Abstract
Background
Although colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common causes of cancer mortality, early-stage detection improves survival rates dramatically. Because cancer impacts important metabolic pathways, the alteration of metabolite levels as a potential biomarker of early-stage cancer has been the focus of many studies. Here, we used CE-TOFMS, a novel and promising method with small injection volume and high resolution, to separate and detect ionic compounds based on the different migration rates of charged metabolites in order to detect metabolic biomarkers in patients with CRC.
Methods
A total of 56 patients with CRC (n = 14 each of Stages I-IV), 60 healthy controls, and 59 patients with colonic adenoma were included in this study. Metabolome analysis was conducted by CE-TOFMS on serum samples of patients and controls using the Advanced Scan package (Human Metabolome Technologies).
Results
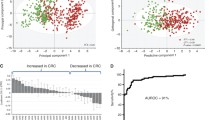
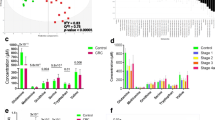
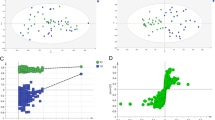
We obtained 334 metabolites in the serum, of which 139 were identified as known substances. Among these 139 known metabolites, 16 were correlated with CRC stage by upregulation and 44 by downregulation, with benzoic acid (r = −0.649, t = 11.653, p = 6.07599E−24), octanoic acid (r = 0.557, t = 9.183, p = 7.9557E−17), decanoic acid (r = 0.539, t = 8.749, p = 1.24352E−15), and histidine (r = −0.513, t = 8.194, p = 3.90224E−14) exhibiting significant correlation.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to determine the correlation between serum metabolites and CRC stage using CE-TOFMS. Our results show that benzoic acid exhibited excellent diagnostic power and could potentially serve as a novel disease biomarker for CRC diagnosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CE-TOFMS:
-
Capillary electrophoresis-time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- HCA:
-
Hierarchical cluster analysis
References
Herszenyi L, Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14(4):249–58 (epub 2010/05/26).
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29 (epub 2015/01/07).
Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL, et al. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia: implications for screening. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6(11):871–6 (epub 2005/11/01).
Asayama N, Oka S, Tanaka S, et al. Long-term outcomes after treatment for T1 colorectal carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016;31(3):571–8 (epub 2015/12/23).
Tanaka S, Saitoh Y, Matsuda T, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for management of colorectal polyps. J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(3):252–60 (epub 2015/01/07).
Yoshida N, Hisabe T, Inada Y, et al. The ability of a novel blue laser imaging system for the diagnosis of invasion depth of colorectal neoplasms. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49(1):73–80 (epub 2013/03/16).
Asayama N, Oka S, Tanaka S, et al. Long-term outcomes after treatment for pedunculated-type T1 colorectal carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. J Gastroenterol. 2016;51(7):702–10 (epub 2015/11/18).
Takeuchi Y, Hanafusa M, Kanzaki H, et al. An alternative option for “resect and discard” strategy, using magnifying narrow-band imaging: a prospective “proof-of-principle” study. J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(10):1017–26 (epub 2015/02/19).
Bretthauer M. Evidence for colorectal cancer screening. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24(4):417–25 (epub 2010/09/14).
Duffy MJ, van Rossum LG, van Turenhout ST, et al. Use of faecal markers in screening for colorectal neoplasia: a European group on tumor markers position paper. Int J Cancer Journal International du Cancer. 2011;128(1):3–11 (epub 2010/09/09).
Shimwell NJ, Wei W, Wilson S, et al. Assessment of novel combinations of biomarkers for the detection of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(3):123–32 (epub 2011/01/26).
Tanaka T, Tanaka M, Tanaka T, et al. Biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2010;11(9):3209–25 (epub 2010/10/20).
Fletcher RH. Carcinoembryonic antigen. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104(1):66–73 (epub 1986/01/01).
Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, et al. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996;348(9040):1467–71 (epub 1996/11/30).
Mandel JS, Bond JH, Church TR, et al. Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal occult blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(19):1365–71 (epub 1993/05/13).
Tiziani S, Lopes V, Gunther UL. Early stage diagnosis of oral cancer using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Neoplasia. 2009;11(3):269–76 (4p following epub 2009/02/27).
Kim K, Aronov P, Zakharkin SO, et al. Urine metabolomics analysis for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP. 2009;8(3):558–70 (epub 2008/11/15).
Denkert C, Budczies J, Kind T, et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolic profiling reveals different metabolite patterns in invasive ovarian carcinomas and ovarian borderline tumors. Cancer Res. 2006;66(22):10795–804 (epub 2006/11/17).
Jain M, Nilsson R, Sharma S, et al. Metabolite profiling identifies a key role for glycine in rapid cancer cell proliferation. Science. 2012;336(6084):1040–4 (epub 2012/05/26).
Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009;457(7231):910–4 (epub 2009/02/13).
Wise DR, Thompson CB. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010;35(8):427–33 (epub 2010/06/24).
Munoz-Pinedo C, El Mjiyad N, Ricci JE. Cancer metabolism: current perspectives and future directions. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e248 (epub 2012/01/13).
Gross S, Cairns RA, Minden MD, et al. Cancer-associated metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in acute myelogenous leukemia with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations. J Exp Med. 2010;207(2):339–44 (epub 2010/02/10).
Patti GJ, Yanes O, Siuzdak G. Innovation: metabolomics: the apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(4):263–9 (epub 2012/03/23).
Gu H, Gowda GA, Raftery D. Metabolic profiling: are we en route to better diagnostic tests for cancer? Future Oncol. 2012;8(10):1207–10 (epub 2012/11/08).
Gowda GA, Zhang S, Gu H, et al. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8(5):617–33 (epub 2008/09/13).
Scalbert A, Brennan L, Fiehn O, et al. Mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics: limitations and recommendations for future progress with particular focus on nutrition research. Metabolomics. 2009;5(4):435–58 (epub 2010/01/05).
Fan TW, Lane AN. NMR-based stable isotope resolved metabolomics in systems biochemistry. J Biomol NMR. 2011;49(3–4):267–80 (epub 2011/02/26).
Reaves ML, Rabinowitz JD. Metabolomics in systems microbiology. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011;22(1):17–25 (epub 2010/11/06).
Bain JR, Stevens RD, Wenner BR, et al. Metabolomics applied to diabetes research: moving from information to knowledge. Diabetes. 2009;58(11):2429–43 (epub 2009/10/31).
Yanes O, Tautenhahn R, Patti GJ, et al. Expanding coverage of the metabolome for global metabolite profiling. Anal Chem. 2011;83(6):2152–61 (epub 2011/02/19).
Nishiumi S, Kobayashi T, Ikeda A, et al. A novel serum metabolomics-based diagnostic approach for colorectal cancer. PloS one. 2012;7(7):e40459 (epub 2012/07/14).
Denkert C, Budczies J, Weichert W, et al. Metabolite profiling of human colon carcinoma–deregulation of TCA cycle and amino acid turnover. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:72 (epub 2008/09/19).
Guertin KA, Loftfield E, Boca SM, et al. Serum biomarkers of habitual coffee consumption may provide insight into the mechanism underlying the association between coffee consumption and colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;101(5):1000–11 (epub 2015/03/13).
Yoshida M, Hatano N, Nishiumi S, et al. Diagnosis of gastroenterological diseases by metabolome analysis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47(1):9–20 (epub 2011/11/02).
Amiot A, Dona AC, Wijeyesekera A, et al. (1)H NMR spectroscopy of fecal extracts enables detection of advanced colorectal neoplasia. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(9):3871–81 (epub 2015/07/28).
