Abstract
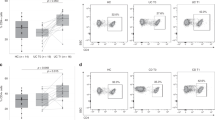
Evidence suggests that CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells play a crucial role in the suppression of intestinal inflammation. However, their role in the suppression of inflammatory bowel disease has not yet been addressed. We examined the proportion of regulatory T cells in inflammatory bowel disease. First, we isolated CD4+CD45RO+CD25+ T cells from the peripheral blood of healthy persons and showed that these cells suppressed T cell proliferation profoundly and expressed FoxP3 abundantly, revealing that they are regulatory cells. Then the proportion of CD45RO+CD25+ in peripheral blood CD4+ T cells was analyzed in patients and healthy controls by flow cytometry. CD4+CD45RO+CD25+ T cell frequency was significantly lower in active ulcerative colitis than in the control and inactive ulcerative colitis. CD4+CD45RO+CD25+ T cell frequency was inversely correlated with the clinical and endoscopic severity of ulcerative colitis. These results suggest that a deficiency of regulatory T cells is associated with the progression of ulcerative colitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiocchi C: Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 115:182–205, 1998
Bouma G, Strober W: The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 3:521–533, 2003
Strober W, Nakamura K, Kitani A: The SAMP/1/it mouse: another step closer to modeling human inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest 107:667–670, 2001
Asano M, Toda M, Sakaguchi N, Sakaguchi S: Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T cell subpopulation. J Exp Med 184:387–396, 1996
Takahashi T, Kuniyasu Y, Toda M, Sakaguchi N, Itoh M, Iwata M, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi S: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells: induction of autoimmune disease by breaking their anergi/c/uppressive state. Int Immuol 10:1969–1980, 1998
Thornton AM, Shevach EM: CD25+CD4+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med 188:287–296, 1998
Sakaguchi S: Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 22:531–562, 2004
Shevach EM: CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol 2:389–400, 2002
Read S, Malmstrom V, Powrie F: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25+CD4+ regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 192:295–302, 2000
Mottet C, Ublig HH, Powrie F: Cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 170:3939–3943, 2003
Itoh M, Takahashi T, Sakaguchi N, Kuniyasu Y, Shimizu J, Otsuka F, Sakaguchi S: Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunologic self-tolerance. J Immunol 162:5317–5326, 1999
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Stassen M, Tuettenberg A, Knop J, Enk AH: Identification and functional characterization of human CD4+CD25+ T cells with regulatory properties isolated from peripheral blood. J Exp Med 193:1285–1294, 2001
Levings MK, Sangregorio R, Roncarolo MG: Human CD25+CD4+ T regulatory cells suppress naive and memory T cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of function. J Exp Med 193:1295–1301, 2001
Dieckmann D, Plottner H, Berchtold S, Berger T, Schuler G: Ex vivo isolation and characterization of CD4+CD25+ T cells with regulatory properties from human blood. J Exp Med 193:1303–1310, 2001
Baecher-Allan C, Brown JA, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA: CD4+CD25high regulatory cells in human peripheral blood. J Immunol 167:1245–1253, 2001
Taylor PA, Lees CJ, Blazar BR: The infusion of ex vivo activated and expanded CD4+CD25+ immune regulatory cells inhibits graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood 99:3493–3499, 2002
Salomon B, Lenschow DJ, Rhee L, Ashourian N, Singh B, Sharpe A, Bluestone JA: B/7/D28 costimulation is essential for the homeostasis of the CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells that control autoimmune diabetes. Immunity 12:431–440, 2000
Liu MF, Wang CR, Fung LL, Wu CR: Decreased CD4+CD25+ T cells in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol 59:198–202, 2004
de Kleer IM, Wedderburn LR, Taams LS, Patel A, Varsani H, Klein M, de Jager W, Pugayung G, Giannoni F, Rijkers G, Albani S, Kuis W, Prakken B: CD4+CD25bright regulatory T cells actively regulate inflammation in the joints of patients with the remitting form of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Immunol 172:6435–6443, 2004
