Abstract
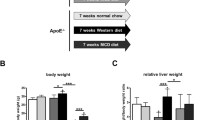
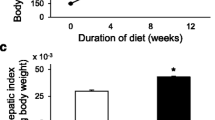
The present study was aimed (1) to investigate the effect of cholesterol and fat enriched diets on the development of steatohepatitis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice, and (2) to study the chronological relationships between the development of hepatic alterations, hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerotic lesions in this experimental model. The study consisted of two protocols. Protocol 1 was used in 90 mice subdivided in groups of 18. For 10 weeks, each group was given a diet with different fat and cholesterol contents. Protocol 2 was used in 42 mice, subdivided in four groups. Each group was given a diet enriched with cholesterol and palm oil and they were sacrificed at 8, 13, 18 and 24 weeks of age. Results were as following. (1) Mice given high fat/high cholesterol diets developed an impairment of liver histology consisting of fat accumulation, macrophage proliferation, and inflammation. (2) These effects were modulated by the type of fat: olive oil was mainly associated with macrovesicular steatosis and cholesterol plus palm oil with severe steatohepatitis. (3) There was a chronological and quantitative relationship between liver impairment and the formation of atheromatous lesions. We conclude that apolipoprotein E-knockout mice may be a useful model for investigating the mechanisms of diet-induced steatohepatitis. (Mol Cell Biochem 268: 53–58, 2008)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moghadasian MH: Experimental atherosclerosis. A historical overview. Life Sci 70: 855–865, 2002
Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrahita JA, Maeda N: Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science 258: 468–471, 1992
Plump AS, Smith JD, Hayek T, Aalto-Setala K, Walsh A, Verstuyft JG, Rubin EM, Breslow JL: Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell 71: 343–353, 1992
van Ree JH, van der Broek WJ, Dahlmans VE, Groot PH, Vidgeon-Hart M, Frants RR, Wieringa B, Havekes LM, Hofker MH: Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in heterozygous apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 111: 25–37, 1994
Hofker MH, van Vlijmen BJ, Havekes LM: Transgenic mouse models to study the role of ApoE in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 137: 1–11, 1998
Moghadasian MH, Pritchard HP, McManus BM, Frohlich JJ: “Tall-oil” derived phytosterol mixture reduces atherosclerosis in apo E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17: 11, 1997
Osada J, Joven J, Maeda N: The value of apolipoprotein E knockout mice for studying the effects of dietary fat and cholesterol on atherogenesis. Curr Opin Lipidol 11: 25–29, 2000
Tous M, Ferré N, Camps J, Joven J: Efectos de la dieta hipercolesterolemiante en el animal de experimentación. Clin Invest Arterioscler 14: 107, 2002
Koteish A, Diehl AM: Animal models of steatosis. Sem Liver Dis 21: 89–104, 2001
Piedrahita JA, Zhang SH, Hagaman JR, Oliver PM, Maeda N: Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E-gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 4471–4475, 1992
Calleja L, París MA, Paul A, Vilella E, Joven J, Jiménez A, Beltran G, Uceda M, Maeda N, Osada J: Low-cholesterol and high-fat diets reduce atherosclerotic lesion development in apoE-knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 2368–2375, 1999
Laurila A, Cole SP, Merat S, Obonyo M, Palinski W, Fierer J, Witztum JL: High-fat, high-cholesterol diet increases the incidence of gastritis in LDL receptor-negative mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 21: 991–996, 2001
Tangirala RK, Rubin EM, Palinski Q: Quantitation of atherosclerosis in murine models: Correlation between lesions in the aortic origin and in the entire aorta, and differences in the extent of lesion between sexes in LDL receptor-deficient and apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Lipid Res 36: 2320–2328, 1995
Paigen B, Morrow A, Holmes PA, Mitchell D, Williams RA: Quantitative assessment of atherosclerotic lesions in mice. Atherosclerosis 68: 231–240, 1987
Vilella E, Joven J, Fernandez M, Vilaró S, Brunzell JD, Olivecrona T, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G: Lipoprotein lipase in human plasma is mainly inactive and associated with cholesterol-rich lipoproteins. J Lipid Res 34: 1555–1564, 1993
Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Ott BJ: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc 55: 434–438, 1980
