Abstract
Background Recent studies have suggested that selenium intake may prevent the risk of developing prostate cancer. Results from some of these studies have given conflicting results. Because of these discrepant results we sought to explore the association between selenium intake and prostate cancer by conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature.
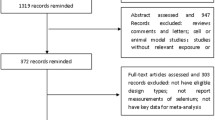
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE and Cochrane Library between 1966 and May 2005 for articles that examined the association between intake of selenium and the risk of prostate cancer. We abstracted the data from relevant studies. A random effects model was used to estimate pooled relative risks for both cohort and case–control studies. Heterogeneity was assessed graphically using a Funnel Plot.
Results: Sixteen studies (eleven cohort studies and five case–control studies) were included in the final analysis. The pooled relative risk of prostate cancer for any intake of selenium was 0.72 (0.61–0.84) for cohort studies and 0.74 (0.61–1.39) for case–control studies. The pooled relative risk of moderate intake was 0.74 (0.61–0.90) for cohort studies and 0.74 (0.39–1.39) for case–control studies. A dose-response trend was observed when we stratified the studies by disease severity.
Conclusion: The results of our systematic review suggest that selenium intake may reduce the risk of prostate cancer. The results confirm the need for large randomized controlled trials, which are ongoing, to answer this question.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C Redman MJ Xu YM Peng JA Scott C Payne LC Clark et al. (1997) ArticleTitleInvolvement of polyamines in selenomethionine induced apoptosis and mitotic alterations in human tumor cells Carcinogenesis 18 1195–202 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/18.6.1195 Occurrence Handle9214603
AC Griffin (1979) ArticleTitleRole of selenium in the chemoprevention of cancer Adv Cancer Res 29 419–442 Occurrence Handle382777
DJ Waters S Shen DM Cooley (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of dietary selenium supplementation on DNA damage and apoptosis in canine prostate J Natl Cancer Inst. 95 237–241 Occurrence Handle12569146
LC Clark GF Combs SuffixJr BW Turnbull EH Slate DK Chalker J Chow (1996) ArticleTitleEffects of selenium supplementation for cancer prevention in patients with carcinoma of the skin A randomized controlled trial. Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Study Group JAMA 276 1957–1963 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.276.24.1957 Occurrence Handle8971064
PA Brandt ParticleVan den MP Zeegers P Bode RA Goldbohm (2003) ArticleTitleToenail selenium levels and the subsequent risk of prostate cancer: A prospective cohort study Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12 866–871 Occurrence Handle14504196
DW West ML Slattery ML Robison TK French AW Mahoony (1991) ArticleTitleAdult dietary intake and prostate cancer risk in Utah: a case–control study with special emphasis on aggressive tumors Cancer Causes and Control 2 85–93 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00053126 Occurrence Handle1873441
M Etminan B Takkouche F. Caamano-Isorna (2004) ArticleTitleThe role of tomato products and lycopene in the prevention of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13 340–345 Occurrence Handle15006906
AJ Sutton KR Abrams DR Jones TA Sheldon F Song (2000) Methods for meta-analysis in medical research John Wiley & Sons Chichester 58
AM Walker JM Martin-Moreno FR. Artalejo (1988) ArticleTitleOdd man out: a graphical approach to meta-analysis Am J Public Health 78 961–966 Occurrence Handle3260455
B Takkouche C Cadarso-Suarez D. Spiegelman (1999) ArticleTitleEvaluation of old and new tests of heterogeneity in epidemiologic meta-analysis Am J Epidemiol 150 206–215 Occurrence Handle10412966
J Costa-Bouzas B Takkouche C Cadarso-Suarez D. Spiegelman (2001) ArticleTitleHepiMA: software for the identification of heterogeneity in meta-analysis Comput Methods Programs Biomed 64 101–107 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-2607(00)00087-0 Occurrence Handle11137192
LC Clark B Dalkin Krongrad GF Combs SuffixJr BW Turnbull HE Slate et al. (1998) ArticleTitleDecreased incidence of prostate cancer with selenium supplementation: results of a double-blind cancer prevention trial Br J Urol 81 730–734 Occurrence Handle9634050
AJ Duffield-Lillico BL Dalkin ME Reid BW Turnbull EH Slate ET Jacobs et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSelenium supplementation, baseline plasma selenium status and incidence of prostate cancer: an analysis of the complete treatment period of the nutritional prevention of cancer trial BJU Int. 91 608–612 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1464-410X.2003.04167.x Occurrence Handle12699469
