Abstract
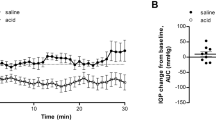
Mainly composed of mucins, mucus secreted by goblet cells in the intestinal epithelium is critically involved in the protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa. The hypothesis that bile and some bile salts can induce mucus secretion was tested in the isolated perfused rat colon. Mucus release was evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and supported by histological analysis. Luminal administration of bile extract (1%) provoked mucus secretion in the rat colon. Deoxycholate (0.5–10 mM) induced a dose-dependent increase in rat colonic mucus release. Chenodeoxycholate (10 mM) and hyodeoxycholate (10 mM) also evoked mucus discharge, whereas 10 mM cholate, 10 mM ursodeoxycholate, or Tween-20 did not release mucus. Taurine-conjugated bile salts (deoxycholate, hyodeoxycholate, and chenodeoxycholate) were less potent mucus secretagogues than the corresponding unconjugated forms. The deoxycholate-induced mucus discharge was not altered by pharmacological blockers (tetrodotoxin, atropine), indomethacin, mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen, doxantrazole), H1 histamine receptor antagonist (pyrilamine), or 5-HT receptor antagonists (ketanserin, ondansetron, SDZ 205-557). Our findings suggest that some bile salts, especially in the unconjugated form, may provoke colonic mucus secretion, probably through a direct action on mucus-secreting cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forstner G, Forstner J: Gastrointestinal mucus. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1994, pp 1255–1283
Barcelo A, Claustre J, Moro F, Chayvialle JA, Cuber JC, Plaisancié P: Mucin secretion is modulated by luminal factors in the isolated vascularly perfused rat colon. Gut 46:218–224, 2000
Satchithanandam S, Vargofcak-Apker M, Calvert RJ, Leeds AR, Cassidy MM: Alteration of gastrointestinal mucin by fiber feeding in rats. J Nutr 120:1179–1184, 1990
Sharma R, Schumacher U, Ronaasen V, Coates M: Rat intestinal mucosal responses to a microbial flora and different diets. Gut 36:209–214, 1995
Sharma R, Schumacher U: Morphometric analysis of intestinal mucins under different dietary conditions and gut microflora in rats. Dig Dis Sc 40(12):2532–2539, 1995
Potter GD, Sellin JH, Burlingame SM: Bile acid stimulation of cyclic AMP and ion transport in developing rabbit colon. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 13:335–341, 1991
Hofman AF: Intestinal absorption of bile acids and biliary constituents. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1994, pp 1845–1865
Ballantyne GH, Longo WE, Savoca PE, Adrian TE, Vukasin AP, Bilchik AJ, Sussman J, Modlin IM: Deoxycholatestimulated release of peptide YY from the isolated perfused rabbit left colon. Am J Physiol 257:G715–G724, 1989
Plaisancié P, Dumoulin V, Chayvialle JA, Cuber JC: Luminal peptide YY-releasing factors in the isolated vascularly perfused rat colon. J Endocrinol 151:421–429, 1996
Eusufai S: Bile acid malabsorption: Mechanisms and treatment. Dig Dis 13(5):312–321, 1995
Hofmann AK: The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch Intern Med 159(22):2647–2658, 1999
Aldi R, Roda A, Festi D, Sama C, Mazzella G, Bazzoli F, Moeselli AM, Roda E, Barbara L: Bile acid malabsorption and bile acid diarrhea in intestinal resection. Dig Dis Sci 27(6):495–502, 1982
Nakamura T, Imamura K, Kasai F, Tsushima F, Kikuchi H Takebe K: Fecal excretions of hydroxy fatty acid and bile acid in diabetic diarrheal patients. J Diabetes Complications 7(1):8–11, 1993
Kruis W, Kalek HD, Stellaard F, Paumgartner G: Altered fecal bile acid pattern in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 35(4):189–198, 1986
Ejderhamn J, Rafter JJ, Strandvik B: Faecal bile acid excretion in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 32(11):1346–1351, 1991
Plaisancié P, Bernard C, Chayvialle JA, Cuber JC: Regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1–(7-36) amide secretion by intestinal neurotransmitters and hormones in the isolated vascularly perfused rat colon. Endocrinology 135:2398–2403, 1994
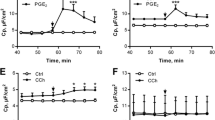
Plaisancié P, Barcelo A, Moro F, Claustre J, Chayvialle JA, Cuber JC: Effects of neurotransmitters, gut hormones, and inflammatory mediators on mucus discharge in rat colon. Am J Physiol 275:G1073–G1084, 1998
Guesdon JL, Ternynck T, Avrameas S: The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem 27:1131–1139, 1979
Hinegardner TT: An improved fluorimetric assay for DNA. Anal. Biochem 39:197–201, 1971
Plaisancié P, Bosshard A, Meslin JC, Cuber JC: Colonic mucin discharge by a cholinergic agonist, prostaglandins, and peptide YY in the isolated vascularly perfused rat colon. Digestion 58:168–175, 1997