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Med Clin North Am 80: 1147–1166, 1996
Ludwig J, McGill DB, Lindor KD: Review: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12: 398–403, 1997
Baffy G, Zhang CY, Glickman JN, Lowell BB: Obesity-related fatty liver is unchanged in mice deficient for mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2. Hepatology 35: 753–761, 2002
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Besceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroentrol 94: 2467–2474, 1999
Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Hwang J, Chacko VP, Diehl AM: Hepatic hyperplasia in noncirrhotic fatty livers: Is obesity-related hepatic steatosis a premalignant condition? Cancer Res 61: 5016–5023, 2001
Koteish A, Diehl AM: Animal models of steatohepatitis. Best Practice Res Clin Gastroenterol 16: 679–690, 2002
Shimano H, Horton JD, Hammer RE, Shimomura I, Brown MS, Goldstein JL: Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J Clin Invest 98: 1575–1584, 1996
Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Richardson JA, Ikemoto S, Bashmakov Y, Goldstein JL, Brown MS: Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in transgenic mice expressing nuclear SREP-1c in adipose tissue: Model for congenital generalized lipodystrophy. Genes Dev 12: 3182s–3194s, 1998
Moitra J, Mason MM, Olive M, Krylov D, Gavrilova O, Marcus-Samuels B, Feigenbaum L, Lee E, Aoyama T, Eckhaus M, Reitman ML, Vinson C: Life without white fat: A transgenic mouse. Genes Dev 12: 3168–3181, 1998
Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Lane MD, Clemens M, Diehl AM: Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: Implications for pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 2557–2562, 1997
Chavin KD, Yang S, Lin HZ, Chatham J, Chacko VP, Hoek JB, Walajtys-Rode E, Rashid A, Chen CH, Huang CC, Wu TC, Lane MD, Diehl AM: Obesity induces expression of uncoupling protein-2 in hepatocytes and promotes liver ATP depletion. J Biol Chem 274: 5692–5700, 1999
Faggioni R, Fantuzzi G, Gabay C, Moser A, Dinarello CA, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C: Leptin deficiency enhances sensitivity to endotoxin-induced lethality. Am J Physiol 276: R136–R142, 1999
Poulsom R: Morphological changes of organs after sucrose or fructose feeding. Progr Biochem Pharmacol 21: 104–134, 1986
Kuipers F, van Ree JM, Hofker MH, Wolters H, In’t Veld G, Havinga R, Vonk RJ, Princen HM, Havekes LM: Altered lipid metabolism in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice does not affect cholesterol balance across the liver. Hepatology 24: 241–247, 1996
Sehayek E, Shefer S, Nguyen LB, Ono JG, Merkel M, Breslow JL: Apolipoprotein E regulates dietary cholesterol absorption and biliary cholesterol excretion: Studies in C57BL/6 apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3433–3437, 2000
Ferré N, Camps J, Paul A, Cabré M, Calleja L, Osada J, Joven J: Effects of high-fat, low-cholesterol diets on hepatic lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biochem 218: 165–169, 2001
Diehl AM: Nonalcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis IV. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease abnormalities in macrophage function and cytokines. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G1–G5, 2002
Pessayre D, Mansouri A, Fromenty B: Nonalcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis V. Mitochondrial dysfunction in steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G193–G199, 2002
Sanyal AJ, Campbell-Sargent C, Mirshahi F, Rizzo WB, Contos MJ, Sterling RK, Luketic VA, Shiffman ML, Clore JN: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 120: 1183–1192, 2001
Chitturi S, Farrell GC: Ethiopathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitits. Sem Liver Dis 21: 27–41, 2001
Liao F, Andalibi A, Qiao JH, Allayee H, Fogelman AM, Lusis AJ: Genetic evidence for a common pathway mediating oxidative stress, inflammatory gene induction, and aortic fatty streak formation in mice. J Clin Invest 94: 877–884, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tous, M., Ferré, N., Camps, J. et al. Feeding apolipoprotein E-knockout mice with cholesterol and fat enriched diets may be a model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol Cell Biochem 268, 53–58 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-2997-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-2997-0