Abstract
Background
The international consensus guidelines (the guidelines) for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas recommend surgical resection of branch duct IPMNs with any of the following features: cyst size >30 mm, mural nodules, main pancreatic duct diameter >6 mm, positive cytology, and symptoms. The aim of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of these guidelines for resection of branch duct IPMNs.
Methods
We reviewed 84 consecutive patients with branch duct IPMNs who underwent surgical resection at our hospital between January 1984 and December 2007.
Results
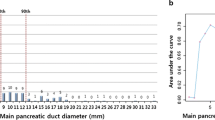
Sixty-nine patients had indications for resection according to the guidelines. Malignant IPMNs had significantly larger cysts than benign tumors (P = 0.026). Patients with malignant IPMNs had significantly more indications for resection than those with benign IPMNs (2.6 ± 1.0 vs. 1.7 ± 0.9, P < 0.001), and 36 of the 37 patients with malignant IPMNs had indications. The sensitivity of the guidelines for predicting malignancy was 97.3%. One of 15 patients without indications had malignancy, and the specificity was low (29.8%).
Conclusions
The guidelines show a high sensitivity for predicting malignancy of branch duct IPMNs, but the specificity is low. The cyst size and the total number of indications in each patient should be taken into account when predicting the risk of malignancy for branch duct IPMNs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimura W. IHPBA in Tokyo, 2002: surgical treatment of IPMT vs MCT: a Japanese experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2003;10:156–62.
Seki M, Yanagisawa A, Ohta H, Ninomiya Y, Sakamoto Y, Yamamoto J, et al. Surgical treatment of intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor (IPMT) of the pancreas: operative indications based on surgico-pathologic study focusing on invasive carcinoma derived from IPMT. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2003;10:147–55.
Nishikawa N, Kimura Y, Okita K, Zembutsu H, Furuhata T, Katsuramaki T, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of protein expression and clinical features. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13:327–35.
Fukushima N, Fukayama M. Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: pathology and molecular genetics. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007;14:238–42.
Kobayashi N, Inamori M, Fujita K, Fujisawa T, Fujisawa N, Takahashi H, et al. Characterization of K-ras gene mutations in association with mucinous hypersecretion in intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008;15:169–77.
Kim SC, Park KT, Lee YJ, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of 118 consecutive patients from a single center. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008;15:183–8.
Ohashi K, Murakami Y, Maruyama M, Takekoshi T, Ohta H, Ohashi I, et al. Four cases of mucous secreting pancreatic cancer (in Japanese with English abstract). Prog Dig Endosc. 1982;20:348–51.
Kloppel G, Solcia E, Longnecker DS, Capella C, Sobin LH. Histological typing of tumours of the exocrine pancreas. World Health Organization international histological classification of tumours. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; 1996.
Longnecker DS, Adler G, Hruban RH, Kloppel G. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumors of the digestive system (World Health Organization classification of tumours). Lyon: IARC Press; 2000. p. 237–40.
Tanaka M, Kobayashi K, Mizumoto K, Yamaguchi K. Clinical aspects of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:669–75.
Doi R, Fujimoto K, Wada M, Imamura M. Surgical management of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas. Surgery. 2002;132:80–5.
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Fukushima N, Campbell KA, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an updated experience. Ann Surg. 2004;239:788–97.
Wada K, Kozarek RA, Traverso LW. Outcomes following resection of invasive and noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg. 2005;189:632–6.
Nagai K, Doi R, Kida A, Kami K, Kawaguchi Y, Ito T, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinicopathologic characteristics and long-term follow-up after resection. World J Surg. 2008;32:271–8. discussion 9–80.
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, et al. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2006;6:17–32.
Kobari M, Egawa S, Shibuya K, Shimamura H, Sunamura M, Takeda K, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas comprise 2 clinical subtypes: differences in clinical characteristics and surgical management. Arch Surg. 1999;134:1131–6.
Matsumoto T, Aramaki M, Yada K, Hirano S, Himeno Y, Shibata K, et al. Optimal management of the branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36:261–5.
Sugiyama M, Izumisato Y, Abe N, Masaki T, Mori T, Atomi Y. Predictive factors for malignancy in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumours of the pancreas. Br J Surg. 2003;90:1244–9.
Salvia R, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Bassi C, Thayer SP, Falconi M, Mantovani W, et al. Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival following resection. Ann Surg. 2004;239:678–85.
Pelaez-Luna M, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Clain JE, Levy MJ, et al. Do consensus indications for resection in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm predict malignancy? A study of 147 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1759–64.
Wakabayashi T, Kawaura Y, Morimoto H, Watanabe K, Toya D, Asada Y, et al. Clinical management of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas based on imaging findings. Pancreas. 2001;22:370–7.
Yamaguchi K, Sugitani A, Chijiiwa K, Tanaka M. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor of the pancreas: assessing the grade of malignancy from natural history. Am Surg. 2001;67:400–6.
Irie H, Yoshimitsu K, Aibe H, Tajima T, Nishie A, Nakayama T, et al. Natural history of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of branch duct type: follow-up study by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004;28:117–22.
Kobayashi G, Fujita N, Noda Y, Ito K, Horaguchi J, Takasawa O, et al. Mode of progression of intraductal papillary-mucinous tumor of the pancreas: analysis of patients with follow-up by EUS. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:744–51.
Salvia R, Crippa S, Falconi M, Bassi C, Guarise A, Scarpa A, et al. Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: to operate or not to operate? Gut. 2007;56:1086–90.
Bassi C, Sarr MG, Lillemoe KD, Reber HA. Natural history of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN): current evidence and implications for management. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:645–50.
Rautou PE, Levy P, Vullierme MP, O’Toole D, Couvelard A, Cazals-Hatem D, et al. Morphologic changes in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a midterm follow-up study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:807–14.
Tanno S, Nakano Y, Nishikawa T, Nakamura K, Sasajima J, Minoguchi M, et al. Natural history of branch duct intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas without mural nodules: long-term follow-up results. Gut. 2008;57:339–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, K., Doi, R., Ito, T. et al. Single-institution validation of the international consensus guidelines for treatment of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16, 353–358 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0068-8