Abstract
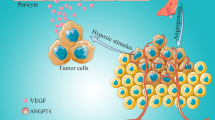
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) is a member of the Ang family, which plays an important role in angiogenesis during the development and growth of human cancers. Ang2’s role in angiogenesis generally is considered as an antagonist for Ang1, inhibiting Ang1-promoted Tie2 signaling, which is critical for blood vessel maturation and stabilization. Ang2 modulates angiogenesis in a cooperative manner with another important angiogenic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor A. Genetic studies have revealed that Ang2 also is critical in lymphangiogenesis during development. However, new evidence suggests more complicated roles for Ang2 in angiogenesis in physiologic processes and invasive phenotypes of cancer cells during progression of human cancers. This article discusses recent studies of Ang2 in angiogenesis and the implication of Ang2 as a therapeutic target as well as a potential inhibitor for antiangiogenesis treatment for cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Carmeliet P, Jain RK: Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407:249–257.
Shim WS, Ho IA, Wong PE: Angiopoietin: a TIE(d) balance in tumor angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 2007, 5:655–665.
Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, et al.: Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning [see comments]. Cell 1996, 87:1161–1169.
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, et al.: Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis [see comments]. Cell 1996, 87:1171–1180.
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, et al.: Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 1998, 282:468–471.
Thurston G, Suri C, Smith K, et al.: Leakage-resistant blood vessels in mice transgenically overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 1999, 286:2511–2514.
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, et al.: Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis [see comments]. Science 1997, 277:55–60.
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, et al.: Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 1999, 284:1994–1998.
Lobov IB, Brooks PC, Lang RA: Angiopoietin-2 displays VEGF-dependent modulation of capillary structure and endothelial cell survival in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99:11205–11210.
Gale NW, Thurston G, Hackett SF, et al.: Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by Angiopoietin-1. Dev Cell 2002, 3:411–423.
Dellinger M, Hunter R, Bernas M, et al.: Defective remodeling and maturation of the lymphatic vasculature in Angiopoietin-2 deficient mice. Dev Biol 2008, 319:309–320.
Rao S, Lobov IB, Vallance JE, et al.: Obligatory participation of macrophages in an angiopoietin 2-mediated cell death switch. Development 2007, 134:4449–4458.
Jones N, Iljin K, Dumont DJ, et al.: Tie receptors: new modulators of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001, 2:257–267.
Scharpfenecker M, Fiedler U, Reiss Y, et al.: The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 destabilizes quiescent endothelium through an internal autocrine loop mechanism. J Cell Sci 2005, 118:771–780.
Hildbrand P, Cirulli V, Prinsen RC, et al.: The role of angiopoietins in the development of endothelial cells from cord blood CD34+ progenitors. Blood 2004, 104:2010–2019.
Lemieux C, Maliba R, Favier J, et al.: Angiopoietins can directly activate endothelial cells and neutrophils to promote proinflammatory responses. Blood 2005, 105:1523–1530.
Tait CR, Jones PF: Angiopoietins in tumours: the angiogenic switch. J Pathol 2004, 204:1–10.
Cao Y, Sonveaux P, Liu S, et al.: Systemic overexpression of angiopoietin-2 promotes tumor microvessel regression and inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cancer Res 2007, 67:3835–3844.
Lee OH, Fueyo J, Xu J, et al.: Sustained angiopoietin-2 expression disrupts vessel formation and inhibits glioma growth. Neoplasia 2006, 8:419–428.
Bach F, Uddin FJ, Burke D: Angiopoietins in malignancy. Eur J Surg Oncol 2007, 33:7–15.
Imanishi Y, Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, et al.: Angiopoietin-2 stimulates breast cancer metastasis through the {alpha}5{beta}1 integrin-mediated pathway. Cancer Res 2007, 67:4254–4263.
Guo P, Imanishi Y, Cackowski FC, et al.: Up-regulation of angiopoietin-2, matrix metalloprotease-2, membrane type 1 metalloprotease, and laminin 5 gamma 2 correlates with the invasiveness of human glioma. Am J Pathol 2005, 166:877–890.
Hu B, Guo P, Fang Q, et al.: Angiopoietin-2 induces human glioma invasion through the activation of matrix metalloprotease-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100:8904–8909.
Eklund L, Olsen BR: Tie receptors and their angiopoietin ligands are context-dependent regulators of vascular remodeling. Exp Cell Res 2006, 312:630–641.
Kanda S, Miyata Y, Mochizuki Y, et al.: Angiopoietin 1 is mitogenic for cultured endothelial cells. Cancer Res 2005, 65:6820–6827.
