Abstract
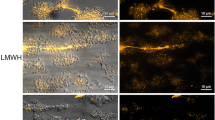
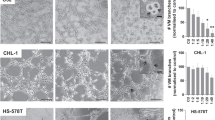
Expression of tissue factor (TF) in the endothelium has been observed only rarely in human disease and has been thought to be elaborated on the surface of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) in vitro as an artifact of tissue culture. Using monoclonal antibodies and a novel probe for functional TF, we have localized TF to the VECs (and tumor cells) within the tumors of seven patients with invasive breast cancer but not in the VECs (or tumor cells) of benign tumors from ten patients with fibrocystic disease of the breast. The potent procoagulant TF was shown to be a marker of the initiation of angiogenesis in human breast cancer. Further evidence that the TF was the demonstration of a similar distribution of cross–linked fibrin only in the VECs of the malignant tumors. We interpret these data as further support for the concept that tumor cells can activate nearby VECs and regulate blood vessel growth in vivo. Large clinicalpathologic studies will be necessary to determine whether TF is a useful marker for the “switch to the angiogenic phenotype” in human breast disease and/or correlates with the thromboembolic complications of breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nature Med. 1, 27–31 (1995).
Weidner, N. et al. Tumor angiogenesis: A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 84, 1875–1887 (1992).
Van Hoef, M.E.H.M., Knox, W.F., Dhesi, S.S., Howell, A. & Schor, A.M. Assessment of tumour vascularity as a prognostic factor in lymph node negative invasive breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 29A, 1141–1145 (1993).
Gasparini, G. et al. Tumor microvessel density, p53 expression, tumor size and peritumoral lymphatic vessel invasion are relevant prognostic markers in node-negative breast carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 454–466 (1994).
Folkman, J. Angiogenesis and breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 441–443 (1994).
Weidner, N., Carroll, P.R., Flax, J., Blumenfeld, W. & Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 143, 401–409 (1993).
Li, V.W. et al. Microvessel count and cerebrospinal fluid basic fibroblast growth factor in children with brain tumors. Lancet 344, 82–86 (1994).
Nemerson, Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood 71, 1–8 (1988).
Rickles, F.R., Levine, M.N. & Edwards, R.L. Hemostatic alterations in cancer patients. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 11, 237–248 (1992).
Dvorak, H.F., Dickersin, G.R., Dvorak, A.M., Manseau, J.E. & Pyne, K. Human breast carcinoma: Fibrin deposits and desmoplasia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 67, 335–340 (1981).
Maynard, J.R., Dreyer, B.E., Stemerman, M.B. & Pitlick, F.A. Tissue factor coagulant activity of cultured human endothelial and smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Blood 50, 387–396 (1977).
Stern, D.M., Nawroth, P.P., Handley, D. & Kisiel, W. An endothelial cell-dependent pathway of coagulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 2523–2527 (1982).
Colucci, M. et al. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J. Clin. Invest. 71, 1893–1896 (1983).
Lyberg, T., Galdal, K.S., Evensen, S.A. & Prydz, H. Cellular cooperation in endothelial thromboplastin synthesis. Br. J. Haematol. 53, 85–95 (1983).
Bevilacqua, M.P., Pober, J.S., Majeau, G.R., Cotran, R.S. & Gimbrone, M.A., Jr., Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial Cells. J. Exp. Med. 160, 618–623 (1984).
Tannenbaum, S.H., Finko, R. & Cines, D.B. Antibody and immune complexes induce tissue factor production by human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 137, 1532–1537 (1986).
Conway, E.M., Bach, R., Rosenberg, R.D. & Konigsberg, W.H. Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thromb. Res. 53, 231–241 (1989).
Crossman, D.C., Carr, D.P., Tuddenham, E.G.D., Pearson, J.D. & McVey, J.H. The regulation of tissue factor mRNA in human endothelial cells in response to endotoxin or phorbol ester. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 9782–9787 (1990).
Kirchhofer, D. et al. Relationship between tissue factor expression and deposition of fibrin, platelets and leukocytes on cultured endothelial Cells under venous blood flow conditions. Blood 81, 2050–2058 (1993).
Wilcox, J.N., Smith, K.M., Schwartz, S.M. & Gordon, D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 2839–2843 (1989).
Drake, T.A., Morrissey, J.H. & Edgington, T.S., Selective Cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 134, 1087–1097 (1989).
Drake, T.A., Cheng, J., Chang, A. & Taylor, F.B., Jr., Expression of tissue factor, thrombomodulin, and E-selectin in baboons with lethal Escherichia coli sepsis. Am. J. Pathol. 142, 1458–1470 (1993).
Faulk, W.P., Labarrere, C. & Carson, S. Tissue factor: Identification and characterization of cell types in human placentae. Blood 76, 86–96 (1990).
Zhang, Y. et al. Tissue factor controls the balance of angiogenic and antiangiogenic properties of tumor cells in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 94, 1320–1327 (1994).
Rickles, F.R., Hancock, W.W., Edwards, R.L. & Zacharski, L.R. Antimetastatic agents. I. The role of Cellular procoagulants in the pathogenesis of fibrin deposition in cancer and the use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet drugs in cancer treatment. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 14, 126–132 (1988).
Contrino, J., Hair, G.A., Schmeizl, M.A., Rickles, F.R. & Kreutzer, D.L. In situ characterization of antigenic and functional tissue factor expression in human tumors utilizing monoclonal antibodies and recombinant factor Vila as probes. Am. J. Pathol. 145, 1315–1322 (1994).
