Abstract
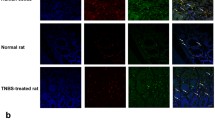
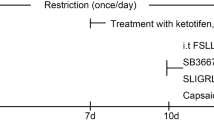
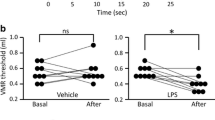
Visceral hypersensitivity is a common feature offunctional bowel disorders, where an increased number ofmast cells have often been described. Thus, weinvestigated the effect of an experimental mast cell degranulation induced by BrX-537A on somatic(tail heating) and visceral (rectal distension)sensitivity in rats and the involvement of histamineand/or serotonin on this last response. After BrX-537Aadministration, the latency of tail withdrawal reflex wasshortened within the 2- to 8-hr period. Moreover,BrX-537A reduced the distension volume threshold from0.8 ml to 0.4 ml inducing allodynia, from 6 to 12 hrafter its administration. This effect was suppressedby doxantrazole (mast cell stabilizing agent) and WAY100635 (5-HT1A receptor antagonist), andreproduced by 5-HTP (5-HT precursor) and 8-OH-DPAT(5-HT1A receptor agonist). However, neither granisetron(5-HT3 receptor antagonist) nor H1, H2, or H3 histaminereceptor antagonists modified the BrX-537A-inducedallodynia. Consequently, mast cell degranulation initiates a delayed somatic and visceralallodynia, with the participation of serotonin, through5-HT1A receptor activation, on the visceralresponse.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mayer EA, Gebhart GF: Basic and clinical aspects of visceral hype ralgesia. Gastroenterology 107:271-293, 1994
Stead RH, Dixon MF, Bramwell NH, Riddell RH, Bienenstock J: Mast cell are closely apposed to nerves in the human gastrointestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology 97:575-585, 1989
Lowman MA, Benyon RC, Church MK: Characterization of neuropeptide-induced histamine re lease from human dispersed skin mast cells. Br J Pharmacol 95:121-130, 1988
Weston AP, Biddle WL, Bhatia PS, Miner PB: Terminal ileal mucosal mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 38:1590-1595, 1993
Dvorak AM, Monahan RA, Osage JE, Dickersin GR: Crohn's disease: Transmission electron microscopic studies. II. Immunologic inflammatory response. Alterations of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and the microvasculature. Hum Pathol 11:606-619, 1980
Pang X, Marchand J, Sant GR, Kream RM, Theoharides TC: Increased number of substance P positive nerve fibres in interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 75:744-750, 1995
Christmas TJ, Rode J, Chapple CR, Milroy EJ, Turner-Warwick RT: Nerve fibre proliferation in interstitial cystitis. Arch A 416:447-451, 1990
Pang X, Boucher W, Triadafilopoulos G, Sant GR, Theoharides TC: Mast cell and substance P-positive nerve involvement in a patient with both irritable bowel syndrome and interstitial cystitis. Urology 47:436-438, 1996
Stephanini GF, Prati E, Albini MC, Piccinini G, Capelli S, Castelli E, Mazzeti M, Gasbarrini G: Oral disodium cromoglycate treatment in irritable bowel syndrome: An open study in 101 subjects with diarrheic type. Am J Gastroenterol 87:55-57, 1992
Miner PB: Systematic mastocytosis and regional gastrointestinal mast cell disease. InIrritable Bowel Syndrome. NW Read (ed). Oxford, Blackwell Scientific, 1990, pp 174-198
Dray A, Bevan S: Inflammation and hyperalgesia. Highlighting the team effort. NIPS 14:287-290, 1993
Levine JD, Taiwo JO, Heller PH: Hyperalgesic pain: Inflammatory and neuropathic. InHyperalgesia and Allodynia. WD Willis, Jr (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1992, pp 117-124
Suh HW, Song DK, Choi YS, Kim YH: Effects of intrathecally injected histamine receptor antagonists on the antinociception induced by morphine, b-endorphine, and U50, 488H administered intrathecally in the mouse. Neuropeptides 30:485-490, 1996
Lamberti C, Bartolini A, Ghelardini C, Malmberg-Aiello P: Investigation into the role of histamine receptors in rodent antinociception. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:567-574, 1996
Levine J, Taiwo Y: Inflammatory pain. InTextbook of Pain. PD Wall, R Lelzack (eds). Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, 1994, pp 45-56
Meller ST, Lewis SJ, Brody MJ, Gebhart GF: Vagal afferent mediated inhibition of a nociceptive reflex by iv serotonin in the rat. II. Role of the 5HT receptor subtypes. Brain Res 585:71-86, 1992
Talley NJ: 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists and antagonists in the modulation of gastrointestinal motility and sensation: Clinical implications. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 6:273-289, 1992
Prior A, Read NW: Reduction of rectal sensitivity and postprandial motility by granisetron, a 5-HT3 rece ptor antagonist, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 31:A1174, 1990
Morteau O, Julia V, Eeckhout C, Bueno L: Influence of 5HT3 receptor antagonists in visceromotor and nociceptive responses to rectal distension before and during experimental colitis in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 8:553-562, 1994
Taiwo YO, Levine JD: Serotonin is a directly-acting hyperalgesic agent in the rat. Neuroscience 48:485-490, 1992
Pearce FL, Befus AD, Gaudie J, Bienenstock J: Mucosal mast cells. II. Effects of anti-allergic compounds on histamine secretion by isolated intestinal mast cells. J Immunol 128:2481-2486, 1982
Ruckebush Y, Fioramonti J: Electrical spiking activity and propulsion in small intestine in fed and fasted rats. Gastroenterology 99:1500-1508, 1975
Million M, Fioramonti J, Gicquel S, Zajac JM, Bueno L: Comparative effects of Phe-Leu-Phe-Gln-Arg-Phe-NH2 analogs on intestinal motility and nociception in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:96-102, 1993
