Abstract
Purpose. The uptake of zinc as acexamic acid salt in the rat gastrointestinal tract, using an in situ static technique, was studied. Our aim was to investigate an absorption window for zinc and the uptake kinetics in the colon.
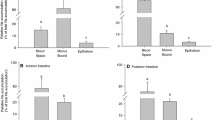
Methods. To detect selectivity phenomena in zinc absorption, buffered saline solutions of zinc (50 µg/ ml) were perfused in stomach, whole colon and three 33-cm fractions of the small intestine (proximal, middle and distal segments). To characterize zinc uptake kinetics in whole colon, five different zinc concentrations (5, 25, 50, 150 y 250 µg/ml) were assayed. Zinc secreted into the gastrointestinal tract during the experiments was deducted from the uptake.
Results. Zinc secretion was characterized as an apparent zero-order process for all the studied segments (mean secretion rate = 0.10 ± 0.03 µg/(ml × min)). The stomach exhibited little ability to absorb zinc (apparent first order rate constant = 0.17 ± 0.07 h−1), whereas the highest transport rates were found in the last two thirds of the small intestine and colon (first order constants: 0.66 ± 0.13 h−1, 1.00 ± 0.06 h−1,0.97 ± 0.14 h−1, 0.96 ± 0.19h−l for proximal, middle, distal and colon segments, respectively). Zinc uptake in the colon was characterized by means of a Michaelis-Menten and first-order combined kinetics, with the following parameters: Vm = 0.36 ± 0.02 µg/(ml × min), Km = 18.01 ± 0.40 µg/ ml and Ka = 0.40 ± 0.01 h−l.
Conclusions. Zinc is preferably absorbed in the middle and distal parts of the rat gastrointestinal tract. In the colon a saturable mechanism may be involved in apparent absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. J. Varas. Estudio comparativo del acexamato de zinc y la ranitidina en el tratamiento a corto y medio plazo de la úlcera gastroduodenal. Valoración de la tasa de recivivas. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9:166–171 (1986).
N. T. Davies. Studies on the absorption of zinc by rat intestine. Br. J. Nutr. 43:189–203, (1980).
A. H. Methfessel, and H. Spencer. Zinc metabolism in the rat. I. Intestinal absorption of zinc. J. Appl. Physiol. 34:58–62 (1973).
D. R. Van Campen, and E. A. Mitchell. Absorption of Cu64, Zn65, Mo99 and Fe59 from ligated segments of the rat gastrointestinal tract. J. Nutr. 86:120–124 (1965).
D. L. Antonson, A. J. Barak, and J. A. Vanderhoof. Determination of the site of zinc absorption in rat small intestine. J. Nutr. 109:142–147, (1979).
S. Kowarski, C. S. Blair-Stanek, and D. Schachter. Active transport of zinc and identification of zinc-binding protein in rat jejunal mucosa. Am. J. Physiol. 226:401–407 (1974).
R. Meneely, and F. K. Ghishan. In vivo intestinal zinc transport in rats, normal and growth retarded. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1:119–124 (1982).
C. J. Seal, and J. C Mathers. Intestinal zinc transfer by everted gut sacs from rats given diets containing different amounts and types of dietary fibre. Br. J. Nutr. 62(1):151–163 (1989).
F. K. Ghishan, and G. Sobo. Intestinal Maturation, in vivo zinc transport. Pediatr. Res. 17:148–151, (1983).
J. E. Hoadley, A. S. Leinart, and R. J. Cousins. Kinetics analysis of zinc uptake and serosal transfer by vascularly perfused rat intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 252 (Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 15):G825–G831 (1987).
F. Torres-Molina, A. Martinez-Coscollá, S. Gisbert, E. Quintana, S. Sendrós, J. E. Peris-Ribera, and J. M. Plá-Delfina. Kinetics of the intestinal uptake of zinc acexamate in normal and zinc-depleted rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 42:679–684 (1990).
M. P. Menard, and R. J. Cousins. Zinc transport by brush-border membrane vesicles from rat intestine. J. Nutr. 113:1434–1442 (1983).
N. Alcok. The measurement of zinc in biological samples. Alcoholism. 5:355–356 (1981).
J. T. Doluisio, N. F. Billus, L. W. Dittert, E. T. Sugita, and J. V. Swintosky. Drug absorption. I. An “in situ” rat gut technique yielding realistic absorption rates. J. Pharm. Sci. 58:1196–1199 (1969).
A. Martin-Villodre, J. M. Plá-Delfina, J. Moreno, M. D. Pérez-Buendía, J. Miralles, E. F. Collado, E. Sánchez-Moyano, and A. Del Pozo. Studies on the reliability of a bihyperbolic functional absorption model. I. Ring-substitued anilines. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:615–633(1986).
V. G. Casabó, E. Nuñez, A. Martínez-Coscollá, E. Miralles, A. Martin-Villodre, and J. M. Plá-Delfina. Studies on the reliability of a bihyperbolic functional absorption model. II. Phenyalkylamines. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:633–643, (1987).
C. Gabus Sannié, and P Buri. Etude comparative des méthodes de détermination du volume d'eau absorbé lors de perfusion de l'intestine grêle du rat. S.T.P. Pharma. 3:856–860, (1987).
J. G. Wagner. Fundamentals of Clinicals Pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publ. Inc. Hamilton, Illinois, 1979.
K. Yamaoka, Y. Tanigawara, T. Nakagawa, T. Uno. A pharmacokinetic analysis program (Multi) for microcomputer. J. Pharmacobia. Dynam. 4:879–885 (1981).
H. Akaike. An information criterion (AIC). Math. Sci. 14:5–9 (1976).
P. E. Johnson, J. R. Hunt, and N. V. C Ralston. The effect of past and current dietary zinc intake on Zn absorption and endogenous excretion in the rat. J. Nutr. 118:1205–1209 (1988).
G. W. Evans, C. I. Grace, and H. J. Votava. A proposed mechanism for zinc absorption in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 228:501–505 (1975).
C. J. Seal, and F. W. Heaton. Chemical factors affecting the intestinal absorption of zinc in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Nutr. 50:317–324, (1983).
R. A. Wapnir, L. A. García Aranda, E. K. Mevorach, and F. Lifshitz. Differential absorption of zinc and low molecular weight ligands in the rat gut in protein-energy malnutrition. J. Nutr. 115:900–908 (1985).
M. C. Rodríguez Yoldi, J. E. Mesonero, and M. J. Rodríguez Yoldi. Effect of zinc on L-threonine transport across the jejunum of rabbit. Biol. Trace Elemen. Res. 37:269–279 (1993).
B. Lönnerdal. Intestinal absorption of zinc. In C. F. Mills (ed.), Zinc human biology, Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 1989, pp: 33–55.
J. Hastewell, I. Williamson, and M. Mackay. Cell biology and active transport processes in the colon. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 7:119–147 (1991).
D. W. Watkins, C. Chenu, P. Ripoche. Zinc inhibition of glucose uptake in brush border membrane vesicles from pig small intestine. Pflügers Arch. 415:165–171 (1989).
M. C. Rodríguez Yoldi, J. E. Mesonero, and M. J. Rodríguez Yoldi. Inhibition of D-galactose transport across the small intestine of rabbit by zinc. Zentralbl-Veterinarmed-A 39:687–695 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gisbert-González, S.L., Torres-Molina, F. Zinc Uptake in Five Sectors of the Rat Gastrointestinal Tract: Kinetic Study in the Whole Colon. Pharm Res 13, 1154–1161 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016095732629
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016095732629