Abstract
Objective
Epidemiological evidences indicate that diabetic individuals may have an increased risk of several cancers; however, the relationships between diabetes and risk of cancers of biliary tract or its subsites remain unclear.
Methods
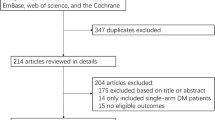
To provide a quantitative assessment of this relationship, we identified studies by a literature search of Medline (from 1 January 1966) and EMBASE (from 1 January 1974), through 31 July 2010, and by searching the reference lists of pertinent articles. Summary relative risks with corresponding 95% confidence intervals were calculated with a random-effect model.
Results
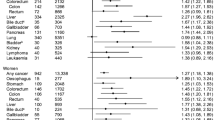
Analysis of 21 studies (8 case–control and 13 cohort studies) found that diabetes was associated with an increased risk of biliary tract cancer, compared with no diabetes (summary RRs = 1.43, 95% CI = 1.18–1.72), with significant heterogeneity among studies (p = 0.001). The positive association was also found between diabetes and risk of gallbladder cancer or extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, but not cancer of ampulla of Vater. No significant publication bias was found.
Conclusion
These findings strongly support the link between diabetes and increased risk of cancer of biliary tract and its subsites: gallbladder cancer or extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, but not cancer of ampulla of Vater.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BTC:
-
Biliary tract cancer
- GBC:
-
Gallbladder cancer
- ECC:
-
Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- AVC:
-
Cancer of ampulla of Vater
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- AORs:
-
Adjusted odds ratios
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
- IGFs:
-
Insulin-like growth factors
- SIR/SMR:
-
Standardized incidence/mortality ratio
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
References
Shaib Y, El-Serag HB (2004) The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 24:115–125
Jin F, Devesa SS, Chow WH et al (1999) Cancer incidence trends in urban shanghai, 1972–1994: an update. Int J Cancer 83:435–440
Shaib YH, Davila JA, McGlynn K, El-Serag HB (2004) Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a true increase? J Hepatol 40:472–477
Seyama Y, Makuuchi M (2007) Current surgical treatment for bile duct cancer. World J Gastroenterol 13:1505–1515
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, DeMatteo RP et al. (2001) Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 234:507–517; discussion 517–509
Larsson SC, Wolk A (2007) Obesity and the risk of gallbladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 96:1457–1461
Welzel TM, Graubard BI, El-Serag HB et al (2007) Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a population-based case–control study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1221–1228
Shaib YH, El-Serag HB, Nooka AK et al (2007) Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a hospital-based case–control study. Am J Gastroenterol 102:1016–1021
Welzel TM, Mellemkjaer L, Gloria G et al (2007) Risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a low-risk population: a nationwide case–control study. Int J Cancer 120:638–641
El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Javadi F (2006) The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:369–380
Ben Q, Cai Q, Li Z et al (2011) The relationship between new-onset diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer risk: a case–control study. Eur J Cancer 48:248–254
Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L et al (2008) The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch Physiol Biochem 114:23–37
Calle EE, Kaaks R (2004) Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 4:579–591
Adami HO, McLaughlin J, Ekbom A et al (1991) Cancer risk in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cancer Causes Control 2:307–314
Verlato G, Zoppini G, Bonora E, Muggeo M (2003) Mortality from site-specific malignancies in type 2 diabetic patients from Verona. Diabetes Care 26:1047–1051
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Grainge MJ, West J, Solaymani-Dodaran M, Aithal GP, Card TR (2009) The antecedents of biliary cancer: a primary care case–control study in the United Kingdom. Br J Cancer 100:178–180
Shebl FM, Andreotti G, Rashid A et al (2010) Diabetes in relation to biliary tract cancer and stones: a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Br J Cancer 103:115–119
La Vecchia C, Negri E, Franceschi S, D’Avanzo B, Boyle P (1994) A case–control study of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk. Br J Cancer 70:950–953
Khan ZR, Neugut AI, Ahsan H, Chabot JA (1999) Risk factors for biliary tract cancers. Am J Gastroenterol 94:149–152
Kuriki K, Hirose K, Tajima K (2007) Diabetes and cancer risk for all and specific sites among Japanese men and women. Eur J Cancer Prev 16:83–89
Tao LY, He XD, Qu Q et al (2010) Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case–control study in China. Liver Int 30:215–221
El-Serag HB, Engels EA, Landgren O et al (2009) Risk of hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancers after hepatitis C virus infection: a population-based study of US veterans. Hepatology 49:116–123
Chen HF, Chen P, Li CY (2010) Risk of malignant neoplasms of liver and biliary tract in diabetic patients with different age and sex stratifications. Hepatology 52:155–163
Ragozzino M, Melton LJ III, Chu CP, Palumbo PJ (1982) Subsequent cancer risk in the incidence cohort of Rochester, Minnesota, residents with diabetes mellitus. J Chronic Dis 35:13–19
Adami HO, Chow WH, Nyren O et al (1996) Excess risk of primary liver cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1472–1477
Wideroff L, Gridley G, Mellemkjaer L et al (1997) Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of patients hospitalized with diabetes mellitus in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:1360–1365
Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW et al (2005) Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA 293:194–202
Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T et al (2006) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Arch Intern Med 166:1871–1877
Khan M, Mori M, Fujino Y et al (2006) Site-specific cancer risk due to diabetes mellitus history: evidence from the Japan collaborative cohort (JACC) study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 7:253–259
Jamal MM, Yoon EJ, Vega KJ, Hashemzadeh M, Chang KJ (2009) Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancer among American veterans. World J Gastroenterol 15:5274–5278
La Vecchia C, Negri E, Decarli A, Franceschi S (1997) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of primary liver cancer. Int J Cancer 73:204–207
Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ (2004) Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol 159:1160–1167
Yagyu K, Lin Y, Obata Y et al (2004) Bowel movement frequency, medical history and the risk of gallbladder cancer death: a cohort study in Japan. Cancer Sci 95:674–678
Swerdlow AJ, Laing SP, Qiao Z et al (2005) Cancer incidence and mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes: a UK cohort study. Br J Cancer 92:2070–2075
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al (2010) Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 362:1090–1101
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787
Hsing AW, Gao YT, Devesa SS, Jin F, Fraumeni JF Jr (1998) Rising incidence of biliary tract cancers in Shanghai, China. Int J Cancer 75:368–370
Cai HH, Sun YM, Bai JF et al (2008) Relationship between the GH-IGFs axis and the proliferation of bile duct cancer cell line QBC939 in vitro. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 7:76–81
Alvaro D, Barbaro B, Franchitto A et al (2006) Estrogens and insulin-like growth factor 1 modulate neoplastic cell growth in human cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 169:877–888
Festi D, Dormi A, Capodicasa S et al (2008) Incidence of gallstone disease in Italy: results from a multicenter, population-based Italian study (the MICOL project). World J Gastroenterol 14:5282–5289
Stone BG, Van Thiel DH (1985) Diabetes mellitus and the liver. Semin Liver Dis 5:8–28
Biddinger SB, Haas JT, Yu BB et al (2008) Hepatic insulin resistance directly promotes formation of cholesterol gallstones. Nat Med 14:778–782
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M (2008) Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 371:569–578
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interest among all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, HB., Yu, T., Liu, C. et al. Diabetes mellitus and increased risk of biliary tract cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 22, 837–847 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9754-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9754-3