Broze, G., Jr., Binding of human factor VII and VIIa to monocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 70, 526–536 (1982).
Kudryk, B., Rohozza, A., Ahadi, M., Chin, J. & Wiebe, M.E. Specificity of a monoclonal antibody for the NH2 terminal region of fibrin. Mol. Immunol. 21, 89–94 (1984).
Kudryk, B., Rohozza, A., Ahadi, M., Gidlund, M. & Harfenist, E.F. Antibodies specific for neoantigens expressed on chains or degradation products of fibrin (ogen). in Fibrinogen 3 — Biochemistry, Biological Functions, Gene Regulation and Expression. (eds. Mosesson, M.W., Armani, D.B, Siebenlist, K.R. & DiOrio, J.P.) 129–132 (Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1988).
Rickles, F.R. & Edwards, R. Leukocytes and tumor cells in thrombosis. inHemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. (eds. Colman, R.W., Hirsh, J., Marder, V.J. & Salzman, E.W.) 1164–1179 (Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1994).
Costantini, V. et al. Fibrinogen deposition without thrombin generation in primary human breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 51, 349–353 (1991).
Callander, N.S., Varki, N. & Rao, L.V.M. Immunohistochemical identification of tissue factor in solid tumors. Cancer 70, 1194–1201 (1992).
Noguchi, M., Sakai, T. & Kisiel, W. Identification and partial purification of a novel tumor-derived protein that induces tissue factor on cultured human endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 160, 222–226 (1989).
Clauss, M. et al. Vascular permeability factor: A tumor-derived polypeptide that induces endothelial cell and monocyte procoagulant activity and promotes monocyte migration. J. Exp. Med. 172, 1535–1545 (1990).
Kao, J. et al. Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II. Biochem. J. 267, 20239–20247 (1992).
Trousseau, A. Phlegmasia alba dolens. in Clinique de líHùtel-Dieu de Paris. vol. 3, 654–712 (Balliere et Fils, Paris, 1865).
Dvorak, H.F. Abnormalities of hemostasis in malignant disease in Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Bask Principles and Clinical Practice, (eds. Colman, R.W., Hirsh, J., Marder, V.J. & Salzman, E.W.) 1238–1254 (Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1994).
Miyauchi, S. et al. Malignant tumor cell lines produce interleukin-1-like factor. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 24, 753–755 (1988).
Brett, J. et al. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J. Exp. Med. 169, 1977–1991 (1989).
McKever, R.P. Leukocyte interactions mediated by selectins. Thromb. Haemost. 66, 80–87 (1991).
Berse, B., Brown, L.F., Van De Water, L., Dvorak, H.F. & Senger, D.R. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol. Biol. Cell 3, 211–220 (1992).
Janicke, F. et al. Urokinase (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-1 are strong and independent prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 24, 195–208 (1993).
Muss, H.B. et al. c-erbB-2 expression and response to adjuvant therapy in women with node-positive early breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 330, 1260–1266 (1994).
Brown, L.F. et al. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer. Res. 53, 4727–4735 (1993).
Morrissey, J.H., Fair, D.S. & Edgington, T.S. Monoclonal antibody analysis of purified and Cell-associated tissue factor. Thromb. Res. 52, 247–261 (1988).
Ruf, W., Rehemtulla, A. & Edgington, T.S. Antibody mapping of tissue factor implicates two different exon-coded regions in function. Biochem. J. 278, 729–733 (1991).
Ruf, W. & Edgington, T.S. An anti-tissue factor monoclonal antibody which inhibits TF-VIIa complex is a potent anticoagulant in plasma. Thromb. Haemost. 66, 529–533 (1992).
Williams, E.B., Krishnaswamy, S. & Mann, K.G. Zymogen/enzyme discrimination using peptide chloromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 7536–7545 (1989).
Guesdon, J.L., Ternynck, T. & Avrameus, S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 1131–1139 (1979).
Sato, Y., Mukai, K., Watanable, S., Goto, M. & Shimosato, Y., The AMeX method. Am. J. Pathol. 125, 431. Pathol. Muk
Reuning, U., Preissner, K.T., Muller-Berghaus, G. Two independent binding sites on monolayers of human endothelial cells are responsible for interaction with coagulation factor VII and factor VIIa. Thromb. Haemost. 69, 197–204 (1993).
Hoffman, M., Monroe, D.M., Roberts, H.R. Human monocytes support factor X activation by factor Vila, independent of tissue factor: implications for the therapeutic mechanism of high-dose factor VIIa in hemophilia. Blood 83, 38–42 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contrino, J., Hair, G., Kreutzer, D. et al. In situ detection of tissue factor in vascular endothelial cells: Correlation with the malignant phenotype of human breast disease. Nat Med 2, 209–215 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0296-209
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0296-209
This article is cited by
-
Tissue factor as a new target for CAR-NK cell immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Analysis of the role of thrombomodulin in all-trans retinoic acid treatment of coagulation disorders in cancer patients
Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling (2019)
-
Patrolling the vascular borders: platelets in immunity to infection and cancer
Nature Reviews Immunology (2019)
-
The relationship between pancreatic cancer and hypercoagulability: a comprehensive review on epidemiological and biological issues
British Journal of Cancer (2019)
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome in Cancer Patients
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs (2018)