K Lipsky MZ Ziguener L Schips K Plummer P Rehak G Humber (2004) ArticleTitleSelenium levels of patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer compared with control group Urology 63 912–916 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.urology.2003.12.028 Occurrence Handle15134980
H Li MJ Stampfer EL Giovannucci JL Morris WC Willett JM Gaziano J Ma et al. (2004) ArticleTitleA prospective study of plasma selenium levels and prostate cancer risk J Natl Cancer Inst 96 696–703 Occurrence Handle15126606
TJ Hartman D Albans P Pietinen AM Hartman M Rautalahti JA Tangrea et al. (1998) ArticleTitleThe association between baseline vitamin e, selenium and prostate cancer in the alpha-tocophorol, beta-carotene cancer prevention Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7 335–339 Occurrence Handle9568790
KJ Helzlsouer H Huang AJ Alberg S Hoffman A Burke EP Norkus et al. (2000) ArticleTitleAssociation between alpha-tocopherol, gamma-tocopherol, selenium, and subsequent prostate cancer J Natl Cancer Inst 92 2018–2023 Occurrence Handle10.1093/jnci/92.24.2018 Occurrence Handle11121464
GE Goodman S Schaffer DD Bankson MP Hughes GS Omenn (2001) ArticleTitlePredictors of serum selenium in cigarette smokers and the lack of association with lung and prostate cancer risk Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10 1069–1076 Occurrence Handle11588133
P Knekt A Aromaa J Maatela G Alfthan RK Aaran M Hakama (1990) ArticleTitleSerum selenium and subsequent risk of cancer among finnish men and women J Natl Cancer Inst 82 864–868 Occurrence Handle2332904
AM Nomura J Lee GN Stemmermann GF Combs (2000) ArticleTitleSerum selenium and subsequent risk of prostate cancer Cancer Epidemiol Biormarkers Prev 9 883–887
RJ Coates NS Weiss JR Daling JS Morris RF Labbe (1988) ArticleTitleSerum levels of selenium and retinol and the subsequent risk of cancer Am J Epidemiol 128 515–522 Occurrence Handle3046338
K Yoshizawa W Willett SJ Morris MJ Stampfer E Giovannucci CK Baskett (1998) ArticleTitleStudy of prediagnostic selenium level in selenium in toenails and the risk of advanced prostate cancer J Nal Cancer Inst 90 1219 Occurrence Handle10.1093/jnci/90.16.1219
JD Brooks EJ Metter DW Chan LJ Sokoll P Landis WG Nelson et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePlasma selenium levels before diagnosis and the risk of prostate cancer development J Urol 166 2034–2038 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005392-200112000-00006 Occurrence Handle11696701
NE Allen JS Morris RA Ngwenyama TJ Key (2004) ArticleTitleA case–control study of selenium in nails and prostate cancer risk in British men Br J Cancer 90 1392–1396 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.bjc.6601701 Occurrence Handle15054461
TM Vogt RG Ziegler BI Graubard (2003) ArticleTitleSerum selenium and risk of prostate cancer in US Blacks and Whites Int J Cancer 103 664–670 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.10866 Occurrence Handle12494476
P Ghadirian P Maisonneuve C Perret G Kennedy P Boyle D Krewsi (2000) ArticleTitleA case–control study of toenail selenium and cancer of the breast, colon and prostate Cancer Detection and Prevention 24 305–313 Occurrence Handle11059562
SA Bingham (1991) Validation of dietary assessment through biomarkers. Biomarkers of dietary exposure AP Kok P ’t Veer Particlevan (Eds) Proceedings of the third meeting on nutritional epidemiology Smith-Gordon London 41–52
DJ Hunter JS Morris CG Chute E Kushner GA Colditz FE Stampfer (1990) ArticleTitlePredictors of selenium concentration in human toenails Am J Epidemiol 132 114–122 Occurrence Handle2356804
Y Xia KE Hill DW Byrne Xu FB Burk (2005) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of selenium supplements in a low-selenium area of China Am J Clin Nurt 4 829–834
EA Klein IM Thompson SM Lippman PJ Goodman D Albanes PR Taylor (2003) ArticleTitleThe selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial Urol Oncol 21 59–65 Occurrence Handle12684129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors: ME initiated the project. ME, MF, MG and KC participated in writing the manuscript. ME will act as guarantor for the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etminan, M., FitzGerald, J.M., Gleave, M. et al. Intake of Selenium in the Prevention of Prostate Cancer: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis*. Cancer Causes Control 16, 1125–1131 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0334-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0334-2