Fargeas MJ, Theodorou V, Fioramonti J, Bueno L: Relationship between mast cell degranulation and jejunal myoelectric alterations in intestinal anaphylaxis in rats. Gastroenterology 102:157-162, 1992
Castex N, Fioramonti J, Fargeas MJ, More J, Bueno L: Role of 5-HT3 receptors and afferent fibers in the effects of mast cell degranulation on colonic motility in rats. Gastroenterology 107:976-984, 1994
Theodorou V, Eutamene H, Fioramonti J, Junien JL, Bueno L: Interleukin-1 induces a neurally mediated colonic secretion in rats: Involvement of mast cells and prostaglandins. Gastroenterology 106:1493-1500, 1994
Fargeas MJ, Fioramonti J, Bueno L: Involvement of different receptors in the central and peripheral effects of histamine on intestinal motility in the rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 41:534-540, 1989
Simone DA, Sorkin LS, Oh U, Chung JM, Owens C, LaMotte RH, Willis WD: Neurogenic hyperalgesia: Central neural correlates in responses of spinothalamic tract neurons. J Neurophysiol 66:228-246, 1991
Willis WD: Mechanical allodynia: A role for sensitized nociceptive tract cells with convergent input from mechanoreceptors and nociceptors? Am Pain Soc J 2:23-33, 1993
Mendell LM: Physiological properties of unmyelinated fiber projection to the spinal cord. Exp Neurol 16:316-332, 1966
Sidall PJ, Cousins MJ: Pain mechanisms and management: An update. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 22:679-688, 1995
Cervero F, Laird JMA, Pozo MA: Selective changes of receptive fields properties of spinal nociceptive neurons induced by noxious visceral stimulation in the cat. Pain 51:335-342, 1992
Cacabelos R: Histaminergic system: Neuroendocrine function of brain histamine. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 12:341-376, 1991
Handwerker HO, Reeh PW: Nociceptors: chemosensitivity and sensitization by chemical agents. InHyperalgesia and Allodynia. WD Willis, Jr (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1992, pp 107-116
Purcell WN, Atterwill CK: Mast cells in neuro-immune function: Neurotoxicological and neuropharmacological perspectives. Neurochem Res 20:521-532, 1995
Cooke HJ, Nemeth PR, Wood JD: Histamine action on guinea pig ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol 246:G372-G377, 1984
Sanuki K: The analgesic effect induced by repeated administration of histamine and histamine liberators. Jpn J Pharmacol 6:69-86, 1957
Castex N, Fioramonti J, Fargeas MJ, Bueno L: Role of serotonin and histamine in colonic motility and transit disturbances induced by mast cell degranulation: An experimental study in the rat. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 17:478-484, 1993
Besson JM, Chaouch A: Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol Rev 67:67-186, 1987
Rueff A, Dray A: 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced sensitization and activation of peripheral fibres in the neonatal rat are mediated via different 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Neuroscience 50:899-905, 1992
Murphy AZ, Murphy RM, Zemlan FP: Role of spinal serotonin 1 receptor subtypes in thermally and mechanical elicited nociceptive reflexes. Psychopharmacology 108:123-130, 1992
Zemlan FP, Murphy AZ, Behbehani MM: 5-HT1A receptors mediate the effect of the bulbospinal serotonin system on spinal dorsal horn nociceptive neurones. Pharmacology 48:1-10, 1994
Blackshaw LA, Grundy D: 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT3) receptor mediated effects on vagal mucosal afferent fibres from the upper gastrointestinal tract of the anae sthetized ferre t. J Physiol 435:64p, 1991 (abstract)
Kumazawa T, Mizumura K, Koda H: Involvement of EP3 subtype of prostaglandin E receptors in PGE2-induced enhancement of the bradykinin response of nociceptors. Brain Res 632:321-324, 1993
White DM: Mechanism of prostaglandin E2-induced substance P release from cultured sensory neurons. Neuroscience 70:561-565, 1996
Horigome K, Pryor JC, Bullock ED, Johnson EM Jr: Mediator release from mast cells by nerve growth factor. Neurotrophin specificity and receptor mediation. J Biol Chem 268:14881-14887, 1993
Leon A, Buriani A, Dal Toso R, Fabris M, Romanello S, Aleo L, Levi-Montalcini R: Mast cells synthesize, store, and release nerve growth factor. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 91:3739-3743, 1994
Lewin GR, Mendell LM: Regulation of cutaneous C-fiber heat nociceptors by nerve growth factor in the developing rat. Neurophysiology 71:941-949, 1994
Woolf CJ, Safieh-Garabedian B, Ma QP, Crilly P, Winter J: Nerve growth factor contributes to the generation of inflammatory sensory hypersensitivity. Neuroscience 62:327-331, 1994
Lewin GR, Rueff A, Mendell LM: Peripheral and central mechanisms of NGF-induced hyperalgesia. Eur J Neurosci 6:1903-912, 1994
Watkins LR, Wiertelack EP, Goehler LE, Smith KP, Martin D, Maier SF: Characterization of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res 654:15-26, 1994
Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB, Bristow AF, Poole S: Interleukin-1b as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature 334:698-700, 1988
Munakata J, Naliboff B, Harraf F, Kodner A, Lembo T, Chang L, Silverman DHS, Mayer EA: Repetitive sigmoid stimulation induces rectal hyperalgesia in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 112:55-63, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coelho, AM., Fioramonti, J. & Bueno, L. Mast Cell Degranulation Induces Delayed Rectal Allodynia in Rats: Role of Histamine and 5-HT. Dig Dis Sci 43, 727–737 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018853728251
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018853728251