Cho CH, Kim KE, Byun J, et al.: Long-term and sustained COMP-Ang1 induces long-lasting vascular enlargement and enhanced blood flow. Circ Res 2005, 97:86–94.
Harfouche R, Hussain SN: Signaling and regulation of endothelial cell survival by angiopoietin-2. Am J Physiol 2006, 291:H1635–H1645.
Lee OH, Xu J, Fueyo J, et al.: Angiopoietin-2 decreases vascular endothelial growth factor expression by modulating HIF-1 alpha levels in gliomas. Oncogene 2008, 27:1310–1314.
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, et al.: Vascularspecific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 2000, 407:242–248.
Carlson TR, Feng Y, Maisonpierre PC, et al.: Direct cell adhesion to the angiopoietins mediated by integrins. J Biol Chem 2001, 276:26516–26525.
Dallabrida SM, Ismail N, Oberle JR, et al.: Angiopoietin-1 promotes cardiac and skeletal myocyte survival through integrins. Circ Res 2005, 96:e8–e24.
Davis S, Papadopoulos N, Aldrich TH, et al.: Angiopoietins have distinct modular domains essential for receptor binding, dimerization and superclustering. Nat Struct Biol 2003, 10:38–44.
Weber CC, Cai H, Ehrbar M, et al.: Effects of protein and gene transfer of the angiopoietin-1 fibrinogen-like receptor-binding domain on endothelial and vessel organization. J Biol Chem 2005, 280:22445–22453.
Cascone I, Napione L, Maniero F, et al.: Stable interaction between alpha5beta1 integrin and Tie2 tyrosine kinase receptor regulates endothelial cell response to Ang-1. J Cell Biol 2005, 170:993–1004.
Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, Guo P, et al.: Angiopoietin 2 induces glioma cell invasion by stimulating matrix metalloprotease 2 expression through the {alpha}v{beta}1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res 2006, 66:775–783.
Wu Y, Chen L, Zheng PS, et al.: beta 1-Integrin-mediated glioma cell adhesion and free radical-induced apoptosis are regulated by binding to a C-terminal domain of PGM/versican. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:12294–12301.
Phelps ED, Updike DL, Bullen EC, et al.: Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of angiopoietin-2 expression mediated by IGF and PDGF in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006, 290:C352–C361.
Kim I, Kim JH, Ryu YS, et al.: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha upregulates angiopoietin-2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 269:361–365.
Huang YQ, Li JJ, Hu L, et al.: Thrombin induces increased expression and secretion of angiopoietin-2 from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood 2002, 99:1646–1650.
Ye F, Florian M, Magder SA, et al.: Regulation of angiopoietin and Tie-2 receptor expression in non-reproductive tissues by estrogen. Steroids 2002, 67:305–310.
Cohen B, Barkan D, Levy Y, et al.: Leptin induces angiopoietin-2 expression in adipose tissues. J Biol Chem 2001, 276:7697–7700.
Yao D, Taguchi T, Matsumura T, et al.: High glucose increases angiopoietin-2 transcription in microvascular endothelial cells through methylglyoxal modification of mSin3A. J Biol Chem 2007, 282:31038–31045.
Potente M, Urbich C, Sasaki K, et al.: Involvement of Foxo transcription factors in angiogenesis and postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Invest 2005, 115:2382–2392.
Xue Y, Cao R, Nilsson D, et al.: FOXC2 controls Ang-2 expression and modulates angiogenesis, vascular patterning, remodeling, and functions in adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105:10167–10172.
Schliemann C, Bieker R, Thoennissen N, et al.: Circulating angiopoietin-2 is a strong prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2007, 21:1901–1906.
Scholz A, Rehm VA, Rieke S, et al.: Angiopoietin-2 serum levels are elevated in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 2007, 102:2471–2481.
Park JH, Park KJ, Kim YS, et al.: Serum angiopoietin-2 as a clinical marker for lung cancer. Chest 2007, 132:200–206.
White RR, Shan S, Rusconi CP, et al.: Inhibition of rat corneal angiogenesis by a nuclease-resistant RNA aptamer specific for angiopoietin-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100:5028–5033.
Oliner J, Min H, Leal J, et al.: Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by selective inhibition of angiopoietin-2. Cancer Cell 2004, 6:507–516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, B., Cheng, SY. Angiopoietin-2: Development of inhibitors for cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 11, 111–116 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-009-0017-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-009-0017-3