Abstract
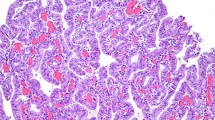
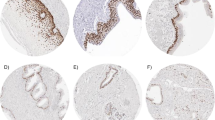
We sought to determine if an immunohistochemicalpanel of p53, PCNA, and c-erbB-2 was a useful biomarkerof transformation in Barrett's metaplasia. P53, PCNA,and c-erbB-2 immunohistochemistry was performed on resected Barrett's specimens selected toshow discrete grades of dysplasia and then onprospectively obtained biopsies. In resection specimens,p53 was positive in 36% with no dysplasia, in 30% with low-grade dysplasia, in 85% with high-gradedysplasia, and in 90% of adenocarcinomas. While anevaluation of proliferation throughout the specimen didnot differ between groups, surface proliferation was significantly higher in high-grade dysplasiathan in low-grade or no dysplasia. All high-gradedysplasia specimens were positive for at least onemarker, compared to 44% with no or low-grade dysplasia. C-erbB-2 was only seen in 31% with high-gradedysplasia and in 10% of adenocarcinomas. Prospectively,the panel had a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of81% and an overall accuracy of 83% in identifying patients who developed high-grade dysplasia orcancer. Thus, overexpression of p53 occurs early in themalignant transformation of Barrett's and increases withhistologic progression, and proliferation at the surface of Barrett's epitheliumincreases with progressive grades of dysplasia. Animmunohistochemical panel of p53 and PCNA is a usefulbiomarker for Barrett's metaplasia.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hesketh PJ, Clapp RW, Doos WG, Spechler SJ: The increasing frequency of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer 64:526–530, 1989
Blot WJ, Devesa SS, Kneller RW, Fraumeni JF. Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA 265:1287–1289, 1991
Pera M, Cameron AJ, Trastek VF, Carpenter HA, Zinmeister AR: Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Gastroenterology 104:510–513, 1993
Naef AP, Savary M, Ozello L: Columnar-lined lower esophagus: An acquired lesion with malignant predisposition. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 70:826–835, 1975
Haggitt RC, Tryzelaar J, Ellis RH, Colcher H: Adenocarcinoma complicating columnar epithelial lined (Barrett's) esophagus. Am J Clin Pathol 70:1–5, 1978
Hamilton SR, Smith RRL: The relationship between columnar epithelial dysplasia and invasive adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Clin Pathol 87:301–305, 1987
Winters C, Spurling TJ, Chobanian SJ, Curtis DJ, Esposito RL, Hacker JF, et al: Barrett's esophagus: A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 92:118–124, 1987
Williamson WA, Ellis FH, Gibb SP, Shahian DM, Aretz HT, Heatley GJ, et al: Barrett's esophagus: Prevalence and incidence of adenocarcinoma. Arch Intern Med 151:2212–2216, 1991
Polepalle SC, McCallum RW: Barrett's esophagus: Current assessment and future perspectives. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 19:733–744, 1990
Spechler SJ, Goyal RK: Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med 315:362–371, 1986
Cameron AJ, Ott BJ, Payne WS: The incidence of adenocarcinoma in columnar-lined (Barrett's) esophagus. N Engl J Med 313:857–859, 1985
Riddell RH, Goldman H, Ransohoff DF, Appelman HD, Fanoglio CM, Haggitt RC, et al: Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: Standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol 14(11):931–968, 1983
Reid BJ, Haggitt RC, Rubin CE, Roth G, Surawicz CM, Van Belle G, et al: Observer variation in the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Hum Pathol 19:166–178, 1988
Hameeteman W, Tytgat GNJ, Houthoff HJ, Van Den Tweel JG: Barrett's esophagus: Development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 96:1249–1256, 1989
Levine DS, Haggitt RC, Blount PL, Rabinovitch PS, Rusch VW, Reid BJ: An endoscopic biopsy protocol can differentiate high-grade dysplasia from early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology 105:40–50, 1993
Thompson JJ, Zinsser KR, Enterline HT: Barrett's metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Hum Pathol 14:42–61, 1983
Flejou JF, Potet F, Muzeau F, Le Pelletier F, Fekete F, Henin D: Overexpression of p53 protein in Barrett's syndrome with malignant transformation. J Clin Pathol 46:330–333, 1993
Reid BJ, Weinstein WM, Lewin KJ, Haggitt RC, VanDeventer G, DenBesten L, et al: Endoscopic biopsy can detect high-grade dysplasia or early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus without grossly recognizable neoplastic lesions. Gastroenterology 94:81–90, 1988
Naef AP, Savary M, Ozello L: Columnar-lined lower esophagus: An acquired lesion with malignant predisposition. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 70:826–835, 1975
Hamilton SR, Smith RRL: The relationship between columnar epithelial dysplasia and invasive adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Clin Pathol 87:301–305, 1987
McArdle JE, Lewin KJ, Randall G, Weinstein W: Distribution of dysplasias and early invasive carcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Hum Pathol 23:479–482, 1992
Blount PL, Ramel S, Raskind WH, Haggitt RC, Sanchez CA, Dean PJ, et al: 17p allelic deletions and p53 protein overexpression in Barrett's adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 51:5482–5486, 1991
Harris CC, Hollstein M: Clinical implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med 329:1318–1327, 1993
Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA: The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 351:453–456, 1991
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC: p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253:49053, 1991
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW: p53 function and dysfunction. Cell 70:532–536, 1992
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H: Use of avidin-biotin complex in immunoperoxidase techniques: A comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580, 1981
McKee PH, Hobbs C, Hall PA: Antigen retrieval by microwave irradiation lowers immunohistological detection thresholds. Histopathology 23:377–379, 1993
Atkinson M: Barrett's oesophagus—to screen or not to screen? Gut 30:2–5, 1989
Ramel S, Reid BJ, Sanchez CA, Blount PL, Levine DS, Neshat K, et al: Evaluation of p53 protein expression in Barrett's esophagus by two-parameter flow cytometry. Gastroenterology 102:1220–1228, 1992
Younes M, Lebovitz RM, Lechago LV, Lechago J: p53 protein accumulation if Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma: A follow-up study. Gastroenterology 105:1637–1642, 1993
Casson AG, Manolopoulos B, Troster M, Kerksliet N, O'Malley F, Inculet R, et al: Clinical implications of p53 gene mutation in the progression of Barrett's epithelium to invasive esophageal cancer. Am J Surg 167:52–57, 1994
Jones DR, Davidson AG, Summers CL, Murray GF, Quinlan DC: Potential application of p53 as an intermediate biomarker in Barrett's esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg 57:598–603, 1994
Rice TW, Goldblum JR, Falk GW, Tubbs RR, Kirby TJ, Casey G: p53 immunoreactivity in Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 108:1132–1137, 1994
Symman PJ, Linehan JM, Brito MJ, Filipe MI: p53 expression in Barrett's oesophagus, dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma using antibody DO-7. J Pathol 173:221–226, 1994
Hardwick RH, Sheperd NA, Moorghen M, Newcomb PV, Alderson D: Adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's oesophagus: Evidence for the participation of p53 dysfunction in the dysplasia/carcinoma sequence. Gut 35:764–768, 1994
Oren M, Maltzman W, Levine AJ: Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol 1:101–120, 1981
Reich NC, Oren M, Levine AJ: Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol 3:2143–2150, 1983
Rogel A, Popliker M, Webb CG, Oren M: p53 cellular tumor antigen: Analysis of mRNA levels in normal adult tissues, embryos, and tumors. Mol Cell Biol 5:2851–2855, 1985
Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA: The p53 tumor suppressor gene. Nature 351:453–456, 1991
Bartek J, Iggo R, Gannon J, Lane DP: Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 5:893–899, 1990
Gannon JV, Greaves R, Iggo R, Lane DP: Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect: A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J 9:1595–1602, 1990
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Tan T-H, Eliyahu D, Oren M, Levine AJ: Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol 8:531, 1988
Srivastava S, Tong YA, Devadas K, Zou ZQ, Sykes VW, Chen Y, et al: Detection of both mutant and wild-type p53 protein in normal skin fibroblasts and demonstration of a shared ‘second hit’ on p53 in diverse tumors from a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Oncogene 7:987–991, 1992
Lu Y, Park SH, Thompson TC: Ras-induced hyperplasia occurs with mutation of p53, but activated ras and myc together can induce carcinoma without p53 mutation. Cell 70:153–161, 1992
Casey G, Lo-Hseuh M, Lopez ME, et al: Growth suppression of human breast cancer cells by introduction of a wild-type p53 gene. Oncogene 6:1791–1797, 1991
Kastan MB, Stone KD, Civin CI: Nuclear oncoprotein expression as function of lineage, differentiation stage, and proliferative status of normal human hematopoietic cells. Blood 74:1517–1524, 1989
Hall PA, McKee PH, Menage HD, Dover R, Lane DP: High levels of p53 protein in UV irradiated human skin. Oncogene 8:203–207, 1992
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW: Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 51:6304–6311, 1991
Maltzman W, Czyzyk I: UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumour antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol 4:1689–1694, 1984
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB: Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7491–7495, 1992
Fritsche M, Haessler C, Brandner G: Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 8:307–318, 1993
Jankowski J, McMenemin R, Yu C, Hopwood D, Wormsley KG: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen in oesophageal diseases; correlation with transforming growth factor alpha expression. Gut 33:587–591, 1992
Gillen P, McDermott M, Grehan D, Hourihane DO'B, Hennessy TPJ: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen in the assessment of Barrett's mucosa. Br J Surg 81:1766–1768, 1994
Flejou JF, Paraf F, Muzeau F, Fekete F, Henin D, Jothy S, Potet F: Expression of c-erbB-2 oncogene product in Barrett's adenocarcinoma: Pathological and prognostic correlations. J Clin Pathol 47:23–26, 1994
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, M.A., Vanbibber, M.M., Safatle-Ribeiro, A.V. et al. Expression of p53, PCNA, and C-erbB-2 in Barrett's Metaplasia and Adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 42, 2453–2462 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018891923998
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018891923998