Abstract
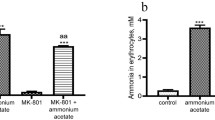
It has been suggested that alterations of GABAergic neurotransmission are implicated in the pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Increased concentrations of endogenous benzodiazepines with positive allosteric modulatory properties at the GABA-A receptor complex were proposed as a pathophysiological mechanism to explain increased GABAergic tone in HE. However, results of controlled trials with benzodiazepine receptor antagonists have yielded equivocal results and increases in benzodiazepine levels in body fluids of cirrhotic patients were suggested to be largely accounted for by previous pharmaceutical benzodiazepine intake. In the present study the issue of benzodiazepine receptor ligands in brains of cirrhotic patients, and their contribution to alterations of GABA-A receptor complex in HE are addressed. “Benzodiazepine-like” ligands were present in trace amounts in autopsied brain tissue from control subjects (0.2 ± 0.2 ng/g tissue), and from cirrhotic patients not previously exposed to benzodiazepine medication (0.8± 0.4 ng/g tissue). In contrast, these ligands accumulate in brain extracts from cirrhotic patients previously exposed to benzodiazepines by up to 200-fold (161.5± 93.2 DE ng/g tissue). Brain extracts from cirrhotic patients increased the binding of the GABA-A receptor agonist [3H]muscimol. This increase was minimal with brain extracts from controls (6.8± 2.8%), but was significant with brain extracts from cirrhotic patients without (29.4± 2.7%), or with (55.1± 7.6%) previous exposure to benzodiazepines. Addition of flumazenil, a selective benzodiazepine receptor antagonist did not significantly modify the increase of [3H]muscimol binding by brain extracts from patients without prior exposure to benzodiazepines and only partially inhibited the increase of [3H]muscimol binding in presence of brain extracts from cirrhotic patients previously exposed to benzodiazepines. These findings suggest the presence of nonbenzodiazepine substances (possibly neurosteroids) with positive allosteric modulatory properties at the GABA-A receptor complex in brain in hepatic encephalopathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ahboucha, S., Dsejardins, P., Chatauret, N., and Butterworth, R.F. (2002). Increased concentrations of endogenous agonists of the neurosteroid site on the GABA-A receptor in human hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 36:318A.
Ahboucha, S., Desjardins, P., Chatauret, N., Pomier-Layrargues, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (2003). Normal coupling of brain benzodiazepine and neurosteroid modulatory sites on the GABA-A receptor complex in human hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 43:551–556.
Bansky, G., Meier, P.S., Ziegler, W.H., Walser, H., Schmid, H., and Huber, M. (1985). Reversal of hepatic coma by benzodiazepine antagonists (Rol5-1788). Lancet 1:1324–1325.
Basile, A.S., Harrison, P.M., Hughes, R.D., Gu, Z.Q., Pannell, L., McKinney, A., Jones, E.A., and Williams, R. (1994). Relationship between plasma benzodiazepine receptor ligand concentrations and severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 19:112–121.
Basile, A.S., Hughes, R.D., Harrison, P.M., Murata, Y., Pannell, L., Jones, E.A., Williams, R., and Skolnick, P. (1991). Elevated brain concentrations of 1,4-benzodiazepines in fulminant hepatic failure. N.Engl.J.Med. 325:473–478.
Butterworth, R.F., Giguere, J.F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J., and Pomier-Layrargues, G. (1987). Ammonia: Key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:1–12.
Butterworth, R.F., Wells, J., and Pomier-Layrargues, G. (1995). Detection of benzodiazepines in hepatic en-cephalopathy: Reply. Hepatology 21:605.
Goodnough, D.B., and Hawkinson, J.E. (1995). Neuroactive steroid modulation of [ 3 H]muscimol binding to the GABA-A receptor complex in rat cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 288:157–162.
Gyr, K., Meier, R., Haussler, J., Bouletreau, P., Fleig, W.E., Gatta, A., Holstege, A., Pomier-Layrargues, G., Schalm, S.W., Groeneweg, M., Scollo-Lavizzari, G., Ventura, E., Zeneroli, M.L., Williams, R., Yoo, Y., and Amrein, R. (1996). Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of flumazenil in the treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy: A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled multicenter trial. Gut 39:319–324.
Ha, J.H., Knauer, S., Moody, E., Jones, E.A., and Basile, A.S. (1997). Direct enhancement of GABA-ergic neurotransmission by ammonia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 420:85–94.
Harrison, N.L., Majewska, M.D., Harrington, J.W., and Barker, J.L. (1987). Structure–activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor complex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241:346–353.
Itzhak, Y., Roig-Cantisano, A., Dombro, R.S., and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Acute liver failure and hyperam-monemia increase peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor binding and pregnenolone synthesis in mouse brain. Brain Res. 705:345–348.
Klotz, U., and Walker, S. (1989). Flumazenil and hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1:155–156.
Mullen, K.D., Szauter, K.M., and Kaminsky-Russ, K. (1990). “Endogenous” benzodiazepine activity in body fluids of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 336:81–83.
Olasmaa, M., Rothstein, J.D., Guidotti, A., Weber, R.J., Paul, S.M., Spector, S., Zeneroli, M.L., Baraldi, M., and Costa, E. (1990). Endogenous benzo-diazepine receptor ligands in human and animal hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 55:2015-2033.
Perney, P., Butterworth, R.F., Mousseau, D.D., Lavoie, J., Fabbro-Peray, P., Blanc, F., and Layrargues, G.P. (1998). Plasma and CSF benzodiazepine receptor ligand concentrations in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy: Relationship to severity of encephalopathy and to pharmaceutical benzodiazepine intake. Metab. Brain Dis. 13:201–210.
Pomier-Layrargues, G., Gigu´ ere, J.F., Lavoie, J., Perney, P., Gagnon, S., D'Amour, M., Wells, J., and Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Flumazenil in cirrhotic patients in hepatic coma: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover trial. Hepatology 19:32-37.
Schafer, D.F., and Jones, E.A. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy and the gamma-aminobutyric-acid neurotransmitter system. Lancet 1:18–20.
Scollo-Lavizzari, G., and Steinmann, E. (1985). Reversal of hepatic coma by benzodiazepine antagonist (RO 15-1788). Lancet 1:1324.
Takahashi, K., Kameda, H., Kataoka, M., Sanjou, K., Harata, N., and Akaike, N. (1993). Ammonia potentiates GABAA response in dissociated rat cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 151:51–54.
Van der Rijt, C.C.D., Schaim, S.W., Meulstree, J., and Stignen, T.H. (1995). Flumazenil therapy for hepatic encephalopathy: A double-blind cross-over study. Gastroenterol. Clin. Dial. 19:572–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahboucha, S., Pomier-Layrargues, G. & Butterworth, R.F. Increased Brain Concentrations of Endogenous (Non-benzodiazepine) GABA-A Receptor Ligands in Human Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 19, 241–251 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MEBR.0000043974.89820.22
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MEBR.0000043974.89820.22