Abstract
Background
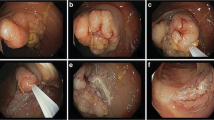
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is used for treatment of sessile and flat colonic adenomas. There is limited data comparing polyp recurrence between piecemeal and en-bloc resections.
Aim
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the incidence density and predictive factors for polyp recurrence after piecemeal and en-bloc resections.
Methods
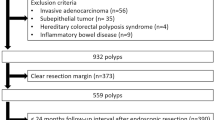
Patients undergoing EMR of flat or sessile adenomas ≥10 mm were included. Incidence density (ID) and incidence rate ratio (IRR) of polyp recurrence were calculated. Predictive factors for recurrence were assessed by multivariate analysis using logistic regression.
Results
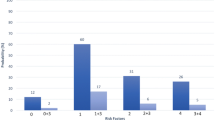
A total of 105 patients (males 54, mean age 68) with 121 polyps were included. Sixty-seven polyps (mean size ± SD, 23.3 ± 9.2 mm) were resected piecemeal and 54 polyps (mean size 14.7 ± 5.1 mm) were resected en-bloc. There were 12 recurrences in the piecemeal group and two in the en-bloc group. The ID of polyp recurrence in the piecemeal group was 13.1 (95% CI 7.43–23.03) and in the en-bloc group was 2.7 (95% CI 0.67–10.78) per 100 person-years of follow-up. Piecemeal resections were 5.5 (95% CI 1.1–30.48, P = 0.045) times and flat polyps were 6.6 (95% CI 1.22–35.53, P = 0.028) times more likely to result in recurrence compared to en-bloc resections and sessile polyps, respectively. In the piecemeal group, additional use of argon plasma coagulation (APC) did not affect the recurrence (OR 0.46, P = 0.29).
Conclusions
Piecemeal resections and flat polyps are associated with higher recurrence following EMR. Additional use of APC did not affect the recurrence rates after piecemeal resection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seewald S, Soehendra N. Perforation: part and parcel of endoscopic resection? Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:602–605.
Fukami N, Lee JH. Endoscopic treatment of large sessile and flat colorectal lesions. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006;22:54–59.
Zlatanic J, Waye JD, Kim PS, Baiocco PJ, Gleim GW. Large sessile colonic adenomas: use of argon plasma coagulator to supplement piecemeal snare polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:731–735.
Arebi N, Swain D, Suzuki N, Fraser C, Price A, Saunders BP. Endoscopic mucosal resection of 161 cases of large sessile or flat colorectal polyps. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:859–866.
Kanamori T, Itoh M, Yokoyama Y, Tsuchida K. Injection-incision–assisted snare resection of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;43:189–195.
Khashab M, Eid E, Rusche M, Rex DK. Incidence and predictors of “late” recurrences after endoscopic piecemeal resection of large sessile adenomas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:344–349.
Hotta K, Fujii T, Saito Y, Matsuda T. Local recurrence after endoscopic resection of colorectal tumors. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24:225–230.
Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J Indian Med Assoc. 2009;107:403–405.
Endoscopic Classification Review Group. Update on the Paris classification of superficial neoplastic lesions in the digestive tract. Endoscopy. 2005;37:570–578.
Kobayashi N, Saito Y, Sano Y, et al. Determining the treatment strategy for colorectal neoplastic lesions: endoscopic assessment or the non-lifting sign for diagnosing invasion depth? Endoscopy. 2007;39:701–705.
Atkin WS, Saunders BP. Surveillance guidelines after removal of colorectal adenomatous polyps. Gut. 2002;51:V6–V9.
Chan YH. Biostatistics 202: logistic regression analysis. Singapore Med J. 2004;45:149–153.
Luigiano C, Consolo P, Scaffidi MG, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection for large and giant sessile and flat colorectal polyps: a single-center experience with long-term follow-up. Endoscopy. 2009;41:829–835.
Chan YH. Biostatistics 203. Survival analysis. Singapore Med J. 2004;45:249–256.
Ferrara F, Luigiano C, Ghersi S, et al. Efficacy, safety and outcomes of ‘inject and cut’ endoscopic mucosal resection for large sessile and flat colorectal polyps. Digestion. 2010;82:213–220.
Hurlstone DP, Sanders DS, Cross SS, George R, Shorthouse AJ, Brown S. A prospective analysis of extended endoscopic mucosal resection for large rectal villous adenomas: an alternative technique to transanal endoscopic microsurgery. Colorectal Dis. 2005;7:339–344.
Regula J, Wronska E, Polkowski M, et al. Argon plasma coagulation after piecemeal polypectomy of sessile colorectal adenomas: long-term follow-up study. Endoscopy. 2003;35:212–218.
Mahadeva S, Rembacken BJ. Standard “inject and cut” endoscopic mucosal resection technique is practical and effective in the management of superficial colorectal neoplasms. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:417–422.
Higaki S, Hashimoto S, Harada K, et al. Long-term follow-up of large flat colorectal tumors resected endoscopically. Endoscopy. 2003;35:845–849.
Hurlstone DP, Sanders DS, Cross SS, et al. Colonoscopic resection of lateral spreading tumours: a prospective analysis of endoscopic mucosal resection. Gut. 2004;53:1334–1339.
Brooker JC, Saunders BP, Shah SG, Thapar CJ, Suzuki N, Williams CB. Treatment with argon plasma coagulation reduces recurrence after piecemeal resection of large sessile colonic polyps: a randomized trial and recommendations. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55:371–375.
Conio M, Repici A, Demarquay JF, Blanchi S, Dumas R, Filiberti R. EMR of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:234–241.
Conflict of interest
Dr K. Ragunath has received speaker honoraria, research support and educational grants from Olympus-Keymed UK, Cook Medical UK, Astra-Zeneca UK and BARRX Medical, USA. Drs J. Mannath, V. Subramanian, R. Singh and E. Telakis have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannath, J., Subramanian, V., Singh, R. et al. Polyp Recurrence After Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Sessile and Flat Colonic Adenomas. Dig Dis Sci 56, 2389–2395 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1609-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1609-y