endoscopic resection of a 40 millimeter flat-elevated tumor in the rectum: endoscopic mucosal resection using sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc 50:701–704
Feitoza A, Gostout CJ, Burgart LJ, Burkert A, Herman LJ, Rajan E (2003) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose: a better submucosal fluid cushion for endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc 57:41–47
Dick HB (2001) Evaluation of viscoelastic substances. J Cataract Refract Surg 27:1711–1712
Ravalico G, Tognetto D, Baccara F, Lovisato A (1997) Corneal endothelial protection by different viscoelastics during phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg 23:433–439
Smith SG, Lindstrom RL (1991) 2% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a viscous surgical adjunct. A multicenter prospective randomized trial. J Cataract Refract Surg 17:839–842
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon, Rectum (1997) Japanese Classification of Colorectal Carcinoma. Kanehara, Tokyo
Kudo S, Tamegai Y, Ymano H et al (2001) Endoscopic mucosal resection of the colon: the Japanese technique. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 11:519–535
Yeh RW, Triadafilopoulos G (2005) Submucosal injection: safety cushion at what cost [editorial]? Gastrointest Endosc 62:943–945
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, Matsuura T, Nakamura N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ichinose M, Omata M (2005) Tissue damage of different submucosal injection solutions for EMR. Gastrointest Endosc 62:933–942
Uraoka T, Fujii T, Saito Y, Sumiyoshi T, Emura F, Bhandari P, Matsuda T, Fu KI, Saito D (2005) Effectiveness of glycerol as a submucosal injection for EMR. Gastrointest Endosc 61:736–740
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K et al (2004) Comparison of various submucosal injection solutions for maintaining mucosal elevation during endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy 36:579–583
Matsui Y, Inomata M, Izumi K et al (2004) Hyaluronic acid stimulates tumor-cell proliferation at wound sites. Gastrointest Endosc 60:539–543
Storr-Paulsen A, Larsen M (1991) Long-term results of extracapsular cataract extraction with posterior chamber lens implantation: sodium hyaluronate 1% vs hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2%. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 69:766–769
Liesegang TJ, Bourne WM, Ilstrup DM (1986) The use of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in extracapsular cataract extraction with intraocular lens implantation. Am J Ophthalmol 102:723–726
Alio JL, Mulet ME, Shalaby AM, Attia WH (2002) Phacoemulsification in the anterior chamber. J Cataract Refract Surg 28:67–75
Heng PW, Chan LW, Easterbrook MG, Li X (2001) Investigation of the influence of mean particle size and number of polymer particles on the release of aspirin from swellable hydrophilic matrix tablets. J Control Release 76:39–49
Katzhendler I, Mader K, Friedman M (2000) Structure and hydration properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices containing naproxen and naproxen sodium. Int J Pharm 200:161–179
Siepmann J, Kranz H, Peppas NA, Bodmeier R (2000) Calculation of the required size and shape of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices to achieve desired drug release profiles. Int J Pharm 201:151–164
Toda I, Shinozaki N, Tsubota K (1996) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for the treatment of severe dry eye associated with Sjogren’s syndrome. Cornea 15:120–128
Osborn E, Baum JL, Ernst C, Koch P (1976) The stability of ten antibiotics in artificial tear solutions. Am J Ophthalmol 82:775–780
Obara S (1992) Primary dermal and eye irritability tests of hydrophobically modified hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in rabbits. J Toxicol Sci 17:21–29
Obara S (1992) Studies on single-dose toxicity of hydrophobically modified hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in rats. J Toxicol Sci 17:13–19
Arantes V, Albuquerque W, Lima D, Vilela S, Lima G Jr, Duarte D, Benfica E, Filho FM, Artifon E, Sakai P (2006) Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) with a new solution: 0.4% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Gastrointest Endosc 63:AB247
Bacani CJ, Woodward TA, Raimondo M, Al-Haddad MA, Noh KW, Pungpapong S, Wallace MB (2007) Efficacy and safety of endoscopic mucosal resection with hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose compared to normal saline. Gastrointest Endosc 65:AB284
Conio M, Repici A, Demarquay JF, Blanchi S, Dumas R, Filiberti R (2004) EMR of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 60:234–241
Doniec JM, Lohnert MS, Schniewind B, Bokelmann F, Kremer B, Grimm H (2003) Endoscopic removal of large colorectal polyps: prevention of unnecessary surgery? Dis Colon Rectum 46:340–348
Jin Hyun J, Rae Chun H, Jai Chun H, Tae Jeen Y, Won Baeck C, Kyun Yu S, Sik Kim Y, Sik Lee H, Ho Um S, Woo Lee S, Hyun Choi J, Duck Kim C, Sang Ryu H, Hai Hyun J (2006) Comparison of the characteristics of submucosal injection solutions used in endoscopic mucosal resection. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:488–492
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arezzo, A., Pagano, N., Romeo, F. et al. Hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose is a safe and effective lifting agent for endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal polyps. Surg Endosc 23, 1065–1069 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0133-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0133-4