Cao D, Malmstrom V, Baecher-Allan C, Hafler D, Klareskog L, Trollmo C: Isolation and function characterization of regulatory CD25brightCD4+ T cells from the target organ of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 33:215–223, 2003
Viglietta V, Baecher-Allan C, Weiner HL, Hafler DA. Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 199:971–979, 2004
Shimoyama T, Sawada K, Hiwatashi N, Sawada T, Matsueda K, Munakata A, Asakura H, Tanaka T, Kasukawa R, Kimura K, Suzuki Y, Nagamachi Y, Muto T, Nagawa H, Iizuka B, Baba S, Nasu M, Kataoka T, Kashiwagi N, Saniabadi AR: Safety and efficacy of granulocyte and monocyte adsorption apheresis in patients with active ulcerative colitis: a multicenter study. J Clin Apheresis 16:1–9, 2001
Hanai H, Watanabe F, Takeuchi K, Iida T, Yamada M, Iwaoka Y, ABBY S, Matsushita I, Sato Y, Tozawa K, Arai H, Furuta T, Sugimoto K, Bjarnason I: Leukocyte adsorptive apheresis for the treatment of active ulcerative colitis: a prospective, uncontrolled, pilot study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:28–35, 2003
Rachmilewitz D: Coated mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) versus sulphasalazine in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis:a randomized trial. Br Med J 298:82–86, 1989
Makita S, Kanai T, Oshima S, Uraushihara K, Totsuka T, Sawada T, Nakamura T, Koganei K, Fukushima T, Watanabe M: CD4+CD25bright T cells in human intestinal lamina propria as regulatory cells. J Immunol 173:3119–3130, 2004
Nakamura K, Kitani A, Fuss I, Pedersen A, Harada N, Nawata H, Strober W: TGF–Β1 plays an important role in the mechanism of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell activity in both humans and mice. J Immunol 172:834–842, 2004
Taams LS, Vukkmannovic-Stejic M, Smith J, Dunne PJ, Fletcher JM, Plunkett FJ, Ebeling SB, Lombardi G, Rustin MH, Bijlsma JWJ, Lafeber FPJG, Salmon M, Akbar AN: Antigen-specific T cell suppression by human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol 32:1621–1630, 2002
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S: Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor FoxP3. Science 299:1057–1061, 2003
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY: FoxP3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330–336, 2003
Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA, Ramsdell F: An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol 4:337–342, 2003
Chatila TA, Blaeser F, Ho N, Lederman HM, Voulgaropoulos C, Helms C, Bowcock AM: JM2, encoding a fork head-related protein, is mutated in X-linked autoimmunity-allergic disregulation syndrome. J Clin Invest 106:75–81, 2000
Wildin RS, Ramsdell F, Peake J, Faravelli F, Casanova JL, Buist N, Levy-Lahad E, Mazzella M, Goulet O, Perroni L, Bricarelli FD, Byrne G, McEuen M, Proll S, Appleby M, Brunkow ME: X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat Genet 27:18–20, 2001
Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA, Wilkinson JE, Galas D, Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F: Disruption of a new forkhea/d/inged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet 27:68–73, 2001
Yagi H, Nomura T, Nakamura K, Yamazaki S, Kitawaki T, Hori S, Maeda M, Onodera M, Uchiyama T, Fujii S, Sakaguchi S: Crucial role of FOXP3 in the development and function of human CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Int Immunol 16:1643–1656, 2004
Asseman C, Mauze S, Leach MW Coffman RL, Powrie F: An essential role for Interleukin 10 in the function of regulatory T cells that inhibit intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 190:995–1004, 1999
Nakamura K, Kiani A, Strober W: Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor Β. J Exp Med 194:629–644, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by Health and Labour Science Research Grants from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and Research on Measures for Intractable Disease.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Nakamura, K., Honda, K. et al. An Inverse Correlation of Human Peripheral Blood Regulatory T Cell Frequency with the Disease Activity of Ulcerative Colitis. Dig Dis Sci 51, 677–686 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3191-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3191-2