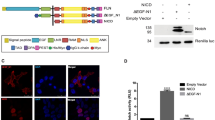
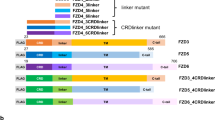
Abstract
NOTCH belongs to a family of transmembrane proteins that are widely conserved from flies to vertebrates and are thought to be involved in cell-fate decisions. In Drosophila, the Suppressor of hairless (Su(H)) gene1,2 and genes of the Enhancer of split (E(Spl)) complex, which encode proteins of the basic helix–loop–helix type3,4 have been implicated in the Notch signalling pathway. Mammalian homologues of E(Spl), such as the mouse Hairy enhancer of split (HES-1 )5, have been isolated. Both HES-1 and the intracellular domain of murine Notch (mNotch) are able to block MyoD-induced myogenesis5-7. Here we show that activated forms of mNotch associate with the human analogue of Su(H), KBF2/RBP-JK (refs 8, 9) and act as transcriptional activators through the KBF2-binding sites of the HES-1 promoter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schweisguth, F. Development 121, 1875–1884 (1995).
Schweisguth, F. & Posakony, J. W. Cell 69, 1199–1212 (1992).
Jennings, B., Preiss, A., Delidakis, C. & Bray, S. Development 120, 3537–3548 (1994).
Tata, F. & Hartley, D. A. Development 29, 139–148 (1993).
Sasai, Y., Kageyama, R., Tagawa, Y., Shigemoto, R. & Nakanishi, S. Genes Dev. 6, 2620–2634 (1992).
Nye, J. S., Kopan, R. & Axel, R. Development 120, 2421–2430 (1994).
Kopan, R., Nye, J. S. & Weintraub, H. Development 120, 2385–2396 (1994).
Israel, A., Yano, O., Logeat, F., Kieran, M. & Kourilsky, P. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 5245–5257 (1989).
Furukawa, T. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 23334–23340 (1991).
Fortini, M. E. & Artavanis Tsakonas, S. Cell 79, 273–282 (1994).
Takebayashi, K. et al. J. biol. Chem. 269, 5150–5156 (1994).
Brou, C. et al. Genes Dev. 8, 2491–2503 (1994).
Kooh, P. J., Fehon, R. G. & Muskavitch, M. A. Development 117, 493–507 (1993).
Fehon, R. G. et al. Cell 61, 523–534 (1990).
Waltzer, L. et al. EMBO J. 13, 5633–5638 (1994).
Zimber Strobl, U. et al. EMBO J. 13, 4973–4982 (1994).
Grossman, S. R., Johannsen, E., Tong, X., Yalamanchili, R. & Kieff, E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 7568–7572 (1994).
Henkel, T., Ling, P. D., Hayward, D. & Peterson, M. G. Science 265, 92–95 (1994).
Ellisen, L. W. et al. Cell 66, 649–661 (1991).
Jhappan, C. et al. Genes Dev. 6, 345–355 (1992).
Tun, T. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 965–971 (1994).
Coffman, C. R., Skoglund, P., Harris, W. A. & Kintner, C. R. Cell 73, 659–671 (1993).
Fortini, M. E., Rebay, I., Caron, L. A. & Artavanis Tsakonas, S. Nature 365, 555–557 (1993).
Rebay, I., Fehon, R. G. & Artavanis Tsakonis, S. Cell 74, 319–329 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarriault, S., Brou, C., Logeat, F. et al. Signalling downstream of activated mammalian Notch. Nature 377, 355–358 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/377355a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/377355a0
This article is cited by
-
Notch intracellular domains form transcriptionally active heterodimeric complexes on sequence-paired sites
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Soluble and multivalent Jag1 DNA origami nanopatterns activate Notch without pulling force
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Evaluation of the anticancer activity of RIN-1, a Notch signaling modulator, in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The Notch-mediated circuitry in the evolution and generation of new cell lineages: the tooth model
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
The mechanism of intestinal stem cells differentiation after ischemia–reperfusion injury in a rat model
Pediatric Surgery International (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.