Zamani Z, Arjmand M, Vahabi F, et al. A metabolic study on colon cancer using (1)h nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochem Res Int. 2014;2014:348712 (epub 2014/09/10).
Zhu J, Djukovic D, Deng L, et al. Colorectal cancer detection using targeted serum metabolic profiling. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(9):4120–30 (epub 2014/08/16).
Suzuki Y, Fujimori T, Kanno K, et al. Metabolome analysis of photosynthesis and the related primary metabolites in the leaves of transgenic rice plants with increased or decreased Rubisco content. Plant Cell Environ. 2012;35(8):1369–79 (epub 2012/02/11).
Soga T, Ohashi Y, Ueno Y, et al. Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2003;2(5):488–94 (epub 2003/10/30).
Soga T, Sugimoto M, Honma M, et al. Serum metabolomics reveals gamma-glutamyl dipeptides as biomarkers for discrimination among different forms of liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;55(4):896–905 (epub 2011/02/22).
Hirayama A, Kami K, Sugimoto M, et al. Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Cancer Res. 2009;69(11):4918–25 (epub 2009/05/22).
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Seoul: From the 59th World Medical Association Assembly [database on the Internet]. 2008. Available from: http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/b3/17c.pdf.
Ohashi Y, Hirayama A, Ishikawa T, et al. Depiction of metabolome changes in histidine-starved Escherichia coli by CE-TOFMS. Mol BioSyst. 2008;4(2):135–47 (epub 2008/01/24).
Ooga T, Sato H, Nagashima A, et al. Metabolomic anatomy of an animal model revealing homeostatic imbalances in dyslipidaemia. Mol BioSyst. 2011;7(4):1217–23 (epub 2011/01/25).
Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, et al. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics. 2010;6(1):78–95 (epub 2010/03/20).
Junker BH, Klukas C, Schreiber F. VANTED: a system for advanced data analysis and visualization in the context of biological networks. BMC Bioinform. 2006;7:109 (epub 2006/03/08).
Brusilow SW, Valle DL, Batshaw M. New pathways of nitrogen excretion in inborn errors of urea synthesis. Lancet. 1979;2(8140):452–4 (epub 1979/09/01).
Ou K, Sarnoski P, Schneider KR, et al. Microbial catabolism of procyanidins by human gut microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014;58(11):2196–205 (epub 2014/07/22).
Chen JL, Fan J, Yan LS, Guo HQ, et al. Urine metabolite profiling of human colorectal cancer by capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry based on MRB. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:125890 (epub 2012/12/18).
Qiu Y, Cai G, Su M, et al. Urinary metabonomic study on colorectal cancer. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(3):1627–34 (epub 2010/02/04).
Fukutake N, Ueno M, Hiraoka N, et al. A novel multivariate index for pancreatic cancer detection based on the plasma free amino acid profile. PloS One. 2015;10(7):e0132223 (epub 2015/07/03).
Narayanan A, Baskaran SA, Amalaradjou MA, et al. Anticarcinogenic properties of medium chain fatty acids on human colorectal, skin and breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(3):5014–27 (epub 2015/03/10).
Murakami Y, Kubo S, Tamori A, et al. Comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and metabolome analysis in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16294 (epub 2015/11/06).
Kami K, Fujimori T, Sato H, et al. Metabolomic profiling of lung and prostate tumor tissues by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics. 2013;9(2):444–53 (epub 2013/04/02).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Kenjiro Kami for metabolomics analysis and Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) (B) to Y.N. (no. 16H05289) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), and by an Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through target-driven R&D (to Y.N.) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) (C) to K.U. (no. 15K08313) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) (C) to T.T. (no. 16K09322) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Kazuhiko Uchiyama and Nobuaki Yagi are equally contributing authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchiyama, K., Yagi, N., Mizushima, K. et al. Serum metabolomics analysis for early detection of colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol 52, 677–694 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1261-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-016-1261-6