Abstract
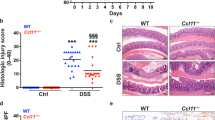
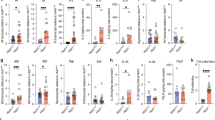
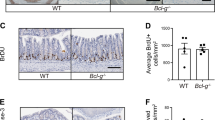
G proteins are involved in cellular signalling and regulate a variety of biological processes including differentiation and development. We have generated mice deficient for the G protein subunit αi2 (Gαi2) by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Gαi2–deficient mice display growth retardation and develop a lethal diffuse colitis with clinical and histopathological features closely resembling ulcerative colitis in humans, including the development of adenocarcinoma of the colon. Prior to clinical symptoms, the mice show profound alterations in thymocyte maturation and function. The study of these animals should provide important insights into the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis as well as carcinogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birnbaumer, L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for βγ dimers as well as for α subunits. Cell 71, 1069–1072 (1992).
Montmayeur, J.-P. & Borrelli, E. Targeting of Gαi2 to the Golgi by alternative spliced carboxyl-terminal region. Science 263, 95–98 (1994).
Simonds, W.F., Goldsmith, P.K., Codina, J., Unson, C.G. & Spiegel, A.M. GB mediates α2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G C-terminal antibodies. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 7809–7813 (1989).
Wong, Y.H. et al. Mutant α subunits of Gi2 inhibit cyclic AMP accumulation. Nature 351, 63–65 (1991).
Taussig, R., Iñiguez-Lluhi, J.A. & Gilman, A.G. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by Giα. Science 261, 218–221 (1993).
Yatani, A., Codina, J., Sekura, R.D., Birnbaumer, L. & Brown, A.M. Reconstitution of somatostatin and muscarinic receptor mediated stimulation of K+ channels by isolated Gk protein in clonal rat anterior pituitary cell membranes. Molec. Endocrinol. 1, 283–289 (1987).
Yatani, A. et al. The G protein-gated atrial K+ channel is stimulated by three distinct G,α-subunits. Nature 336, 680–682 (1988).
Kirsch, G., Codina, J., Birnbaumer, L. & Brown, A.M. Coupling of ATP-sensitive K+ channels to purinergic receptors by G-Proteins in rat ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 259, H820–H826 (1990).
Hermouet, S., Merendino, J.J., Gutkind, J.S. & Spiegel, A.M. Activating and inactivating mutations of the α subunit of Gi2 protein have opposite effects on proliferation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 10455–10459 (1991).
Gupta, S.K., Gallego, C., Johnson, G. & Heasley, L.E. MAP kinase is constitutively activated in gip2 and src transformed Rat-1 a fibroblasts. J. biol. Chem. 267, 7987–7990 (1992).
Watkins, D.C., Johnson, G.L. & Malbon, C.C. Regulation of the differentiation of teratocarcinoma cells into primitive endoderm by Gαi2. Science 258, 1373–1375 (1992).
Moxham, C.M., Hod, Y. & Malbon, C.C. Induction of Gαi2-specific antisense RNA in vivo inhibits neonatal growth. Science 260, 991–995 (1993).
Pace, A.M., Wong, Y.H. & Bourne, H.R. A mutant α subunit of Gi2 induced neoplastic transformation of Rat-1 cells. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 7031–7035 (1991).
Lyons, J. et al. Two G protein oncogenes in human endocrine tumours. Science 249, 655–659 (1990).
Noel, J.P., Hamm, H.E. & Sigler, P.B. The 2.2Å crystal structure of transducin-α complexed with GTPgS. Nature 366, 654–663 (1994).
Rudolph, U., Brabet, P., Hasty, P., Bradley, A. & Birnbaumer, L. Disruption of the Gi2α locus in embryonic stem cells and mice: a modified hit and run strategy with detection by a PCR dependent on gap repair. Transgenic Res. 2, 345–355 (1993).
Fischer, M. et al. Cytokine production by mature and immature thymocytes. J. Immunol. 146, 3452–3456 (1991).
Elson, C.O., Ealding, W. & Lefkowitz, J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J. Immunol. Meth. 67, 101–108 (1984).
Schreiber, S., Raedler, A., Stenson, W.F. & MacDermott, R.P. The role of the mucosal immune system in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 21, 451–502 (1992).
Sadlack, B. et al. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 75, 253–261 (1993).
Kühn, R., Löhler, J., Rennick, D., Rajewsky, K. & MüIIer, W. lnterleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75, 263–274 (1993).
Mombaerts, P. et al. Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell 75, 275–282 (1993).
Morrissey, P.J., Charrier, K., Braddy, S., Liggitt, D. & Watson, J.D. CD4+T cells that express high levels of CD45RB induce wasting disease when transferred into congenic severe combined immunodeficiency mice.Disease development is prevented by cotransfer of purified CD4+ T cells. J. exp. Med. 178, 237–244 (1993).
Powrie, F. et al. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhl CD4+ T cells. Immunity 1, 553–562 (1994).
Chaffin, K.E. et al. Dissection of thymocyte signaling pathways by in vivo expression of pertussis toxin ADP-ribosyltransferase. EMBO J. 9, 3821–3829 (1990).
Chaffin, K.E. & Perlmutter, R.M. A pertussis toxin-sensitive process controls thymocyte emigration. Eur. J. Immunol. 21, 2565–2573 (1991).
Bargatze, R.F. & Butcher, E.C. Rapid G protein-regulated activation event involved in lymphocyte binding to high endothelial venules. J. exp. Med. 178, 367–372 (1993).
Gupta, S.K. et al. Analysis of the fibroblast transformation potential of GTPase-deficient gip2 oncogenes. Mol. cell. Biol. 12, 190–197 (1992).
Hsu, W.H. et al. Molecular cloning of a novel splice variant of the α subunit of the mammalian G0 protein. J. biol. Chem. 265, 11220–11226 (1990).
Codina, J., Grenet, D., Chang, K.-J. & Birnbaumer, L., Gradient/SDS-PAGE: a useful tool in the investigation of signal transducing G proteins. J. Recept. Res. 11, 587–601 (1991).
Scherer, N.M., Toro, M.-J., Entman, M.L. & Birnbaumer, L. G protein distribution in canine cardiac sarcoplasmatic reticulum and sarcolemma.Comparison to rabbit sceletal membranes and brain and erythrocyte G proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 259, 431–440 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudolph, U., Finegold, M., Rich, S. et al. Ulcerative colitis and adenocarcinoma of the colon in Gαi2-deficient mice. Nat Genet 10, 143–150 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-143
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-143
This article is cited by
-
Gαi2-induced conductin/axin2 condensates inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling and suppress cancer growth
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Analyses of Gnai3-iresGFP reporter mice reveal unknown Gαi3 expression sites
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Gut microbiota-mediated inflammation in obesity: a link with gastrointestinal cancer
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2018)
-
RNA virus receptor Rig-I monitors gut microbiota and inhibits colitis-associated colorectal cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2017)
-
Loss of Gαi proteins impairs thymocyte development, disrupts T-cell trafficking, and leads to an expanded population of splenic CD4+PD-1+CXCR5+/− T-cells
Scientific Reports (2017)