Forstner G: Signal transduction, packaging and secretion of mucins. Annu Rev Physiol 57:585–605, 1995
Sakata T, Von Engelhardt W: Influence of short-chain fatty acids and osmolality on mucin release in the rat colon. Cell Tissue Res 219:371–377, 1981
Specian RD, Oliver MG: Functional biology of intestinal goblet cells. Am J Physiol 260:C183–C193, 1991
Klinkspoor JH, Yoshida T, Lee SP: Bile salts stimulate mucin secretion by cultured dog gallbladder epithelial cells independent of their detergent effect. Biochem J 332:257–262, 1998
Dietschy JM: Mechanisms for the intestinal absorption of bile acids. J Lipid Res 9:297–309, 1968
Shekels LL, Lyftogt CT, Ho SB: Bile acid-induced alterations of mucin production in differentiated human colon cancer cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28:193–201, 1996
Klinkspoor JH, Mok KS, Van Klinken BJW, Tytgat GNJ, Lee SP, Groen AK: Mucin secretion by the human colon cell line LS174T is regulated by bile salts. Glycobiology 9:13–19, 1999
Sacquet EC, Raibaud PM, Mejean C, Riottot MJ, Leprince C, Leglise PC: Bacterial formation of omega-muricholic acid in rats. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:1127–1131, 1979
O'Leary DP, Murray FE, Turner BS, LaMont JT: Bile salts stimulate glycoprotein release by guinea pig gallbladder in vitro. Hepatology 13:957–961, 1991
Tazawa Y, Yamada M, Nakagawa M, Suzuki H, Igarashi Y, Konno T, Tada K: Fecal and biliary bile acid patterns in children with bile acid malabsorption. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 3(3):378–384, 1984
Enss ML, Muller H, Schmidt-Wittig U, Kownatzki R, Coenen M, Hedrich HJ: Effects of perorally applied endotoxin on colonic mucins of germfree rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 31:868–874, 1996
Enss ML, Schmidt-Wittig U, Muller H, Mai UE, Coenen M, Hedrich HJ: Response of germfree rat colonic mucous cells to peroral endotoxin application. Eur J Cell Biol 71:99–104, 1996
Binder HJ, Rawlins CL: Effect of conjugated dihydroxy bile salts on electrolyte transport in rat colon. J Clin Invest 52:1460–1466, 1973
Mekhjian HS, Phillips SF: Perfusion of the canine colon with unconjugated bile acids. Effect on water and electrolyte transport, morphology, and bile acid absorption. Gastroenterology 59:120–129, 1970
Wingate DL, Krag E, Mekhjian HS, Phillips SF: Relationships between ion and water movement in the human jejunum, ileum and colon during perfusion with bile acids: Clin Sci Mol Med 45:593–606, 1973
Karlstrom L, Cassuto J, Jodal M, Lundgren O: The importance of the enteric nervous system for the bile-salt-induced secretion in the small intestine of the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol 18:117–123, 1983
Rampton DS, Breuer NF, Vaja SG, Sladen GE, Dowling RH: Role of prostaglandins in bile salt-induced changes in rat colonic structure and function. Clin Sci 61:641–648, 1981
Peregrin AT, Ahlman H, Jodal M, Lundgren O: Involvement of serotonin and calcium channels in the intestinal fluid secretion evoked by bile salt and cholera toxin. Br J Pharmacol 127:887–894, 1999
Gelbmann CM, Schteingart CD, Thompson SM, Hofmann AF, Barrett KE: Mast cells and histamine contribute to bile acidstimulated secretion in the mouse colon. J Clin Invest 95:2831–2839, 1995
Loeschke K, Schmid T, Farack UM: Inhibition by loperamide of mucus secretion in the rat colon in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 170:41–46, 1989
Phillips TE, Stanley CM, Wilson J: The effect of 16,16–dimethyl prostaglandin E2 on proliferation of an intestinal goblet cell line and its synthesis and secretion of mucin glycoproteins. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 48:423–428, 1993
Hata Y, Ota S, Kawabe T, Terano A, Razandi M, Ivey KJ: Bile salts stimulate mucous glycoprotein secretion from cultured rabbit gastric mucosal cells. J Lab Clin Med 124:395–400, 1994
Fitzer CJ, O'Brian CA, Guillem JG, Weinstein IB: The regulation of protein kinase C by chenodeoxycholate, deoxycholate and several structurally related bile acids. Carcinogenesis 8:217–220, 1987
Huang XP, Fan XT, Desjeux JF, Castagna M: Bile acids, non-phorbol-ester-type tumor promoters, stimulate the phosphorylation of protein kinase C substrates in human platelets and colon cell line HT29. Int J Cancer 52:444–450, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barcelo, A., Claustre, J., Toumi, F. et al. Effect of Bile Salts on Colonic Mucus Secretion in Isolated Vascularly Perfused Rat Colon. Dig Dis Sci 46, 1223–1231 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010607127822
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010607127822